(1or0) 2 +´
1
(1or0) 2 +(1or0) 2 +.......(1or0) 2 +.......(1or0) 2´ ´ ´ ´
0 –1 –4 –23
2 Bit
1
2 Bit
0
2 Bit
–1
2 Bit
–4
2 Bit
–23
M0126-01
u
Coefficient
Digit8
u
u u u u
S
x
Coefficient
Digit7
x.
x x x
Coefficient
Digit6
x
x x x
Coefficient
Digit5
x
x x x
Coefficient
Digit4
x
x x x
Coefficient
Digit3
x
x x x
Coefficient
Digit2
x
x x x
Coefficient
Digit1
Fraction
Digit5
Fraction
Digit4
Fraction
Digit3
Fraction
Digit2
Fraction
Digit1
Integer
Digit1
Sign
Bit
Fraction
Digit6
u=unusedordon’tcarebits
Digit=hexadecimaldigit
M0127-01
0
TAS5707, TAS5707A
SLOS556B –NOVEMBER 2008–REVISED NOVEMBER 2009
www.ti.com
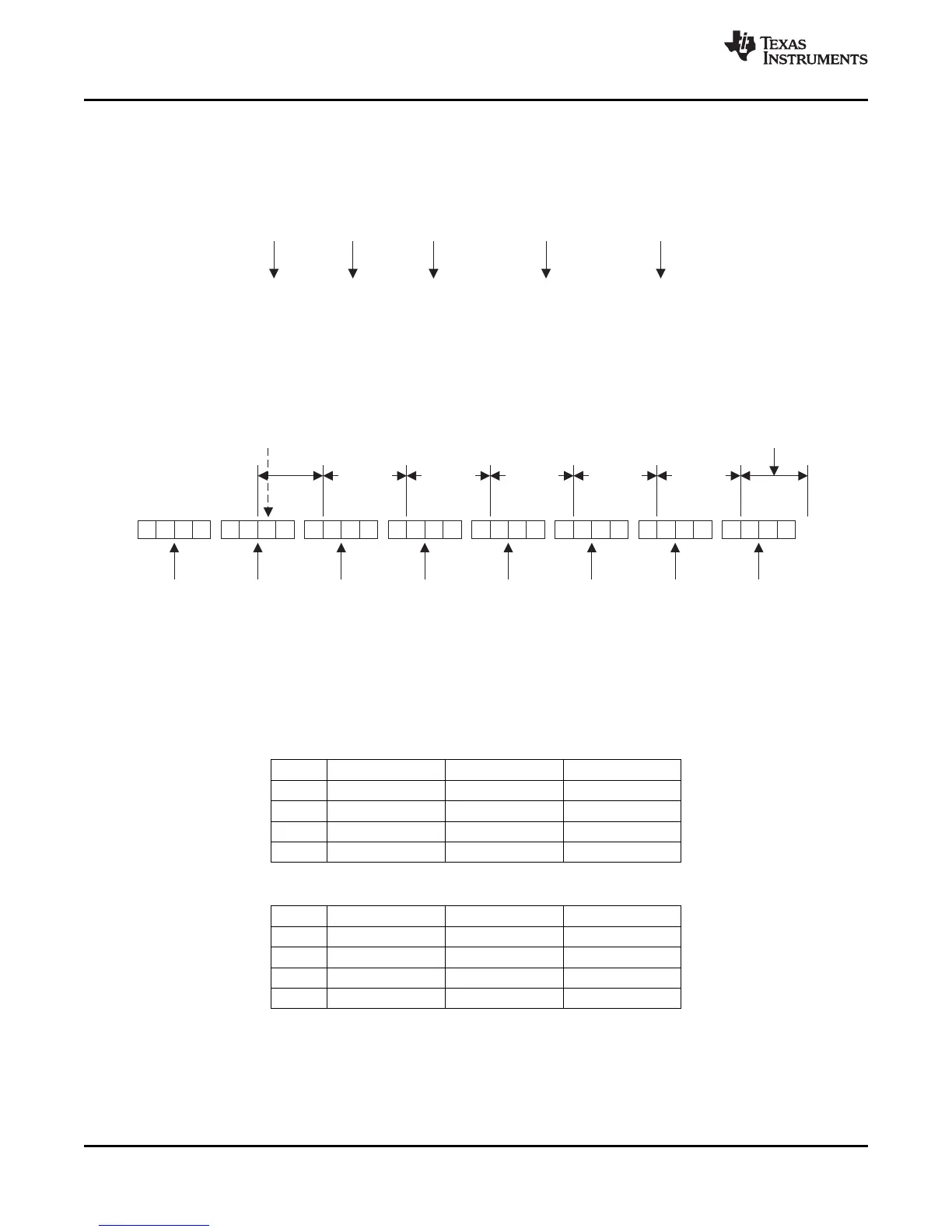
The decimal value of a 3.23 format number can be found by following the weighting shown in Figure 33. If the
most significant bit is logic 0, the number is a positive number, and the weighting shown yields the correct
number. If the most significant bit is a logic 1, then the number is a negative number. In this case every bit must
be inverted, a 1 added to the result, and then the weighting shown in Figure 34 applied to obtain the magnitude
of the negative number.
Figure 34. Conversion Weighting Factors—3.23 Format to Floating Point
Gain coefficients, entered via the I
2
C bus, must be entered as 32-bit binary numbers. The format of the 32-bit
number (4-byte or 8-digit hexadecimal number) is shown in Figure 35
Figure 35. Alignment of 3.23 Coefficient in 32-Bit I
2
C Word
Table 2. Sample Calculation for 3.23 Format
db Linear Decimal Hex (3.23 Format)
0 1 8388608 00800000
5 1.7782794 14917288 00E39EA8
–5 0.5623413 4717260 0047FACC
X L = 10
(X/20)
D = 8388608 × L H = dec2hex (D, 8)
Table 3. Sample Calculation for 9.17 Format
db Linear Decimal Hex (9.17 Format)
0 1 131072 20000
5 1.77 231997 38A3D
–5 0.56 73400 11EB8
X L = 10
(X/20)
D = 131072 × L H = dec2hex (D, 8)
30 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2008–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Link(s): TAS5707 TAS5707A
 Loading...
Loading...