Core peripherals PM0214
196/262 PM0214 Rev 9
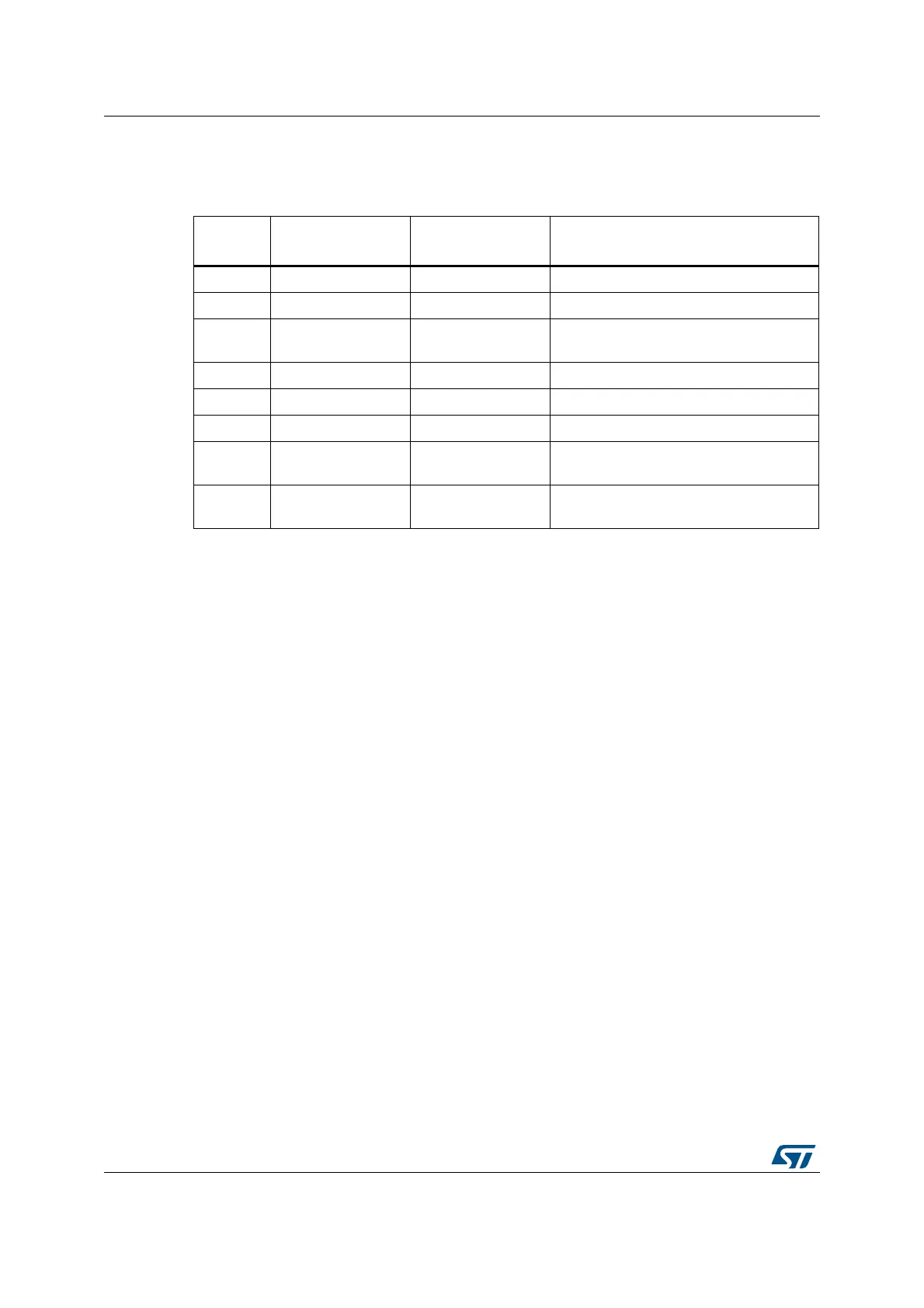
Table 41 shows the AP encodings that define the access permissions for privileged and
unprivileged software.
4.2.2 MPU mismatch
When an access violates the MPU permissions, the processor generates a memory
management fault, see Section 2.1.4: Exceptions and interrupts on page 26. The MMFSR
indicates the cause of the fault. See Section 4.4.15: Memory management fault address
register (MMFAR) on page 242 for more information.
4.2.3 Updating an MPU region
To update the attributes for an MPU region, update the MPU_RNR, MPU_RBAR and
MPU_RASR registers. You can program each register separately, or use a multiple-word
write to program all of these registers. You can use the MPU_RBAR and MPU_RASR
aliases to program up to four regions simultaneously using an STM instruction.
Updating an MPU region using separate words
Simple code to configure one region:
; R1 = region number
; R2 = size/enable
; R3 = attributes
; R4 = address
LDR R0,=MPU_RNR ; 0xE000ED98, MPU region number register
STR R1, [R0, #0x0] ; Region Number
STR R4, [R0, #0x4] ; Region Base Address
STRH R2, [R0, #0x8] ; Region Size and Enable
STRH R3, [R0, #0xA] ; Region Attribute
Disable a region before writing new region settings to the MPU if you have previously
enabled the region being changed. For example:
; R1 = region number
; R2 = size/enable
Table 41. AP encoding
AP[2:0]
Privileged
permissions
Unprivileged
permissions
Description
000 No access No access All accesses generate a permission fault
001 RW No access Access from privileged software only
010 RW RO
Writes by unprivileged software generate
a permission fault
011 RW RW Full access
100 Unpredictable Unpredictable Reserved
101 RO No access Reads by privileged software only
110 RO RO
Read only, by privileged or unprivileged
software
111 RO RO
Read only, by privileged or unprivileged
software

 Loading...
Loading...