56 Motor Overload
3. [Motor OL Hertz] is used to further protect motors with limited speed ranges.
Since many motors do not have sufficient cooling ability at lower speeds, the
overload feature can be programmed to increase protection in the lower speed
areas. This parameter defines the frequency where derating the motor overload
capacity should begin. For all settings of overload Hz other than zero, the
overload capacity is reduced to 70% when output frequency is zero. During DC
injection braking, the motor current may exceed 70% of FLA, but this will cause
the motor overload to trip sooner than when operating at base speed. At low
frequencies, the limiting factor may be the drive overload rather than the motor
overload.
Duty Cycle for the Motor Overload
When the motor is cold, this function will allow 3 minutes at 150%. When the
motor is hot, it will allow 1 minute at 150%. A continuous load of 102% is allowed
to avoid nuisance faults. The duty cycle of the motor overload is defined as follows.
If operating continuous at 100% FLA, and the load increases to 150% FLA for 59
seconds and then returns to 100%FLA, the load must remain at 100% FLA for 20
minutes to reach steady state.
The ratio of 1:20 is the same for all durations of 150%. When operating continuous
at 100%, if the load increases to 150% for 1 second the load must then return to
100% for 20 seconds before another step to 150%.
FLA%
Cold Trip
Time
Hot Trip
Time FLA%
Cold Trip
Time
Hot Trip
Time FLA%
Cold Trip
Time
Hot Trip
Time
105 6320 5995 155 160 50 205 66 14
110 1794 1500 160 142 42 210 62 12
115 934 667 165 128 36 215 58 11
120 619 375 170 115 31 220 54 10
125 456 240 175 105 27 225 51 10
130 357 167 180 96 23 230 48 9
135 291 122 185 88 21 235 46 8
140 244 94 190 82 19 240 44 8
145 209 74 195 76 17 245 41 7
150 180 60 200 70 15 250 39 7
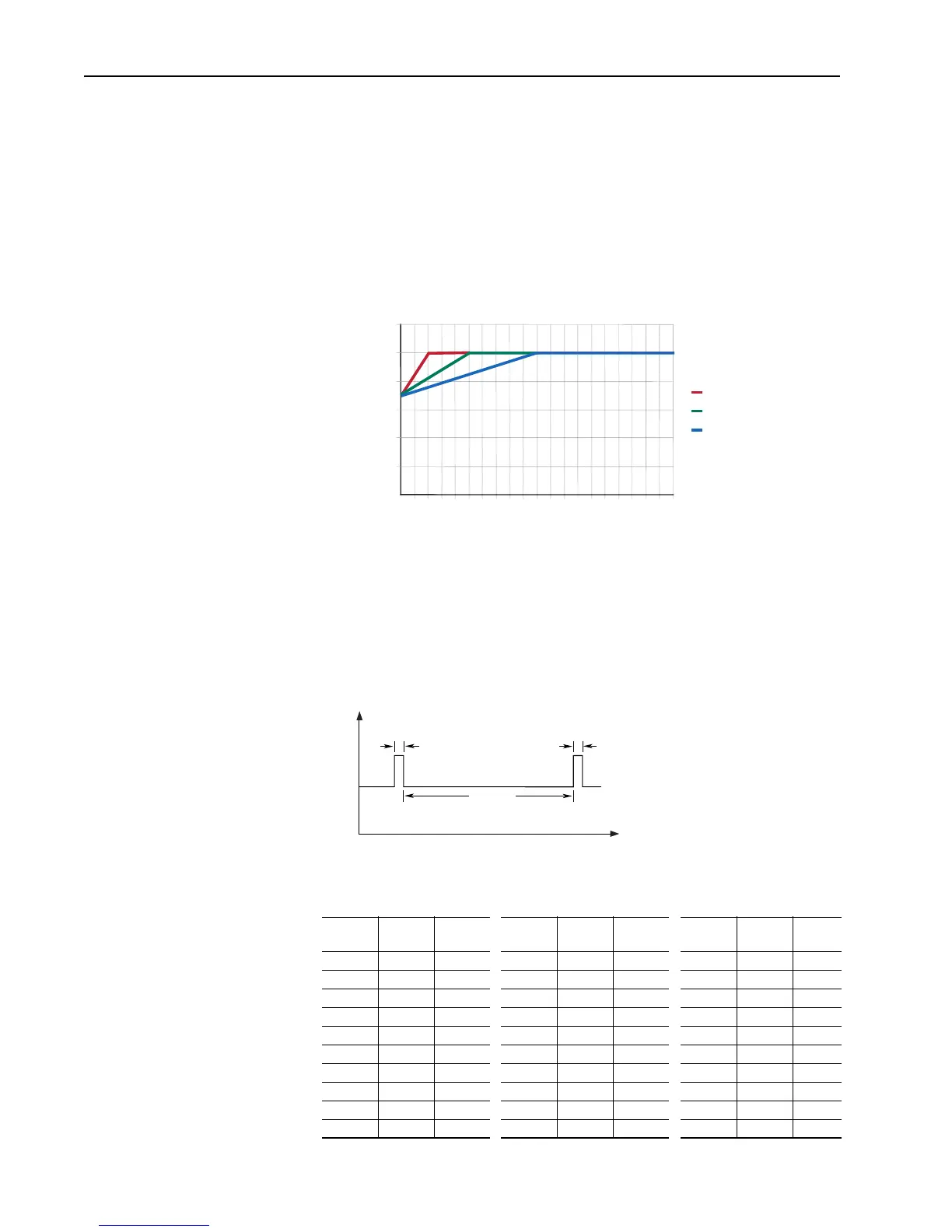
Changing Overload Hz
20
40
60
80
100
120
0 102030405060708090100
Continuous Rating
OL Hz = 10
OL Hz = 25
OL Hz = 50
20 Minutes
1 Minute 1 Minute
100%
150%

 Loading...
Loading...