E N G L I S H
µC
2
- +030220731 - rel. 1.2 - 26.10.2007
• Control settings: parameters (r*)
- Cooling set point
r01: between r13 and r14
r02: cooling differential
- Heating set point (heat pump)
r03: between r15 and r16
r04: heating differential
- Compressor rotation
r05: The rotation of the compressors allows the operating hours to be balanced either statistically, using
FIFO logic, or absolutely, by counting the effective operating hours.
Settings:
r05=0: rotation disabled; The customer can use compressors with different power ratings according
to the desired logic or manage the capacity-control functions. The compressors are started/stopped in
proportional mode.
r05=1: rotation with FIFO logic (first ON, first OFF, and vice-versa first OFF, first ON); in this mode the
operating hours are optimised together with the number of starts, even if the compressor safety times are
always respected.
r05=2: rotation with control of operating hours; in this way the compressors will have the same operating
hours, as the compressor with the least operating hours is always started first, again observing the safety
times. This does not however consider FIFO logic and does not optimise the starts and stops.
In the case of capacity controlled compressors (1 per circuit), FIFO logic or timed operation will refer to
the actual circuit and not the compressor valves. If, for example, when capacity is required from circuit 1,
compressor 1 starts first, capacity controlled (not at full capacity), and then the valve is managed as a se-
cond step, so that the compressor will work at maximum efficiency. If less capacity is required, the second
step will be deactivated first, and then the compressor. There is no rotation between the compressor and
the valve. If extra capacity is required, the second circuit will start with compressor 2 and then, if required,
the valve is operated.
When stopping, the valve is managed first and then the actual compressor as a whole. Both FIFO logic
and timed operation will involve either one circuit or the other. The activation and deactivation of the val-
ves are not subject to timers, but rather only a hysteresis that is equal to the set point and the differential
of the step (in fact the valve performs the same function as a hermetic compressor).
r05=3: direct correspondence between the digital inputs and the compressor relays (condensing units
only).
- Type of compressor control
r06: This parameter is used to set the logic for maintaining the set point:
r06= 0: proportional on inlet
r06= 1: proportional on inlet + dead zone (see Dead zone, below)
r06= 2: proportional on outlet
r06= 3: proportional on outlet with dead zone
r06= 4: on outlet by time with dead zone (see timed outlet temperature control)
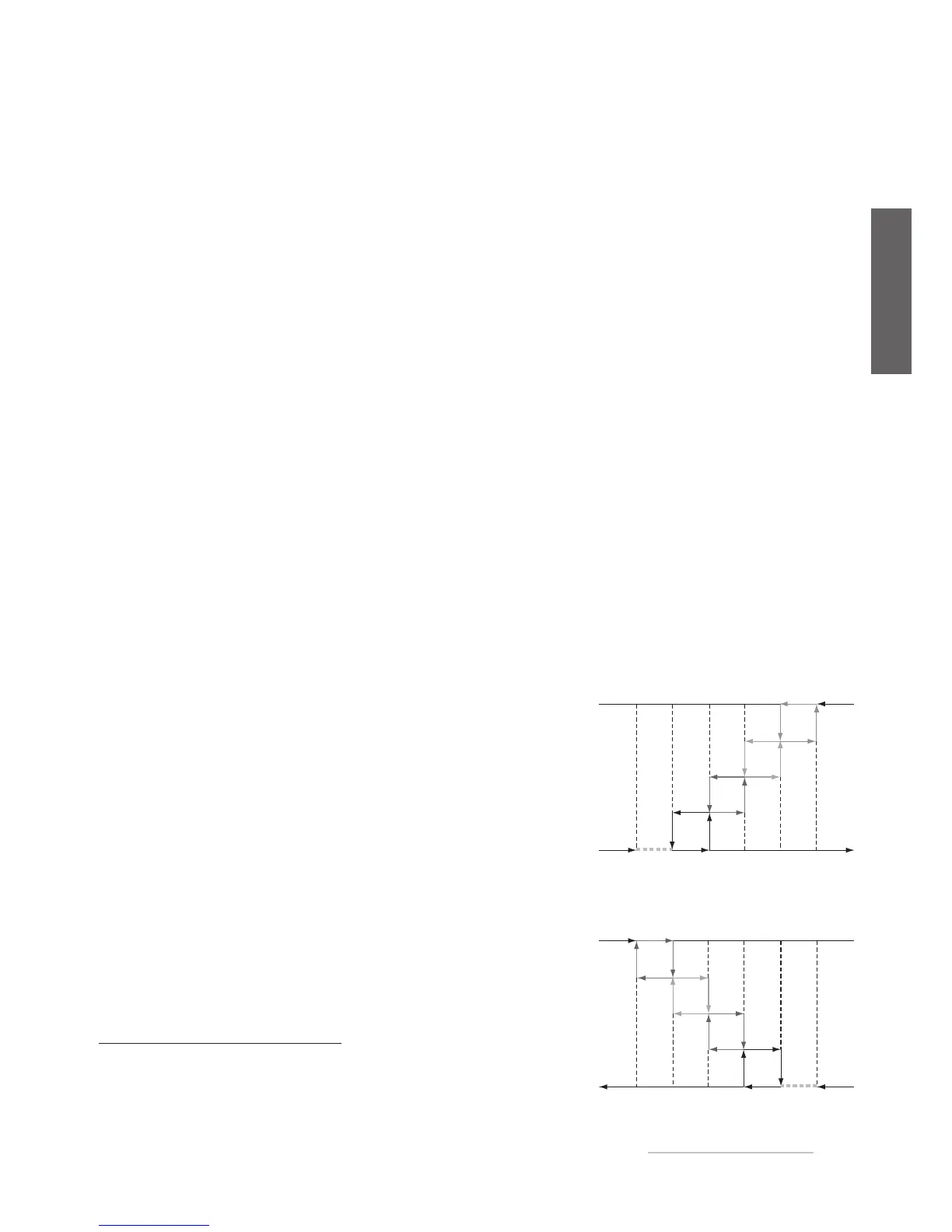
DEAD ZONE
The dead zone essentially shifts the proportional band from the set
point by the value set for the parameter r07.This parameter is valid in
all configurations if enabled (for r07≠0: dead zone set and enabled).
Key Figure 5.b.c:
r06: enable the dead zone (enabled if r06=1 or 3)
r07: dead zone
r01: cooling set point
r02: cooling differential
In chiller (cooling) mode, the dead zone moves the cooling proportional band above the set point by the
value r07.
Key Figure 5.b.d:
r06: enable the dead zone (enabled if r06=1 or 3)
r07: dead zone
r03: heating set point
r04: heating differential
In heat pump (heating) mode, the dead zone moves the heating proportional band below the set point
by the value r07.
Outlet temperature control by time r06 = 4 (only chiller)
This type of control is based on the need to maintain the outlet temperature as constant as possible,
despite the load being variable or the reduced inertia of the system.
The logic has the aim of keeping the temperature inside the dead zone.
If outside the zone, the compressors will be activated with the logic described below, so as to return
inside the dead zone, neither too quickly (using an integral or derivative), nor too slowly, with fixed time
logic. There are two logical times involved: the activation time and deactivation time.
Fig. 5.b.c
Fig. 5.b.d

 Loading...
Loading...