15
0
0,4
0,2
0,6
0,8
1
1,4
1,2
1,6
1,8
2
2,4
2,2
2,6
2,8
3
3,4
3,2
3,6
3,8
4
4,4
4,2
4,6
4,8
5
5,4
5,2
5,6
5,8
6
0
2000
4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 14000 16000 20000 22000 24000 2600018000
Pe rdit
e d
i c
ar ico (m/H )
2
O
350
300
250
200
150
Technical characteristics and dimensions
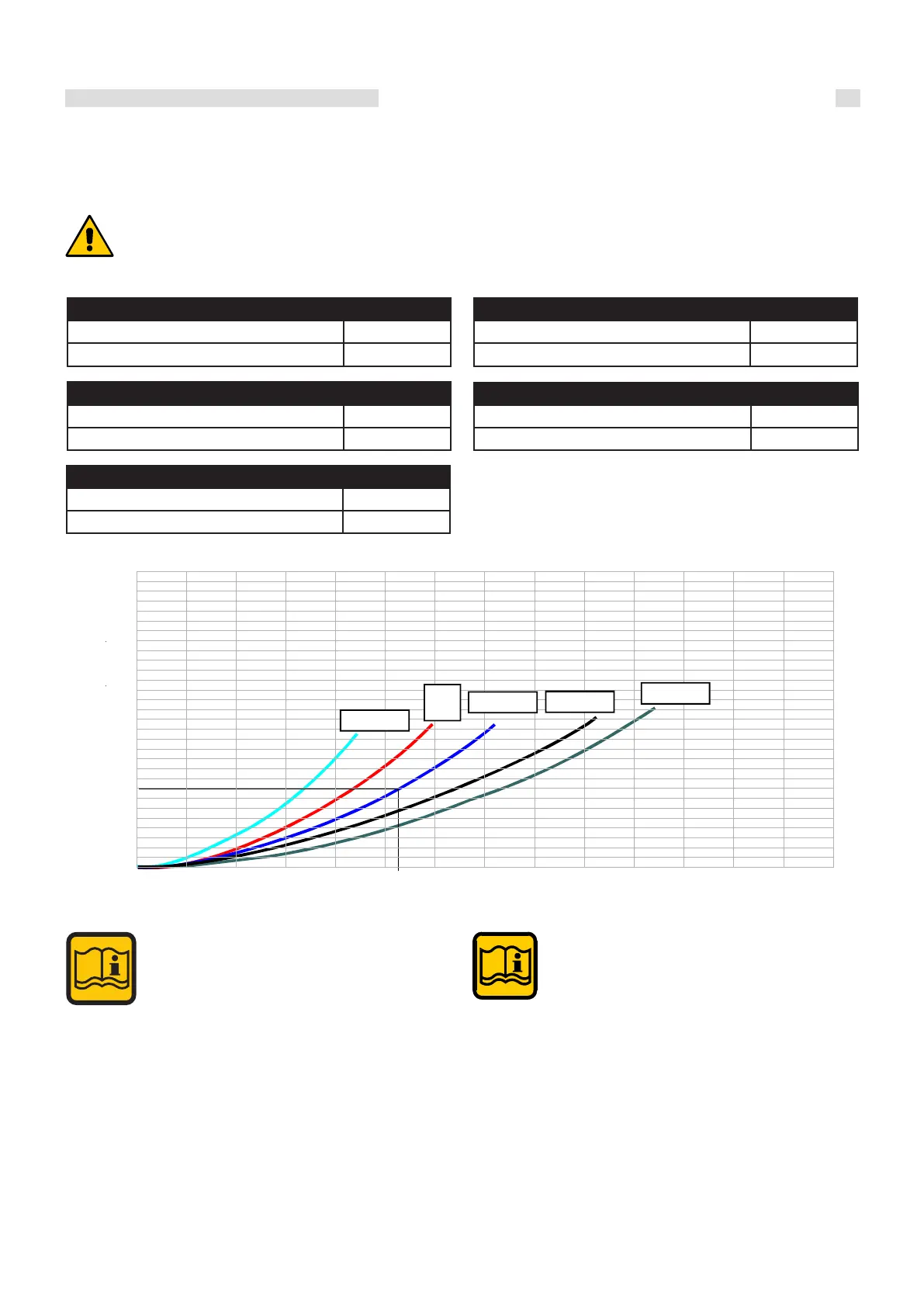
e pump is not an integral part of the boiler. It is advisable to choose a
pump with a ow rate and head of approximately 2/3 of its typical curve.
ARES TEC 200 ErP
Maximum ow rate in l/h (∆t = 15 K) 11.192
Nominal requested ow rate in l/h (∆t = 20 K)
8.394
ARES TEC 350 ErP
Maximum ow rate in l/h (∆t = 15 K) 19.712
Nominal requested ow rate in l/h (∆t = 20 K)
14.784
ARES TEC 150 ErP
Maximum ow rate in l/h (∆t = 15 K) 8.376
Nominal requested ow rate in l/h (∆t = 20 K)
6.282
ARES TEC 300 ErP
Maximum ow rate in l/h (∆t = 15 K) 16.856
Nominal requested ow rate in l/h (∆t = 20 K)
12.642
ARES TEC 250 ErP
Maximum ow rate in l/h (∆t = 15 K) 14.018
Nominal requested ow rate in l/h (∆t = 20 K)
10.514
e boiler pump must have head that can ensure circulator ow rates
according to the circuit’s ∆t.
The pumps must be determined by the installer or
designer based on the data for the boiler and system.
2.4.2 DETERMINING THE PRIMARY CIRCUIT PUMP OR BOILER PUMP
NOTE:
It is always advisable to set up a hydraulic compensator
between the boiler circuit and the system circuit. It
becomes ESSENTIAL if the system requires greater
ow rates than the maximum allowed by the boiler,
i.e. ∆t below 15K.
EXAMPLE:
For a T 20K, of an ARES 250 Tec the maximum
required ow rate is 10514 l/h.
From the head loss graph it is possible to deduce that
the pump must ensure a head of at least 1.6 m/H
2
O.
Flow rate (l/h)
Head loss (m/H2O)
 Loading...
Loading...