Notch Filter 57
Important: If the application requires high overload current for long durations
(e.g. 150% for 60 seconds), heavy duty sizing (between drive and
motor) will be required. See "Normal Duty and Heavy Duty
Operation" on page 39
.
Notch Filter A notch filter exists in the torque reference loop to reduce mechanical resonance
created by a gear train. [Notch Filter Freq] sets the center frequency for the 2 pole
notch filter, and [Notch Filter K] sets the gain.
Figure 9 Notch Filter Frequency
Example
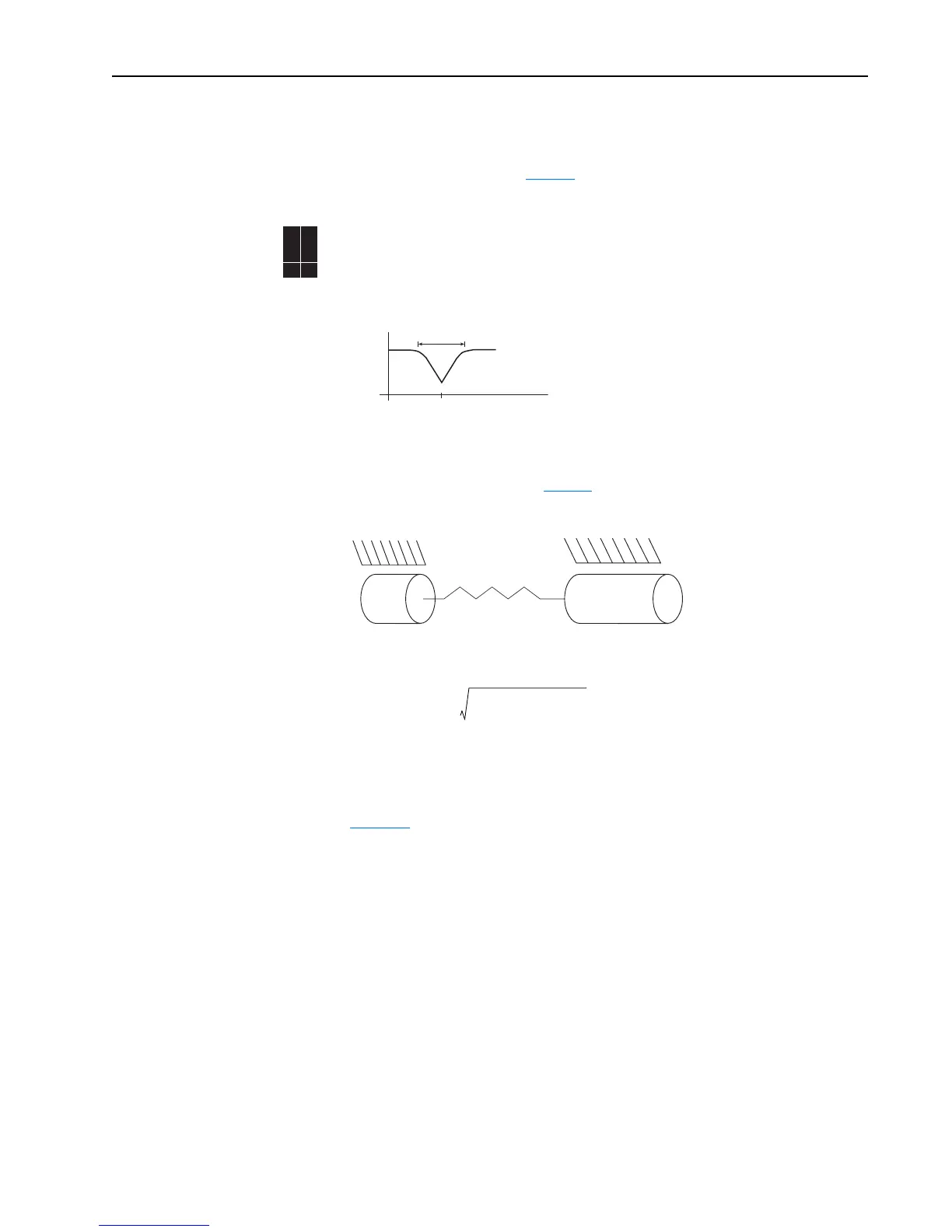
A mechanical gear train consists of two masses (the motor and the load) and spring (mechanical
coupling between the two loads). See Figure 10
.
Figure 10 Mechanical Gear Train
The resonant frequency is defined by the following equation:
Figure 11 shows a two mass system with a resonant frequency of 62 radians/second
(9.87 Hz). One Hertz is equal to 2π radians/second.
70EC
700VC
700H
✔
Gain
0 db
Hz
Notch Filter Frequency
Notch Filter K
Kspring
BLBm
Jm Jload
Jm is the motor inertia (seconds)
Jload is the load inertia (seconds)
Kspring is the coupling spring constant (rad
2
/sec)
resonance Kspring
Jm Jload+()
Jm Jload×
-------------------------------
=

 Loading...
Loading...