Example 2: To determine the logical OR of 1011
2
and 11010
2
(1011
2
or
11010
2
)
1011 (BASE) (or) 11010 0000000000011011
Example 3: To determine the logical XOR of 1010
2
and 1100
2
(1010
2
xor
1100
2
)
1010 (BASE) (xor) 1100 0000000000000110
Example 4: To determine the logical XNOR of 1111
2
and 101
2
(1111
2
xnor
101
2
)
1111 (BASE) (xnor) 101 1111111111110101
Example 5: To determine the bitwise complement of 1010
2
(Not(1010
2
))
(BASE) (Not) 1010 1111111111110101
Example 6: To negate (take the two's complement) of
101101
2
(Neg(101101
2
))
(BASE) (Neg) 101101 1111111111010011
Note
• In the case of a negative binary, octal or hexadecimal value, the calculator converts
the value to binary, takes the two's complement, and then converts back to the original
number base. For decimal (base-10) values, the calculator merely adds a minus sign.
Using VERIFY (VERIF)
VERIFY is a function you can use to verify whether an input equality or
inequality is true (indicated by TRUE) or false (indicated by FALSE). The
following shows the general procedure for using VERIFY.
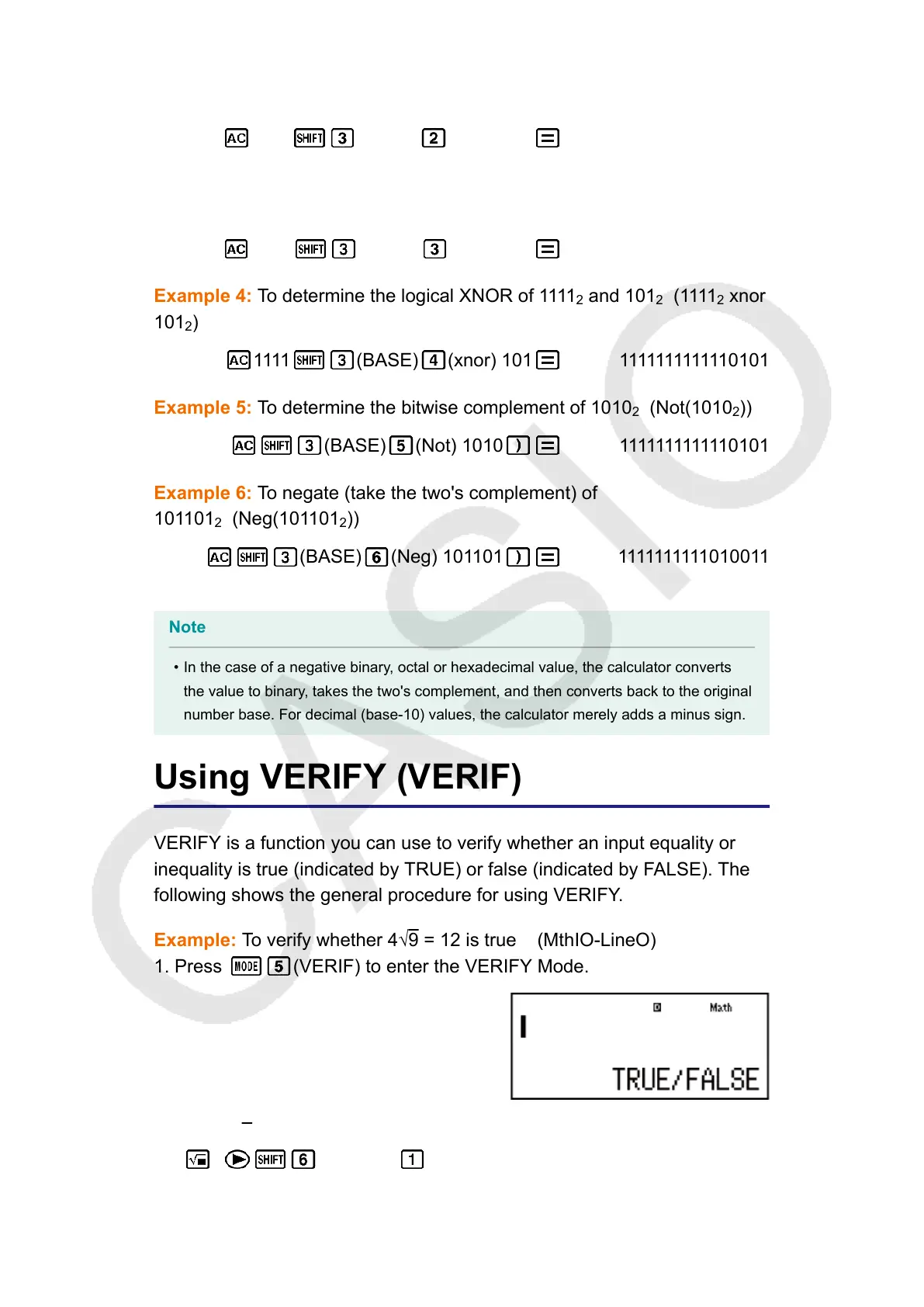
Example: To verify whether 4√
9 = 12 is true (MthIO-LineO)
1. Press (VERIF) to enter the VERIFY Mode.
2. Input 4√9 = 12.
4 9 (VERIFY) (=) 12
53

 Loading...
Loading...