Chapter 7 Tutorial
Remote Programming
159
7
If no load resistor is attached to the power supply output terminal, then the output
voltage will rise linearly at a rate of C
O
/I
L
when programmed upward, and TR = C
O
(E
2
-E
1
)/I
L
, the shortest possible up-programming time.
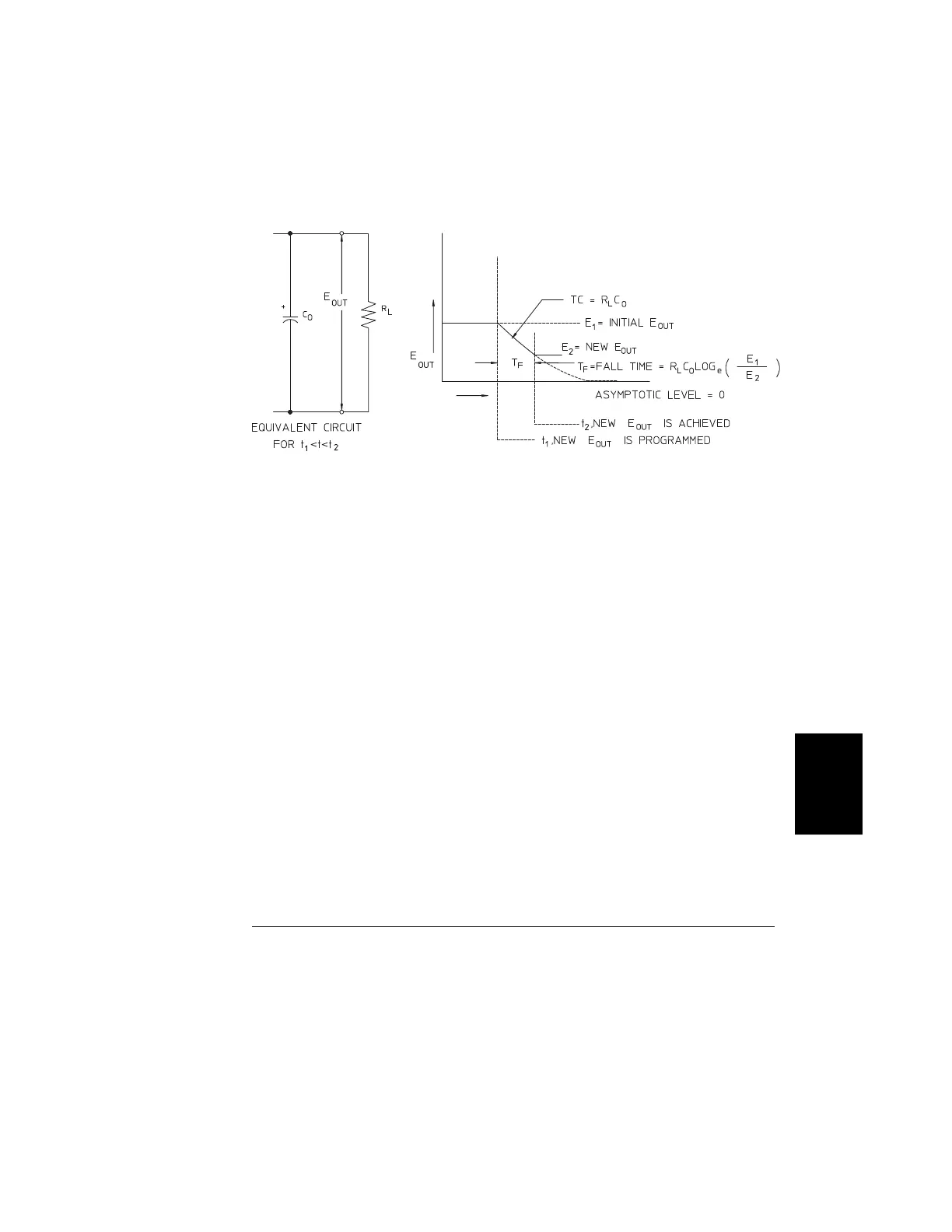
Figure 7-8. Speed of Response - Programming Down
Figure 7-8 shows that when the power supply is programmed down, the regulator
senses that the output voltage is higher than desired and turns off the series transistors
entirely. Since the control circuit can in no way cause the series regulator transistors
to conduct backwards, the output capacitor can only be discharged through the load
resistor and internal current source (I
S
).
The output voltage decays linearly with slope of I
S
/C
O
with no load and stops falling
when it reaches the new output voltage which has been demanded. If full load is
connected, the output voltage will fall exponentially faster.
Since up-programming speed is aided by the conduction of the series regulating
transistor, while down programming normally has no active element aiding in the
discharge of the output capacitor, laboratory power supplies normally program
upward more rapidly than downward.

 Loading...
Loading...











