Configuring ISG Access for IP Subscriber Sessions
Information About ISG Access for IP Subscriber Sessions
5
IP Subscriber Connectivity
IP subscribers connect to ISG through either Layer 2 connected access networks or routed access
networks. The following sections describe these types of IP subscriber connectivity:
• Layer 2 Connected Access Networks
• Routed Access Networks
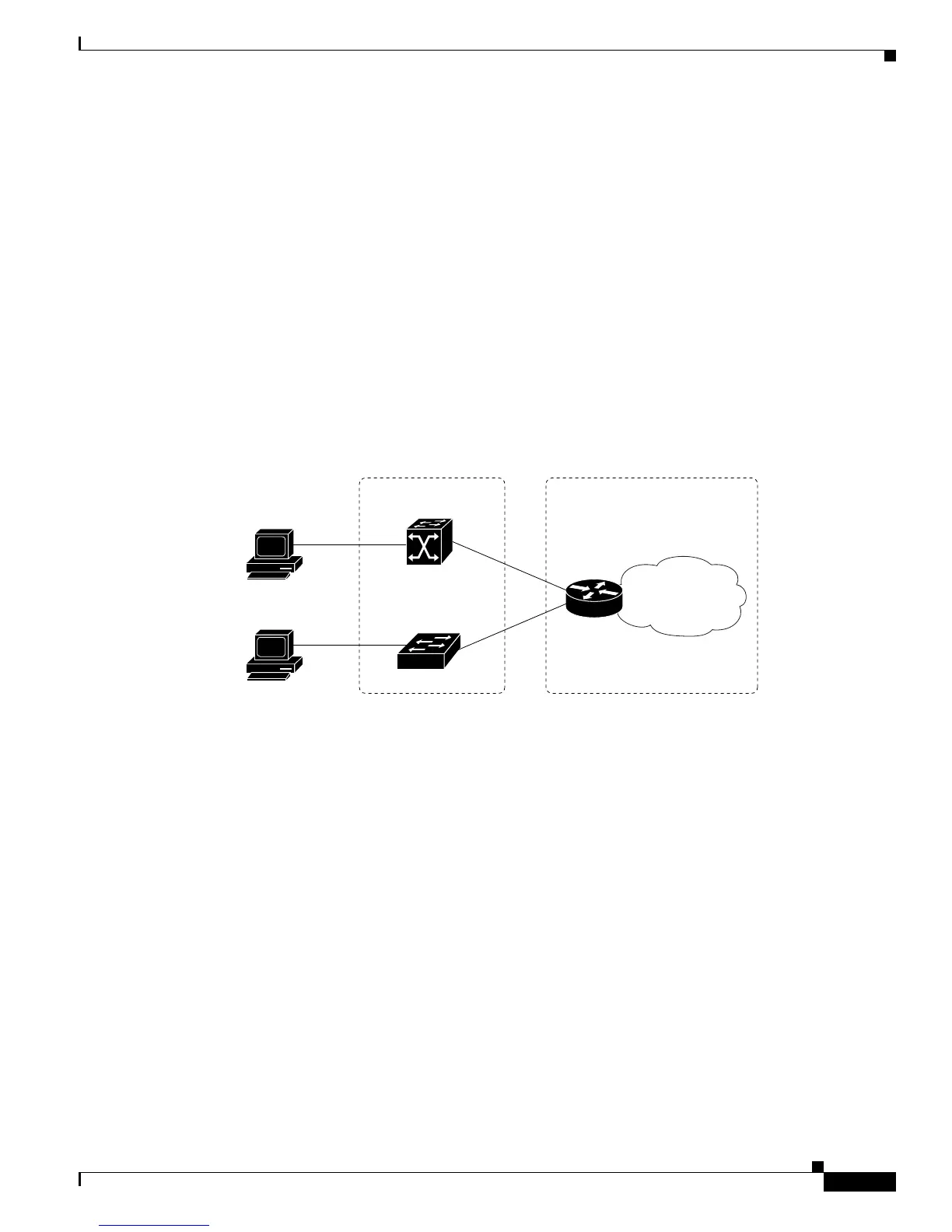
Layer 2 Connected Access Networks
Layer 2 connected subscribers are either directly attached to the physical interfaces of an ISG or
connected to an ISG through a Layer 2 access network, such as a bridged or a switched network. Layer 3
forwarding is either absent or not used to direct subscriber traffic in the Layer 2 access network. IP
addresses of the subscribers may or may not be on the same subnet as the Layer 2 connected physical
interfaces. Figure 1 shows an example of a Layer 2 connected access network.
Figure 1 Layer 2 Connected Access Network
Routed Access Networks
Routed subscriber traffic is routed through a Layer 3 access network with at least one transit router
before reaching the ISG. IP addresses of the subscribers are at least routable in the Layer 3 access
network. Layer 3 access networks contain a single routing domain and therefore do not support
overlapping IP addresses. Figure 2 shows an example of a routed access network.
Bridged/switched
access network
Core network
ISG
IP subscriber
IP subscriber
230024

 Loading...
Loading...











