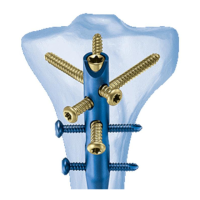
4
Indications for DHS plates
– Pertrochanteric and intertrochanteric fractures of type
31-A in the AO/ASIF classification.
For highly unstable types of fracture, additional implants
such as the DHS trochanter stabilizing plate or DHS locking
device may be required.
– Femoral neck fractures 31-B2/B3, in conjunction with
the use of an anti-rotation screw.
Indications for DHS trochanter stabilizing plates
–Group 31-A2 and A3 fractures, particularly multifragment
fractures.
The DHS Trochanter Stabilizing Plates (281.869 and
281.870) are viewed as an extension of the DHS plate for
stabilizing the greater trochanter and for accepting
an anti-rotation screw.
Where telescoping is present in the fracture zone, the
combination of a DHS plate and a DHS trochanter stabilizing
plate prevents the tendency of the trochanter fragments
to move laterally with consequent medialization of the shaft
in relation to the head-neck fragment. Additionally,
a rotationally unstable head-neck fragment can be stabilized
by inserting an anti-rotation screw cranially and parallel
to the DHS/DCS screw.
DHS trochanter stabilizing plates can also be used to
secure splintered greater trochanter fragments and stabilize
them by using screws or cerclage wires in the scooped
section of the DHS trochanter stabilizing plate.
DHS/DCS Standard System
Indications/Contraindications
 Loading...
Loading...