Chapter 8 Communications ASDA-B2
8-14 Revision May, 2018
LRC and CRC transmission Error Checking:
The error checking in ASCII communication mode is LRC (Longitudinal Redundancy
Check); CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check) is for RTU communication mode.
The algorithm of both is as the following.
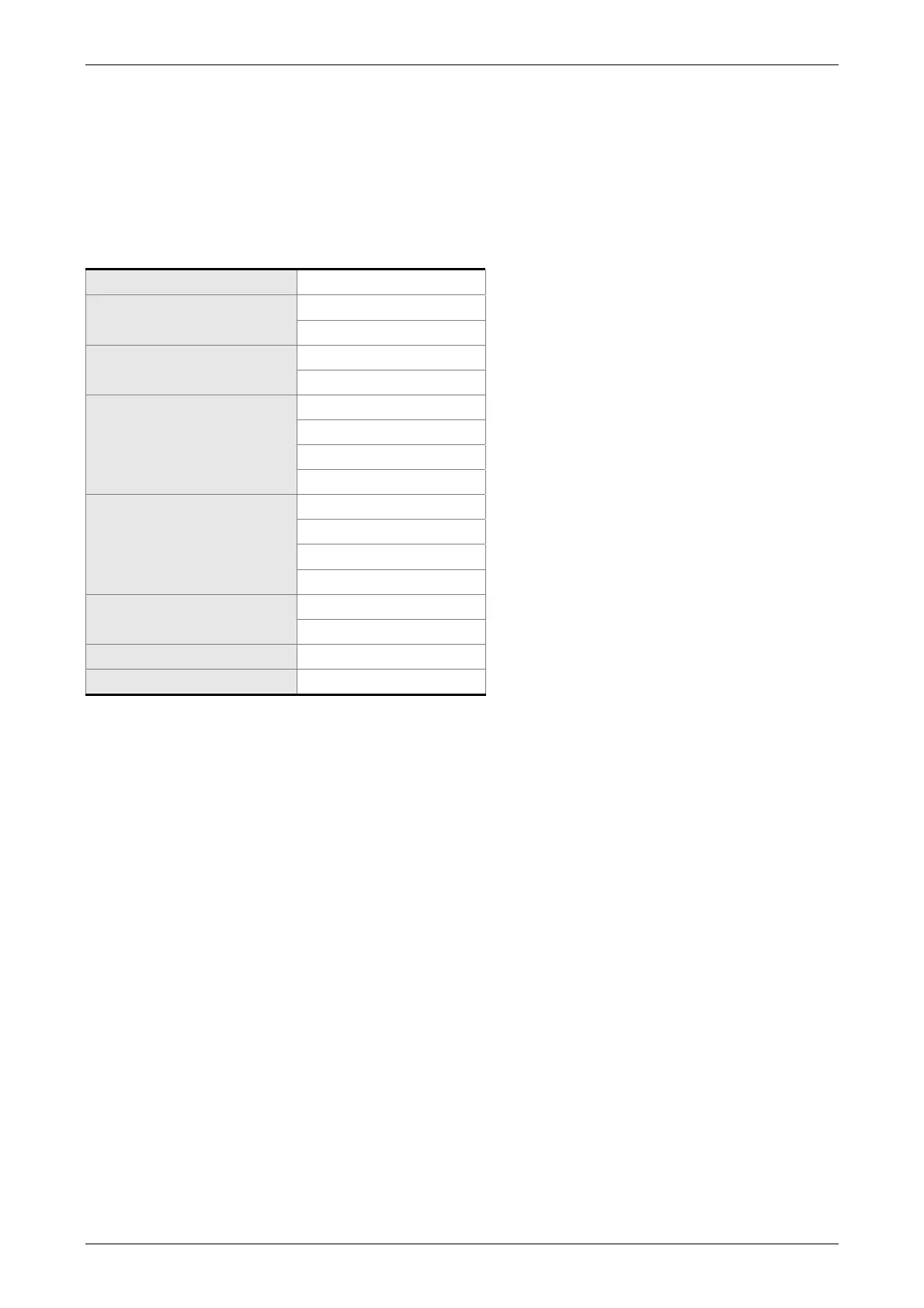
LRC (ASCII mode):
STX ‘:’
ADR
‘7’
‘F’
CMD
‘0’
‘3’
Starting data address
‘0’
‘5’
‘C’
‘4’
Number of data
‘0’
‘0’
‘0’
‘1’
LRC Check
‘B’
‘4’
End 1 (0DH)(CR)
End 0 (0AH)(LF)
The LRC algorithm is: add all byte, round down the carry and take 2’s complement.
For example, 7FH + 03H + 05H + C4H + 00H + 01H = 14CH, round down carry 1 and
take 4CH.
2’s complement of 4CH is B4H.
CRC (RTU Mode):
The description of CRC is as the followings:
Step 1: Load a 16-bits register of FFFFH, which is called “CRC” register.
Step 2: (The low byte of CRC register) XOR (The first byte of command), and save
the result in CRC register.
Step 3: Right move one bit. Check the least significant bit (LSB) of CRC register.
If the bit is 1, then (CRC register) XOR (A001H).
Step 4: Return to Step 3 until Step 3 has been executed for 8 times. Go to Step 5.
Step 5: Repeat the procedure from Step 2 to Step 4 until all byte is processing.
Get the result of CRC value.

 Loading...
Loading...











