ABB 6
1MAC251744 -PG Rev. A
Issued: 03.01.2010
Motor Protection
REM615 ANSI
Product Version 2.0
3. Protection functions
e REM615 relay o ers all the functionality needed
to manage motor starts and normal drive operations
also including protection and fault clearance in
abnormal situations. e main features of this motor
relay include thermal overload protection, motor
start-up time supervision, locked rotor protection
and protection against too frequent motor starts.
Furthermore, the relay o ers negative phase sequence
current unbalance protection, motor running stall
protection, loss-of-load supervision, phase-reversal
protection and a provision to perform a forced
emergency start.
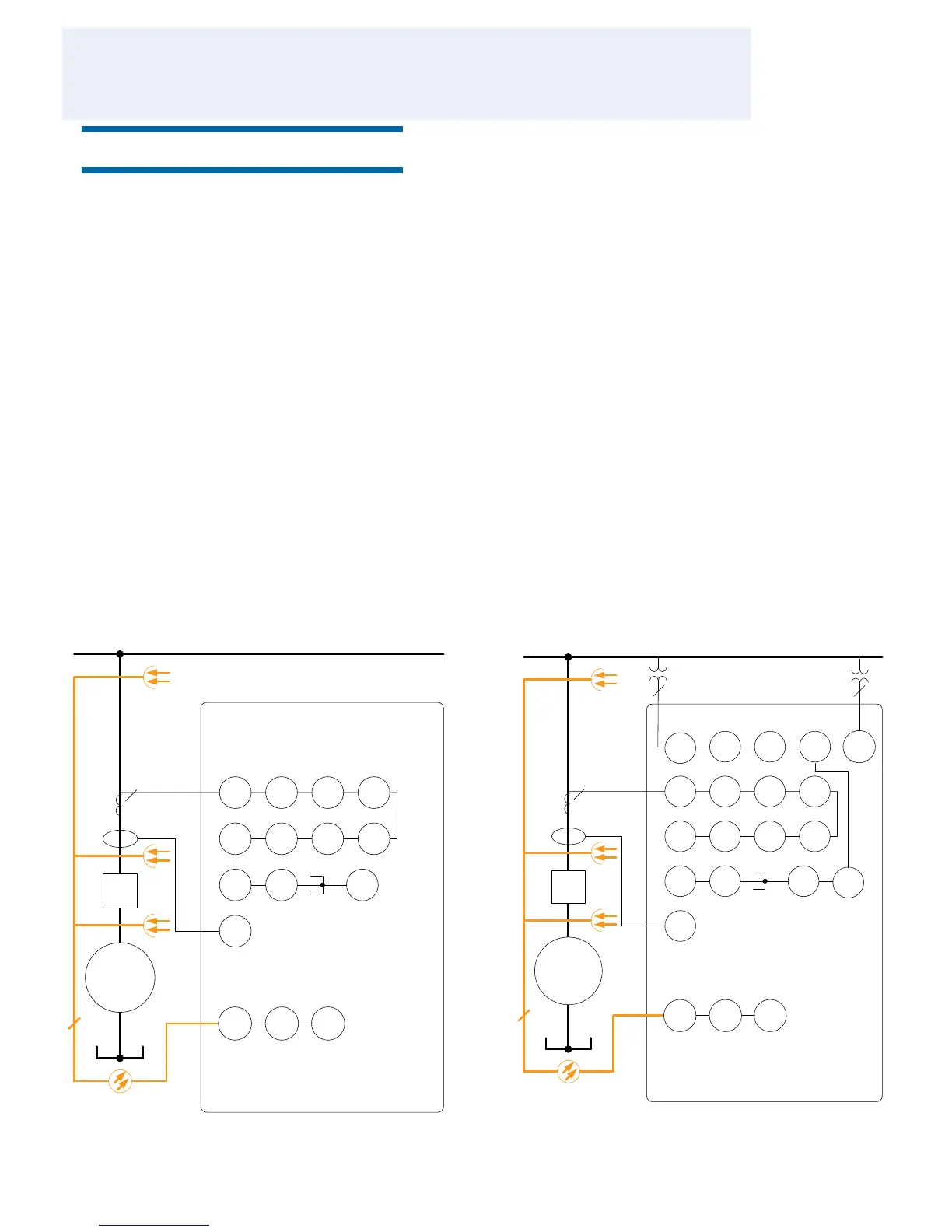
Figure 2. Protection function overview for standard con guration
C with analog inputs “CA”
3
REM615 V2.0 ANSI
M
37
66/
51LRS
51LR
51P 50P
46R49M 46M-1
87
2 or 3
Υor Δ
59G
3
27
27PS
67/
51N
46M-2
50
BF
50N
BF
52
51G
1
Available with Arc Flash Detection (AFD) option
3
AFD-
3
1
AFD-
1
1
AFD-
2
1
6047
Figure 1. Protection function overview for standard con guration
A with analog inputs “AA”
3
REM615 V2.0 ANSI
M
37
66/
51LRS
51LR
51P 50P
46R49M 46M-1
87
46M-2
50
BF
50N
BF
52
51G
1
Available with Arc Flash Detection (AFD) option
3
AFD-
3
1
AFD-
1
1
AFD-
2
1
e REM615 also incorporates non-directional and
directional earth-fault protection, backup overcurrent
protection, three phase undervoltage protection, and
negative phase sequence overvoltage and positive sequence
undervoltage protection. {New paragraph} Enhanced with
optional hardware and so ware, the relay also features three
light detection channels for arc fault protection of the circuit
breaker, busbar and cable compartment of metal-enclosed
indoor switchgear.
e arc-fault protection sensor interface is available on the
optional communication module. Fast tripping increases
personal safety and limits material damage within the
switchgear in an arc fault situation. Figures 1 through 2
show the protection functions available for the two standard
con gurations and their available analog inputs for each
con guration. See section 23. Selection and ordering data
for details on the available analog inputs for each standard
con guration.
 Loading...
Loading...