Practical examples Section 5-2
335
5-2-4 Single axis program
This program is a simple program to run one axis only.
5-2-4-1 Example
'GOSUB homing
BASE(0)
DEFPOS(0)
WA(100)
loop:
MOVE(1440)
WAIT IDLE
WA(100)
GOTO loop
The units are degrees in this example, therefore:
• 13-bit encoder
• Pn202=32
• Pn203=45
• UNITS=32
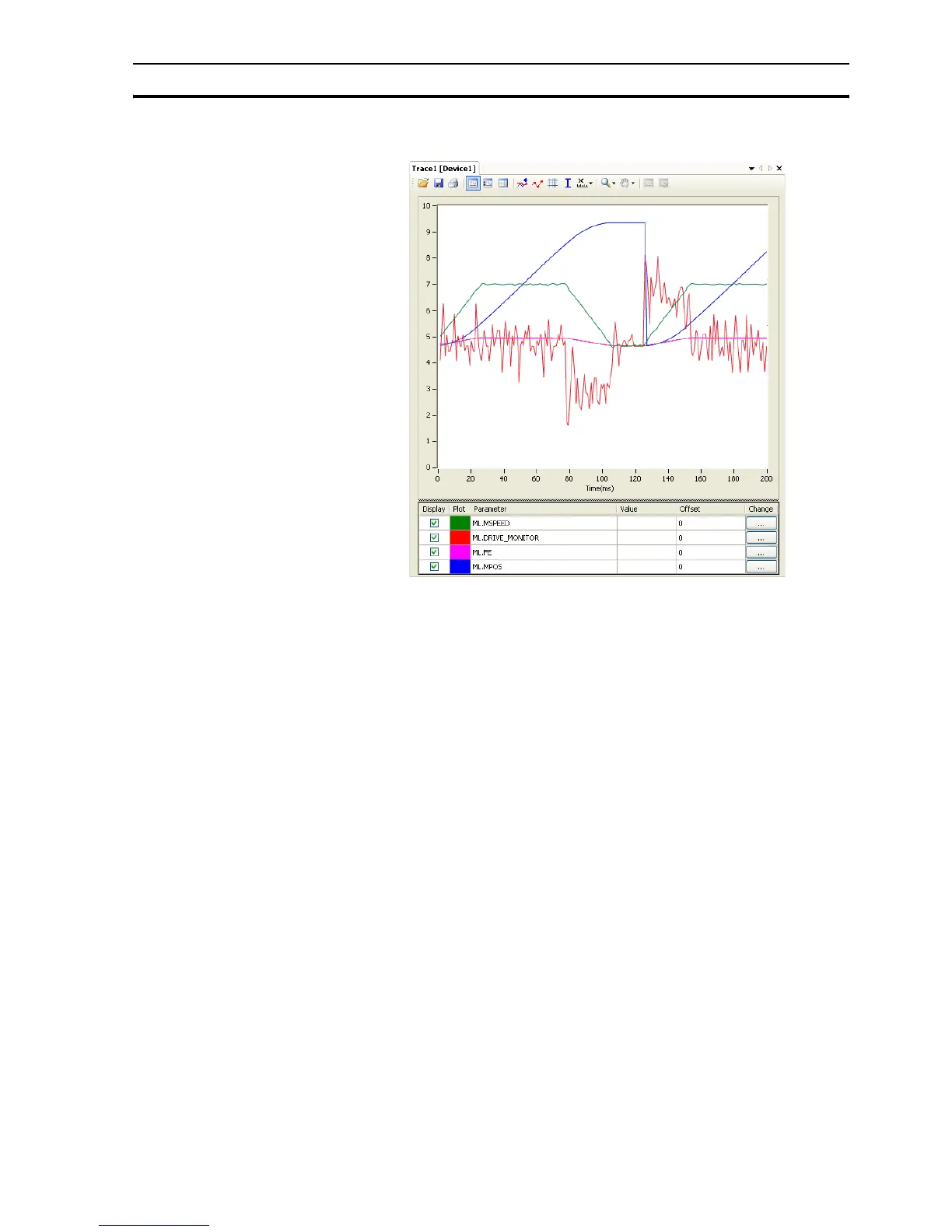
The graph in the figure is typical for this point-to-point movement with linear
acceleration). Note the following:
• During linear acceleration, the graph of the position is parabolic (because
the speed is a derivative of the position).
• During constant speed, the graph of the position is straight.
• During linear deceleration, the graph of the position is counter-parabolic.
• During stop, the graph of the position is constant.
• When an overflow occurs (MPOS>=REP_DIST), the position jumps to 0 if
REP_OPTION=1 or to -REP_DIST if REP_OPTION=0.

 Loading...
Loading...











