19
WT200MP Welding Machine
www.weldtech.net.nz
MILD STEEL :
E6011 - This electrode is used for all-position welding or
for welding on rusty, dirty, less-than- new metal. It has
a deep, penetrating arc and is often the rst choice for
repair or maintenance work.
E6013 - This all-position electrode is used for welding
clean, new sheet metal. Its soft arc has minimal spatter,
moderate penetration and an easy-to-clean slag.
E7014 - All positional, ease to use electrode for use on
thicker steel than E6013. Especially suitable for sheet metal
lap joints, llet welds and general purpose plate welding.
E7018 - A low-hydrogen, all-position electrode used when
quality is an issue or for hard-to-weld metals. It has the ca-
pability of producing more uniform weld metal, which has
better impact properties at low temperatures.
CAST IRON:
ENI-CL -Suitableforjoiningallcastironsexceptwhite
cast iron.
STAINLESS STEEL:
E318L-16 -Highcorrosionresistances.Idealfordairy
work etc.
Electrodes for joining dierent metals:
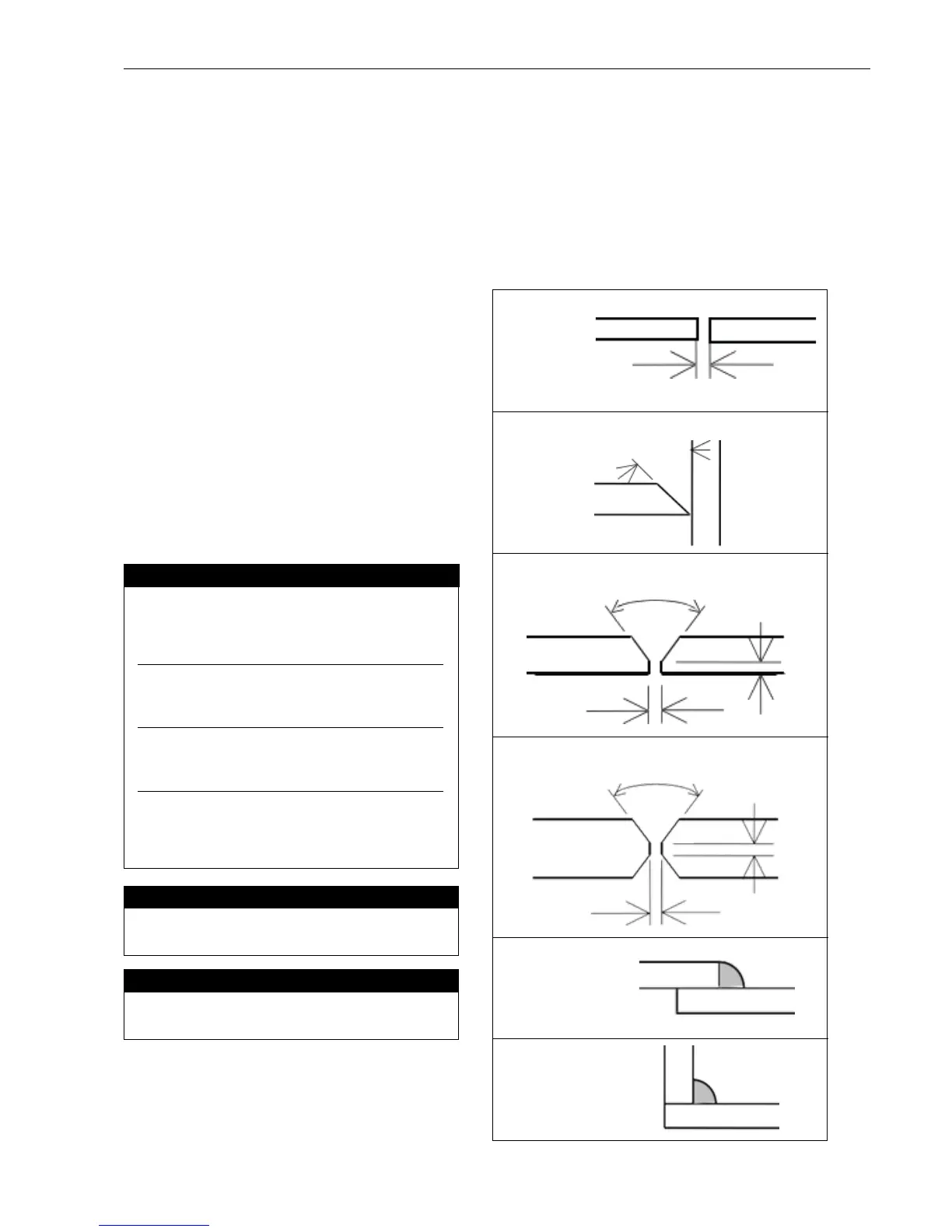
Joint Preparations
In many cases, it will be possible to weld steel sec-
tions without any special preparation. For heavier
Open Square Butt Joint
(Fig 1-19a)
Gapvariesfrom1.6mm(1/16”)
to4.8mm(3/16”)dependingonplatethickness
Single Vee Butt Joint
(Fig 1-19b)
Notlessthan45°
Single Vee Butt Joint
(Fig 1-19c)
Notlessthan70°
1.6mm(1/16”)max.
1.6mm(1/16”)
Double Vee Butt Joint
(Fig 1-19d)
Notlessthan70°
1.6mm(1/16”)max.
1.6mm(1/16”)
Lap Joint (Fig 1-19e)
Fillet Joint (Fig 1-19f)
generally cracks when attempts are made to weld it.
Trouble may also be experienced when welding
white-heart malleable, due to the porosity caused by
gas held in this type of iron.
Copper and Alloys
The most important factor is the high rate of heat
conductivity of copper, making pre-heating of heavy
sections necessary to give proper fusion of weld and
base metal.
Types of Electrodes
Arc Welding electrodes are classied into a number
of groups depending on their applications. There are
a great number of electrodes used for specialised in-
dustrial purposes which are not of particular interest
for everyday general work. These include some low
hydrogen types for high tensile steel, cellulose types
for welding large diameter pipes, etc. The range of
electrodes dealt with in this publication will cover
the vast majority of applications likely to be encoun-
tered; are all easy to use.
sections and for repair work on castings, etc., it will
be necessary to cut or grind an angle between the
pieces being joined to ensure proper penetration of
the weld metal and to produce sound joints.
In general, surfaces being welded should be clean
andfreeofrust,scale,dirt,grease,etc.Slagshouldbe
removed from oxy-cut surfaces. Typical joint designs
areshowninFigure1-19.

 Loading...
Loading...