Page 28 SC2000 Manual – 177/52301 Rev G 22
nd
October
2004
10.1.25 Fail-safe
The controller’s safety system includes a microprocessor watchdog which can detect
software failure, and a hardware fail-safe system which can prevent dangerous runaway
conditions in the event of certain hardware failures.
Every time the controller is powered-up, the software checks that the fail-safe circuit is able to
switch off the Mosfets and open at least 2 contactors.
10.1.26 Dual Motor Operation - General Principles
The SC2000 can drive twin traction motor systems using either a single chopper (non-
proportional control) or a twin chopper (proportional control). In both modes, 2 of the
contactor drive outputs must be assigned as an additional set of direction contactors for the
second motor. Depending on the steering angle, the inner motor of a turn can be reduced in
speed, and then reversed (for 3-wheel vehicles). For increased safety, the overall speed of
the vehicle can also be reduced as it turns.
The steering information can be provided by either 3 switch inputs (inner-left steer switch,
inner-right steer switch and the outer switches connected in parallel) or a steer potentiometer.
Sevcon recommends a steer pot., as this allows linear inner-wheel control on proportional
systems, and linear speed cutback in turns on all vehicles. As the steering characteristics for
a potentiometer can be adjusted via the calibrator (items 1.1.29 and 1.1.31), mechanical
adjustment is not required. See section 7.3.1 for typical values. The inner angle and outer
angles personalities must be at least 5° apart. If problems exist with setting the values, check
the other setting to ensure it is not within 5 degrees.
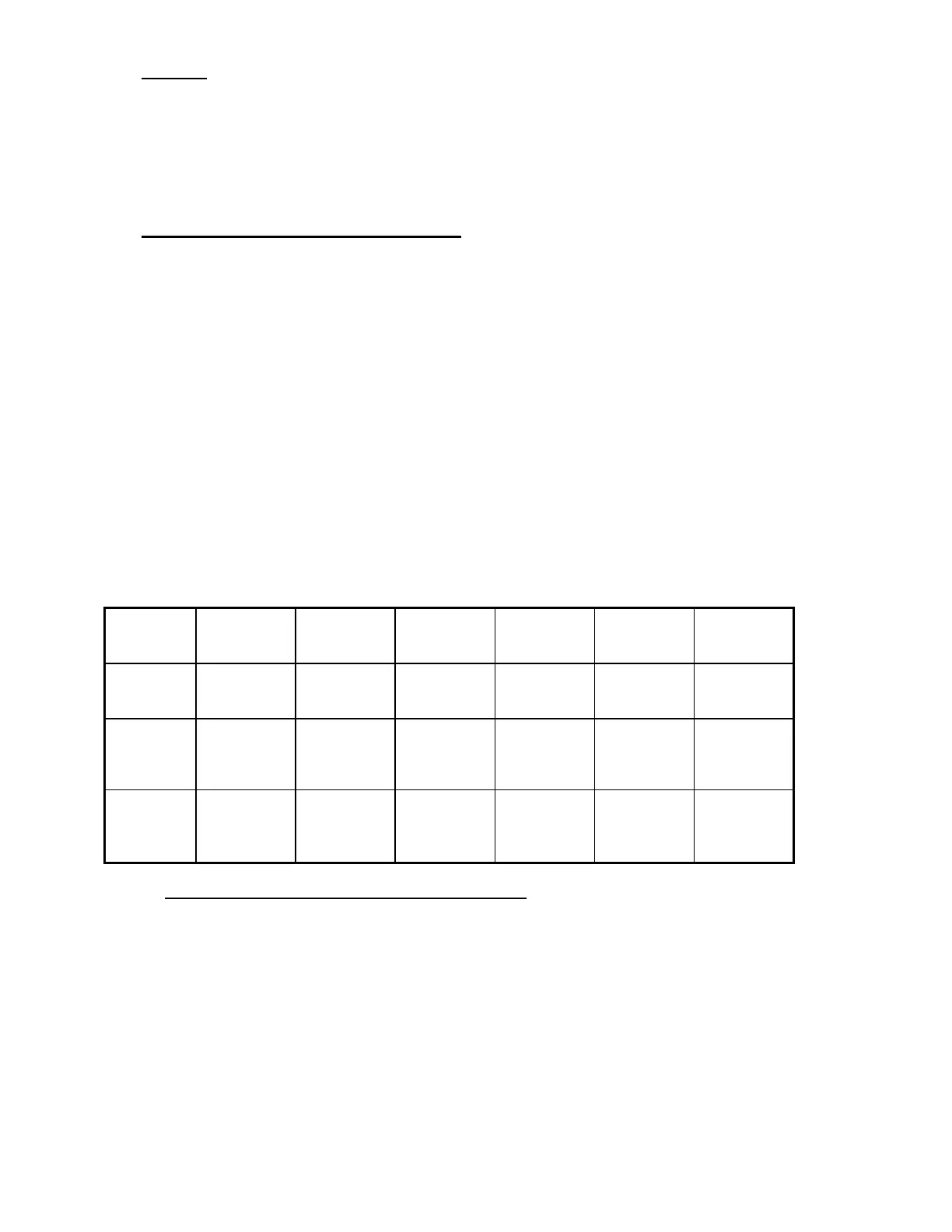
For all dual motor systems, the steering range 0 - 90° is split into 3 sections: the dead-band,
the cut-band and the reverse-band. The characteristics of each are shown below:
Band Definition
for Steer
Pot.
Definition
for Steer
Switches
Maximum
Vehicle
Speed
Inner Motor
Speed
Inner Motor
Direction
Bypass &
Field
Weakening
Dead Band
e.g.
0° - 10°
steer angle
is less than
inner angle
all steer
switches
open
100% 100% Same as
direction
lever
Enabled
Cut Band
e.g.
10° - 70°
steer angle
is between
inner and
outer angles
one inner
switch is
closed
reduced to
cutback
speed #1
reduced to
0%
Same as
direction
lever (or
stationary)
Disabled
Reverse
Band
e.g.
70° - 90°
steer angle
is greater
than outer
angle
one inner
and outer
switch is
closed
reduced to
cutback
speed #2
increased to
cutback
speed #2
Opposite of
direction
lever
Disabled
10.1.27 Dual Motor Non-proportional - Additional Notes
Depending on how closely the motor characteristics are matched and whether circulating
currents exist between the two motors during braking, a balancing contactor may be required
(see Figs 5 & 7). The balance contactor is open when driving, and closed under all other
normal conditions.
To minimise lurches during cornering the chopper is ramped-down using the standard
acceleration delay prior to changing the direction of the inner wheel. Once the contactors
have changed, the chopper is ramped up at one of two rates depending on the type of
direction change: The inner ramp rate is used between the dead-band and the cut band, and
the outer ramp rate is used between the cut band and the reverse band.
 Loading...
Loading...