1-2 The Edge Personal Noise Dosimeter Model EG-4P User Manual
Noise Dosimeter
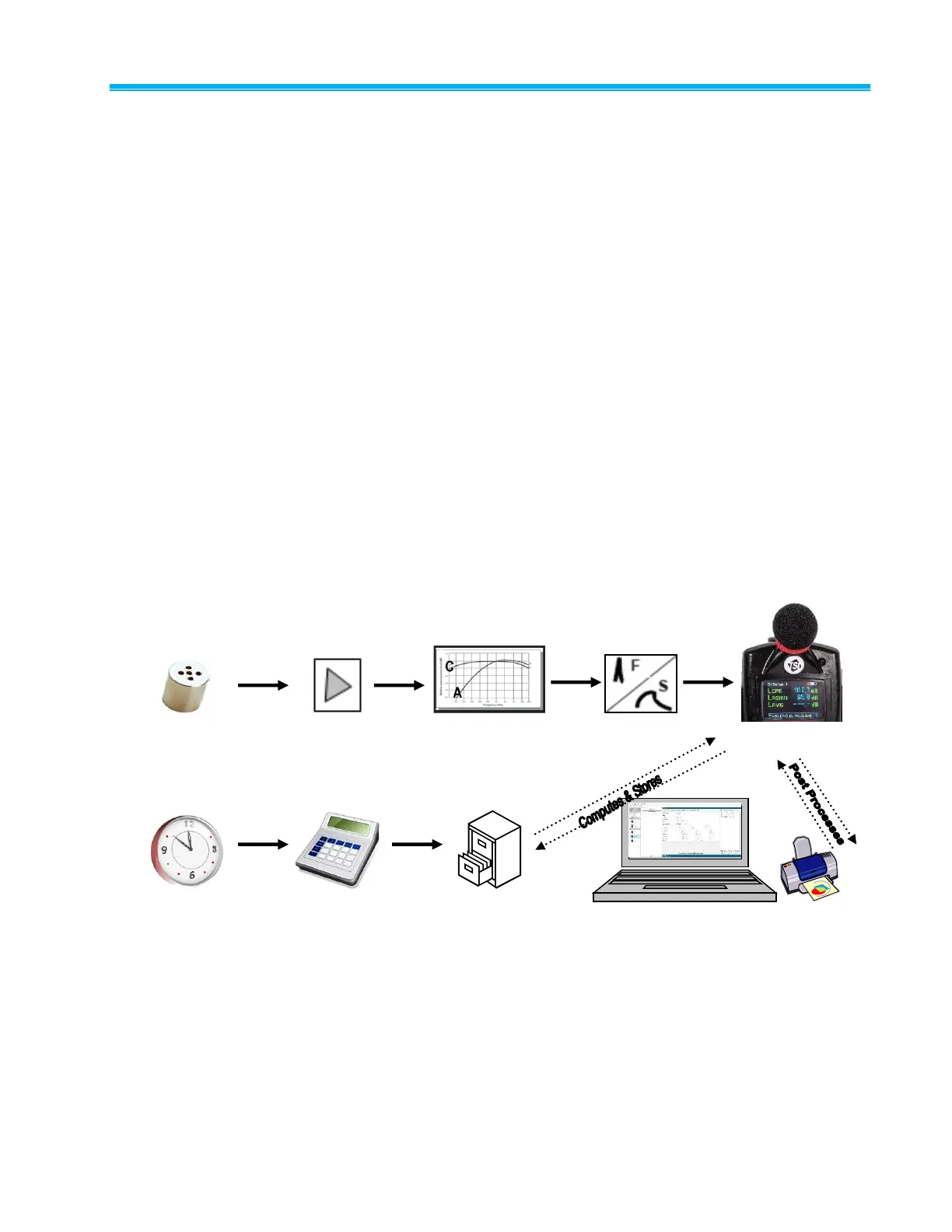
What is a noise dosimeter and how does it compute measurements?
Essentially, a noise dosimeter is composed of the following: a
microphone with a preamplifier, a weighted network, fast or slow
response time, an internal clock, calculator, and memory to store
logged data.
The illustration below is a diagram of a basic noise dosimeter. The
microphone will, when exposed to a sound pressure, generate an
electrical signal. The signal will be increased by a preamplifier, and then
is regulated to an applicable level by the range control (dB range). The
signal then goes through a filter set or weighting system. The next circuit
is the response circuit, which controls the dampening of the readout. The
response choices are typically Slow or Fast. Finally, the results will
display on the dosimeter screen.
For computation and storage, the clock tracks the sampling time.
Dosimeters record how long sound levels exceeded a set upper limit.
The calculator computes an Lavg, a dose, a TWA, and other data. The
memory stores all times, calculations, and measurements.
For post-processing, Detection Management Software is used to view
and analyze your measurement results with the option to view and/or
print reports.
Range control
(70–140 dB)
Apply filters
(A or C weighting)
Measurement
Results on the Edge
DMS – Manage, setup and report
Figure 1-2
Illustration of how the Dosimeter Operates and Processes

 Loading...
Loading...