GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Series Hardware Design
MC60_Series_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 40 / 114
In periodic standby mode, sending ―$PMTK225,0*2B‖ in any time can make the module enter into full on
mode.
In periodic backup mode, sending ―$PMTK225,0*2B‖ during the Run_time or 2nd_run_time period can
also make the module enter into full on mode. But this is hard to operate and thus is not recommended.
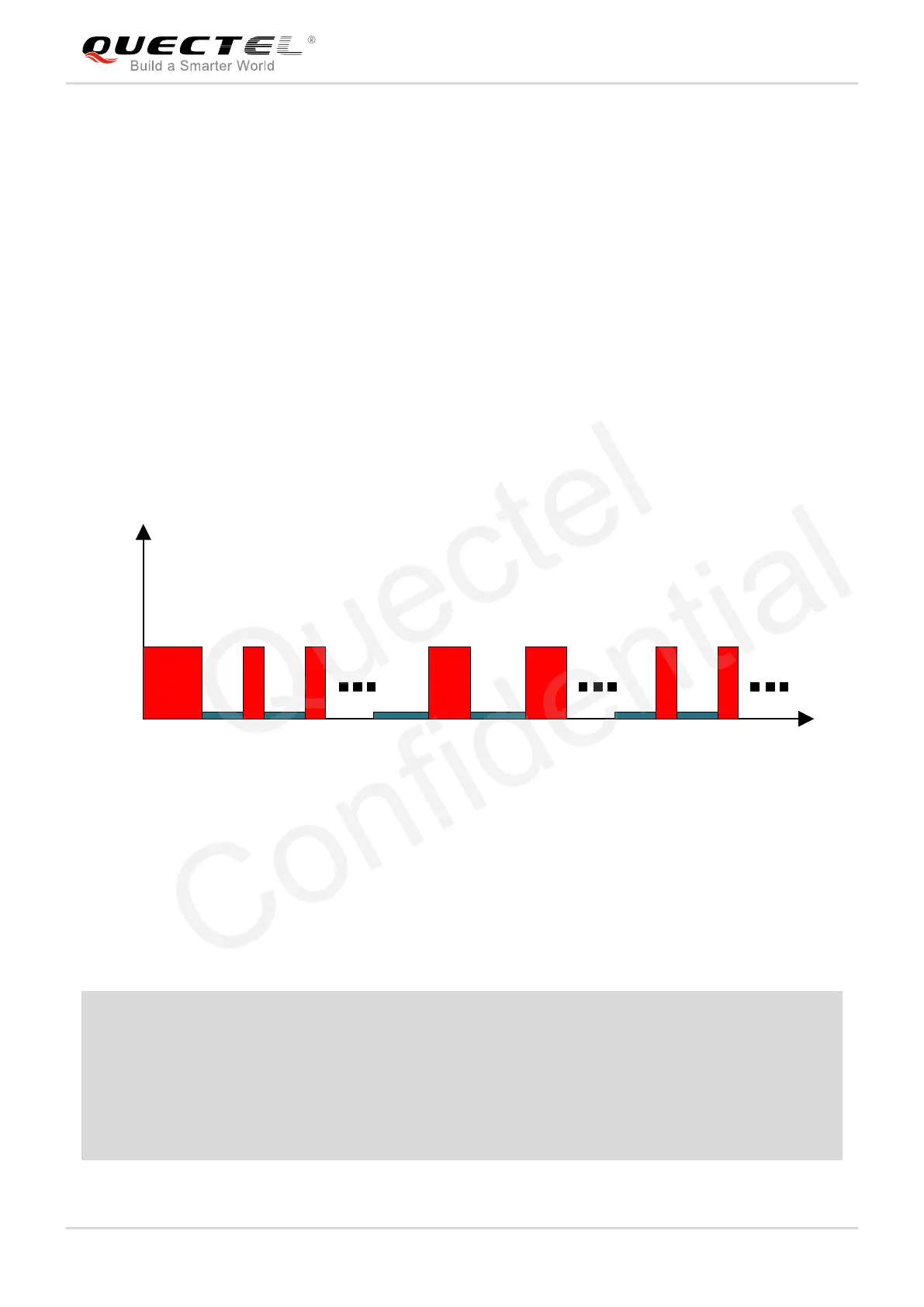
The following figure has shown the operation mechanism of periodic mode. When customers send PMTK
command, the module will be in full on mode first. Several minutes later, the module will enter into
periodic mode according to the parameters set. When the module fails to fix the position during Run_time,
the module will switch to 2nd_run_time and 2nd_sleep_time automatically. As long as the module fixes
the position again successfully, the module will return to Run_time and Sleep_time.
Before entering into periodic mode, please make sure the module is in tracking mode; otherwise the
module may have a risk of failure in satellite tracking. If module is located in weak signal areas, it is better
to set a longer 2nd_run_time to ensure the success of reacquisition.
Power
Run time
Run time
Sleep time
Sleep time
Second run timeSecond run time
Second sleep time Second sleep time
Run time
Run time
Sleep time
Sleep time
Full on
Figure 14: Operation Mechanism of Periodic Mode
The average current consumption in periodic mode can be calculated based on the following formula:
I
periodic
= (I
tracking
*T1+I
standby/backup
*T2)/(T1+T2) T1: Run_time, T2: Sleep_time
Example
PMTK225,2,3000,12000,18000,72000*15 for periodic mode means 3s in tracking mode and 12s in
standby mode based on GPS&GLONASS. The average current consumption is calculated below:
I
periodic
= (I
tracking
*T1+I
standby
*T2)/(T1+T2) = (22mA*3s+0.5mA*12s)/(3s+12s) ≈ 4.8(mA)
PMTK225,1,3000,12000,18000,72000*15 for periodic mode means 3s in tracking mode and 12s in
backup mode based on GPS&GLONASS. The average current consumption is calculated below:
I
periodic
= (I
tracking
*T1+I
backup
*T2)/(T1+T2) = (22mA*3s+0.007mA*12s)/(3s+12s) ≈ 4.4(mA)
 Loading...
Loading...