79
107774-01- 9/17
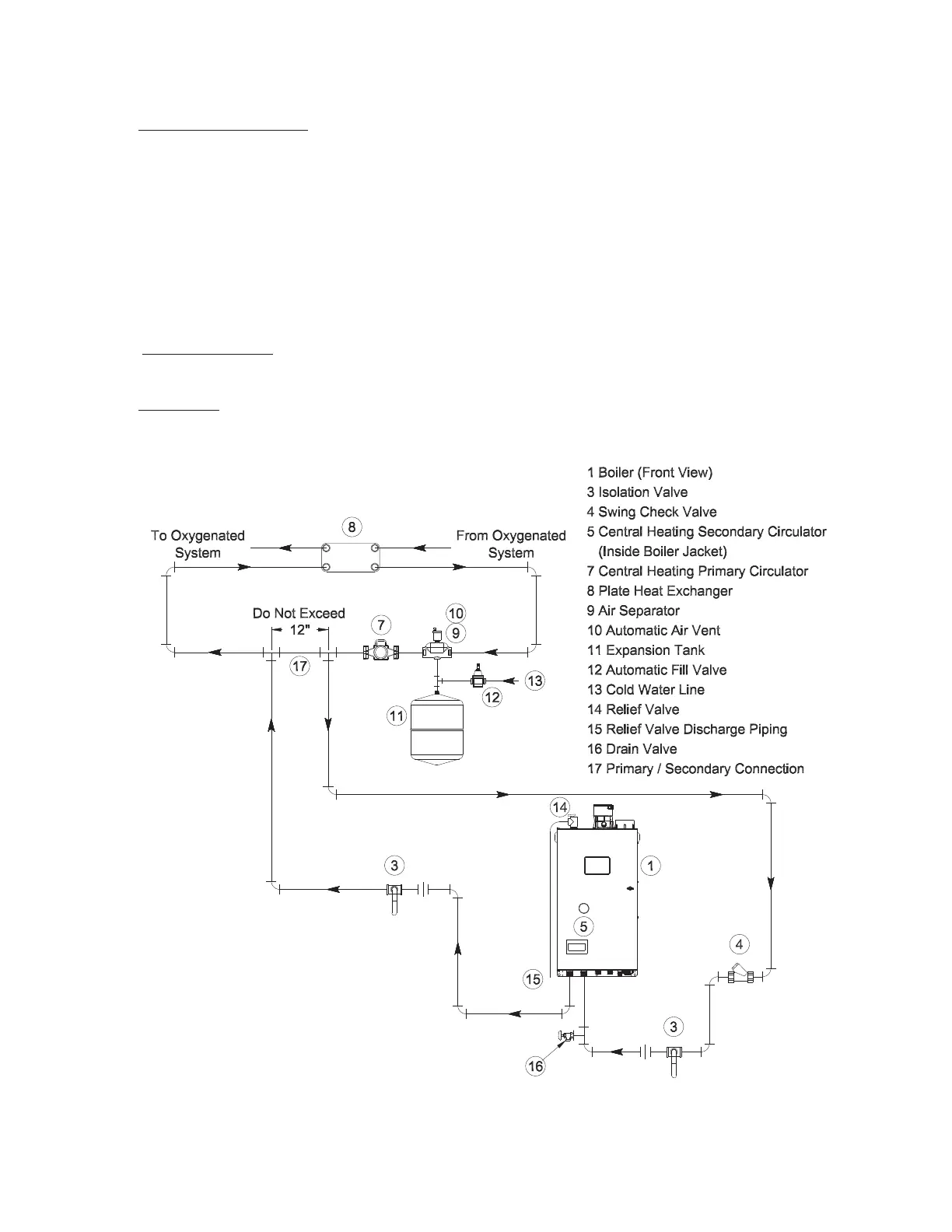
Figure 9.8: Isolation of the Boiler from Oxygenated Water with a Plate Heat Exchanger
1. System containing oxygen - Many hydronic systems contain enough dissolved oxygen to cause severe corrosion damage
to a boiler. Some examples include:
• Radiant systems that employ tubing without an oxygen barrier.
• Systems with routine additions of fresh water.
• Systems which are open to the atmosphere.
If the boiler is to be used in such a system, it must be separated from the oxygenated water being heated with a heat
exchanger as shown in Figure 9.8. Consult the heat exchanger manufacturer for proper heat exchanger sizing as well as
owandtemperaturerequirements.Allcomponentsontheoxygenatedsideoftheheatexchanger,suchasthepumpand
expansion tank, must be designed for use in oxygenated water.
2. Piping with a Chiller - If the boiler is used in conjunction with a chiller, pipe the boiler and chiller in parallel. Use
isolation valves to prevent chilled water from entering the boiler.
3. Air Handlers-Wheretheboilerisconnectedtoairhandlersthroughwhichrefrigeratedairpasses,useowcontrol
valves in the boiler piping or other automatic means to prevent gravity circulation during the cooling cycle.
IX. System Piping (continued)
D. Piping for Special Situations
 Loading...
Loading...