Example applications of the dc outputs include sweep control of the
gain, offset, or both ports of voltage-controlled amplifiers (VCAs) while
measuring their gain, distortion, or noise and plotting those values
versus control voltage. The dc output can also be used to control the
position of a dc-controlled turntable while measuring polar response
patterns of a loudspeaker or microphone. Manually operated test
equipment with a dc control port (such as the VCF input of a function
generator) may be controlled by the dc outputs. Tape machines with
dc-controllable bias oscillators may be connected, enabling MOL, SOL,
sensitivity, and other data to be taken automatically.
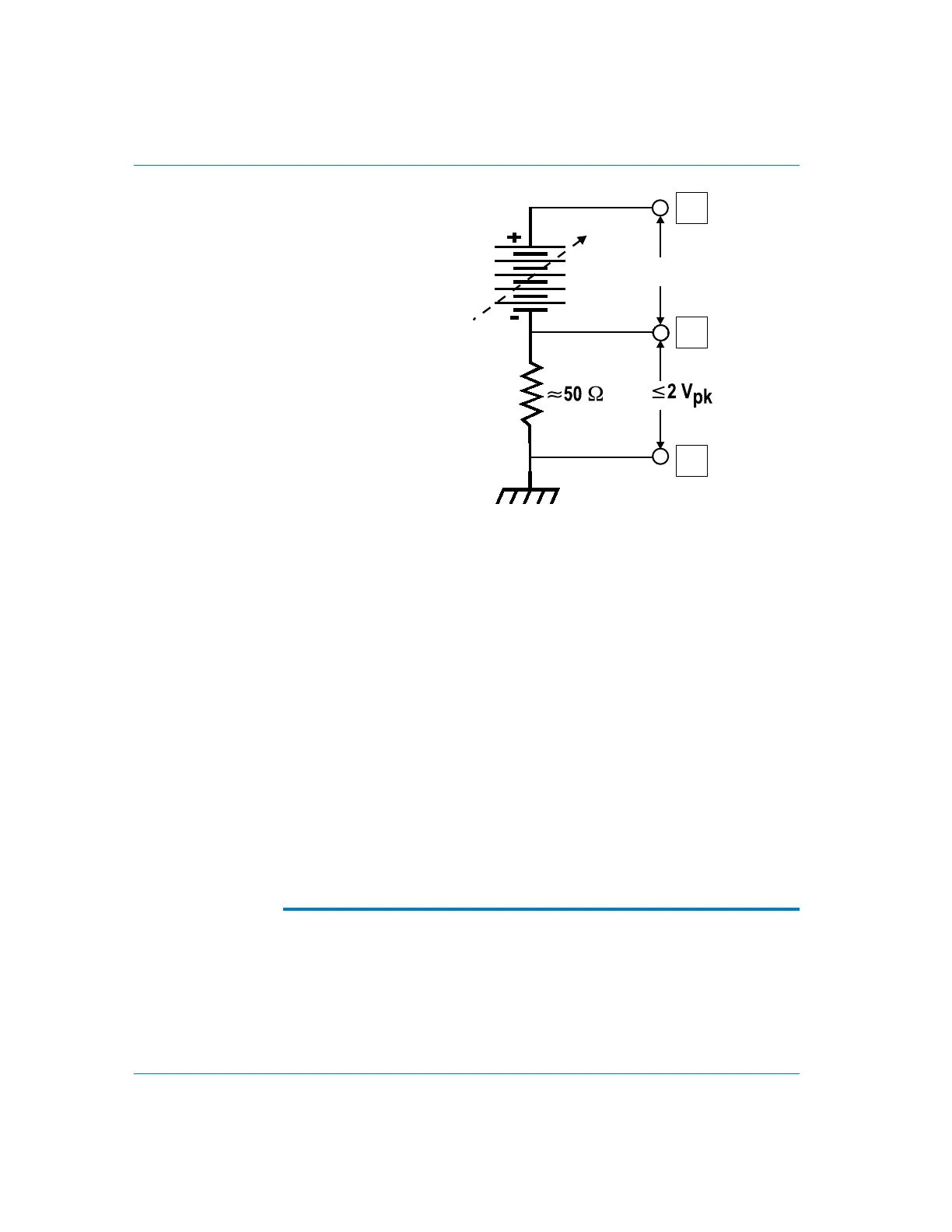
The dc outputs may be floated up to 2 volts away from ground.
See Figure 3 for the equivalent output circuit of both dc outputs.
Maximum current sourced from each is 20 milliamperes. The
maximum current that the DC outputs can sink is 10 milliamperes.
Digital Input
A common application of the digital input is in static (DC) linearity
testing of A/D converters. The digital input may also be used to
interface readings from a BCD-display instrument such as a
capacitance meter to the audio test system.
Digital Input Description
Page 6 DCX-127 Multifunction Module User’s Guide
+
T
-
V
out
Figure 3.
Equivalent
circuit, DC
Outputs 1 or 2
 Loading...
Loading...