10 Installation
3.3 Wiring connections
External DC powering
Powering via 4~20mA loop
( Negative referenced )
Powering via 4~20mA loop
( Positive referenced )
Wiring requirements : Use multi-core screened twisted pair instrument cable ( 0.25 – 0.5mm
2
) for electrical
connection between the RT and any remote flowmeter or receiving instrument. The screen needs to be earthed to the
signal ground of the receiving instrument only to protect the transmitted signal from mutual inductive interference.
Instrument cabling should not be run in a common conduit or parallel with power and high inductive load carrying
cables, power surges & power line frequencies may induce erroneous noise transients onto the signal. Run instrument
cables in a separate conduit or with other instrument cables.
Installation 11
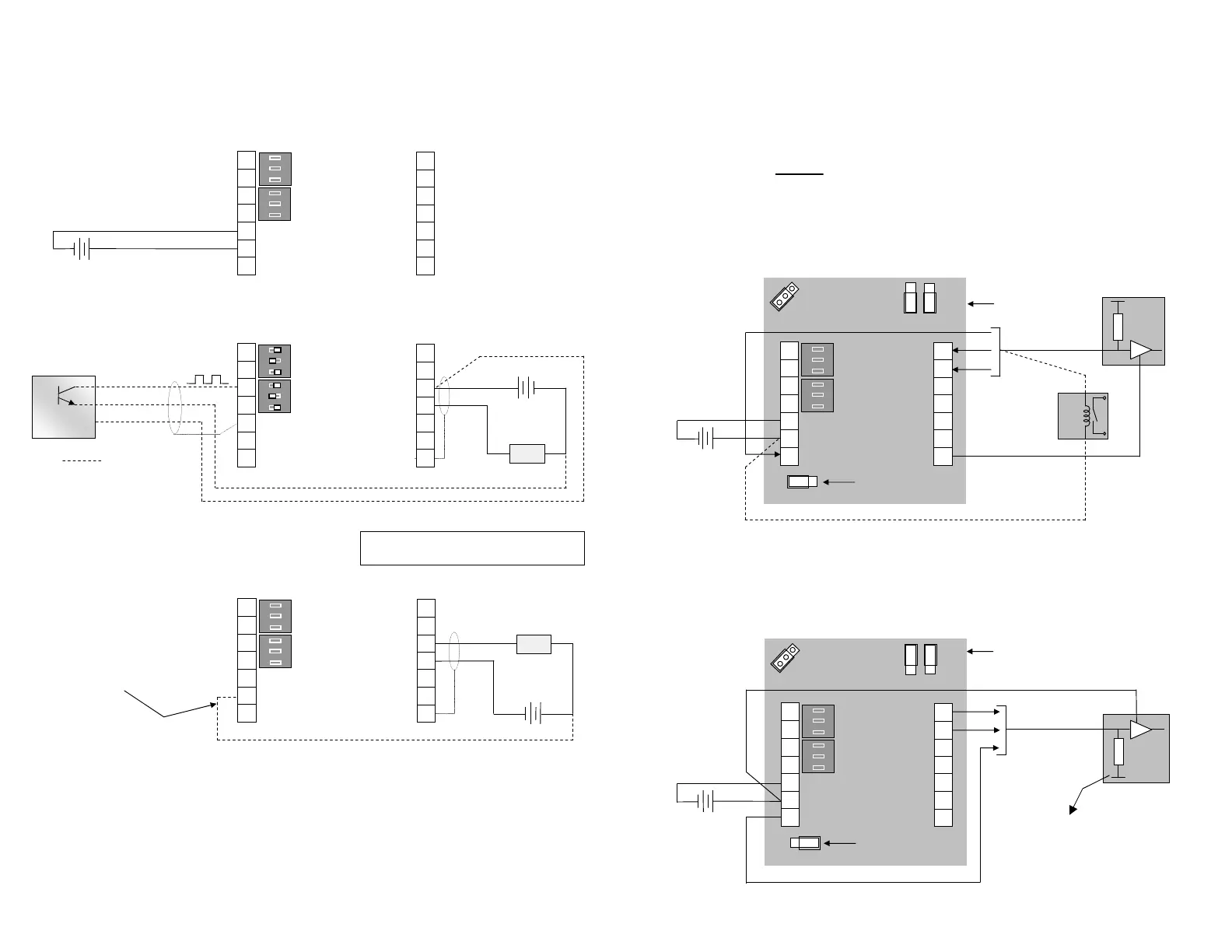
Pulse & Alarm Outputs
Current Sinking outputs ( NPN )
Current sinking derives its name from the fact that it “sinks current from a load”. When activated the
current flows from the load into the appropriate output (7,13 & 14).
Driving a logic input The output voltage pulse is typically the internal voltage of the load.
The load would normally have an internal pull up resistor on its input as shown.
Driving a coil - - - - - - - The NPN style of output is to be used when diving a coil. The coil load is
obtained by dividing the coil voltage by coil impediance (
Ω ), is expressed in amps & is not to exceed
0.1A. The coil voltage is connected across & must match the RT supply voltage & the output (7,13 & 14).
Current Sourcing outputs ( PNP )
Current sourcing gets its name from the fact that it “sources current to a load”. When activated the
current flows from the output (7,13 & 14) into the load. When wired as below the output voltage pulse
is the supply voltage of the load. The load would normally have an internal pull down resistor on its
input as shown.
Set jumper(s)
to NPN
_
logic
input
coil
+8~24Vdc in
Pulse output
-0V (ground)
-
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
0
PNP
NPN
13
0
14
SPO scaled pulse
7A
REP repeater pulse
PNP
NPN
7B
to NPN
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
NPN
to PNP
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
+8~24Vdc in
Pulse output
-0V (ground)
-
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
PNP
NPN
0
13
0
14
SPO scaled pulse
7A
REP repeater pulse
PNP
NPN
7B
Set jumper
to PNP
PNP
Do not tie 0 volts of the
logic input to 0 volts of
the RT when wired in
PNP configuration
_
logic
input
Avoid using low
cost digital switch
mode power packs
8~24 Vdc
regulated supply
+8~24Vdc in
Pulse output
-0V (ground)
Flow
Input A
-4~20mA output
-
not used
+4~20mA output
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Input B
+
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
regulated
12~28 Vdc
Load
+
+
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
+8~24Vdc in
Pulse output
-0V (ground)
Flow
Input A
-4~20mA output
-
not used
+4~20mA output
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
n
Input B
2
1
N
2
1
N
Hall effect
Vdc supply
- Negative
+ Signal out
optional wiring
above shows powering of a
Hall Effect device using the
Load
+
regulated
12~28 Vdc
+
6
5
4
3
2
1
7
+8~24Vdc in
Pulse output
-0V (ground)
Flow
Input A
-4~20mA output
-
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
High flow ala
Input B
When wired in this manner the one
loop power supply (limited to 24Vdc)
may be used to also power active flow
sensors, scaled pulse & alarm outputs
at terminals 7, 13 & 14 & / or multiple
RT12’s.
Loop load specification :
where : V = loop voltage, R = max. load Ω
 Loading...
Loading...