Using Your Computer 25
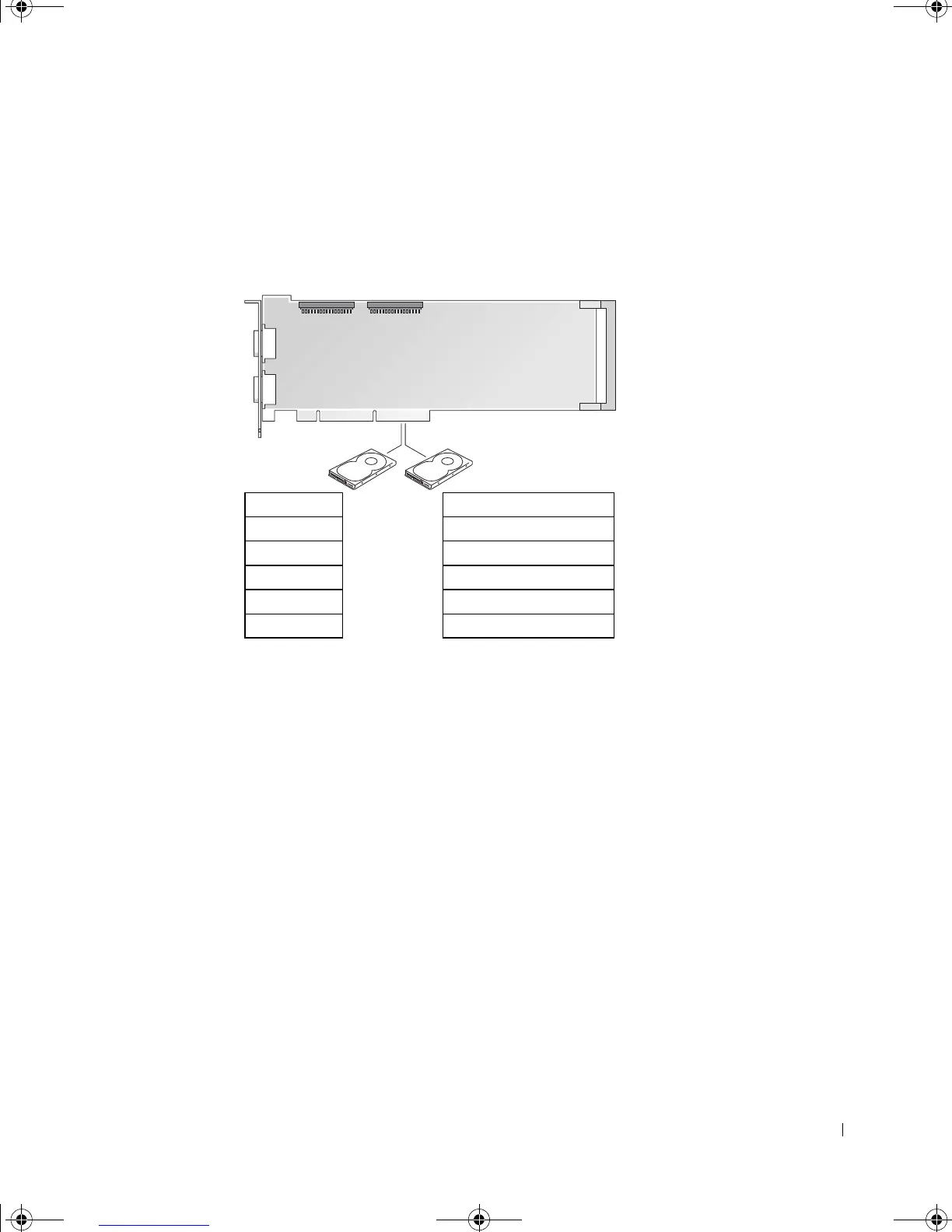
RAID Level 1
RAID level 1 uses a data-redundancy storage technique known as "mirroring." When data is
written to the primary drive, it is then duplicated, or mirrored, on the other drive. A RAID
level 1 configuration sacrifices high data access rates for its data redundancy advantages.
If a drive failure occurs, subsequent read and write operations are directed to the surviving
drive. A replacement drive can then be rebuilt using the data from the surviving drive. Also,
because data is duplicated on both drives, two 120-GB RAID level 1 drives collectively have
a maximum of 120-GB on which to store data.
Transferring Information to a New Computer
The Microsoft
®
Windows
®
XP operating system provides a Files and Settings Transfer
wizard to move data from the source computer to the new computer. You can move data
such as:
•E-mails
• Toolbar settings
• Window sizes
• Internet bookmarks
serial ATA RAID PCI card
configured for RAID level 1
hard drive
segment 1
segment 2
segment 3
hard drive
segment 4
segment 5
segment 6
segment 1 duplicated
segment 2 duplicated
segment 3 duplicated
segment 4 duplicated
segment 5 duplicated
segment 6 duplicated
G0550bk1.book Page 25 Thursday, July 10, 2003 1:55 PM

 Loading...
Loading...