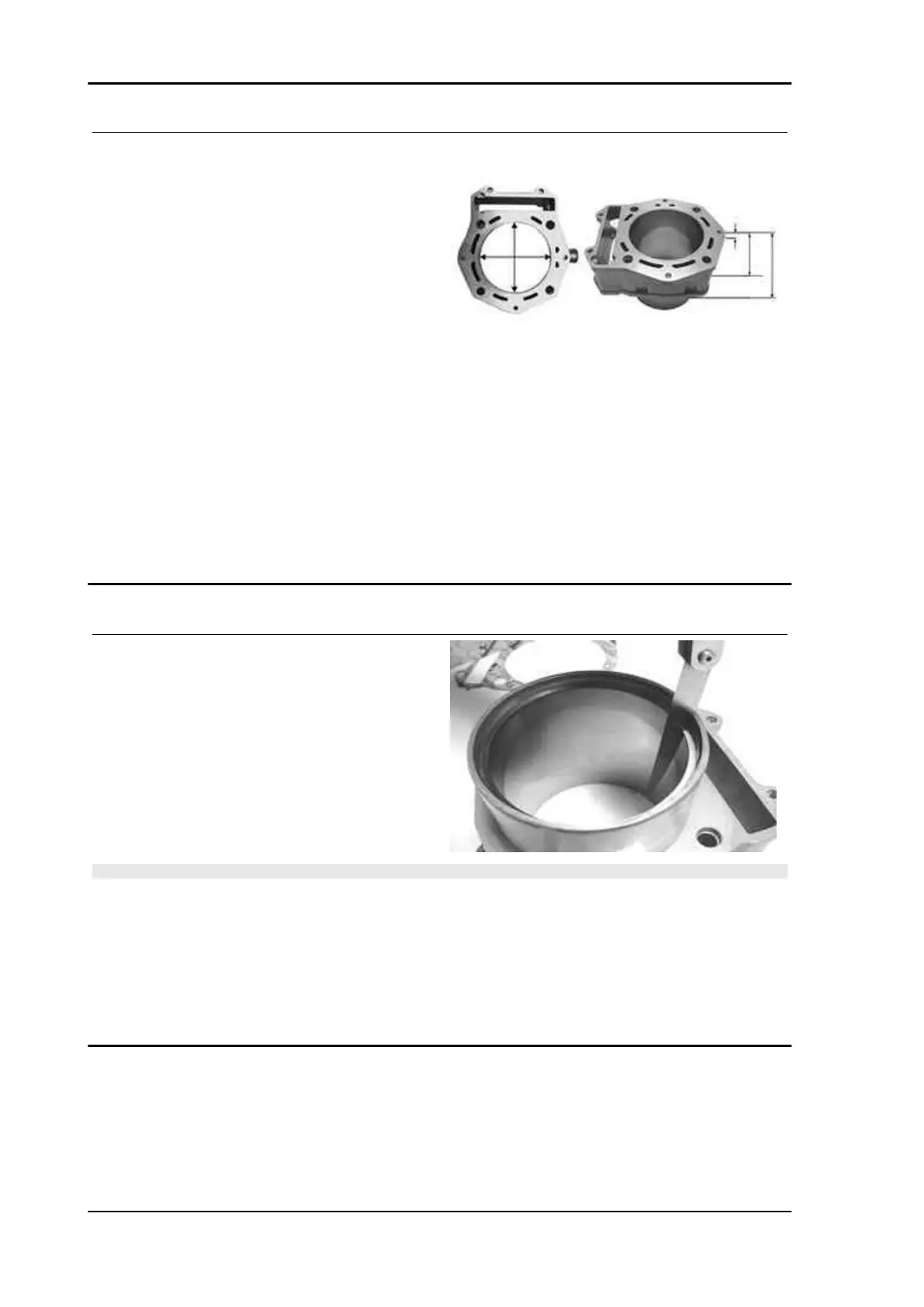
- Using a bore meter, measure the inner cylinder
diameter at three different points according to the
directions shown in the figure.
Characteristic
Standard diameter:
92 + 0.018 +0.010 mm
- Check that coating is free from flakes.
- Check that the head matching surface exhibits no deformations or wear.
Characteristic
Maximum allowable run-out:
0.05 mm
- Pistons and cylinders are classified into categories based on their diameter. The coupling is carried
out in pairs (A-A, B-B, C-C, D-D).
Inspecting the piston rings
- Alternately insert the three sealing rings into the
cylinder, in the area where it retains its original di-
ameter. Using the piston, insert the rings perpen-
dicularly to the cylinder axis.
- Measure the opening (see figure) of the sealing
rings using a feeler gauge.
- If higher values than those prescribed are meas-
ured, replace the linings.
N.B.
BEFORE REPLACING ONLY THE PISTON RINGS, ENSURE THAT THE CLEARANCE BETWEEN
THE PISTON RINGS AND THE PISTON RING GROOVES, AND BETWEEN THE PISTON AND THE
CYLINDER, IS AS SPECIFIED. IN ANY CASE, NEW PISTON RINGS USED IN COMBINATION WITH
A USED CYLINDER MAY HAVE DIFFERENT BEDDING CONDITIONS THAN THE STANDARD.
Fitting clearance (Cylindrin/Pison)
Compression ring 0.15 ÷ 0.35 mm Max. value. 0.5 mm </> Oil scraper ring 0.25 ÷ 0.50 mm Max.
value. 0.65 mm </> Oil scraper ring 0.25 ÷ 0.50 mm Max. value. 0.65 mm </>
Engine X9 Evolution 500
ENG - 148
 Loading...
Loading...











