Chapter 16 PLC Function ApplicationsMS300 (High Speed Model)
16-45
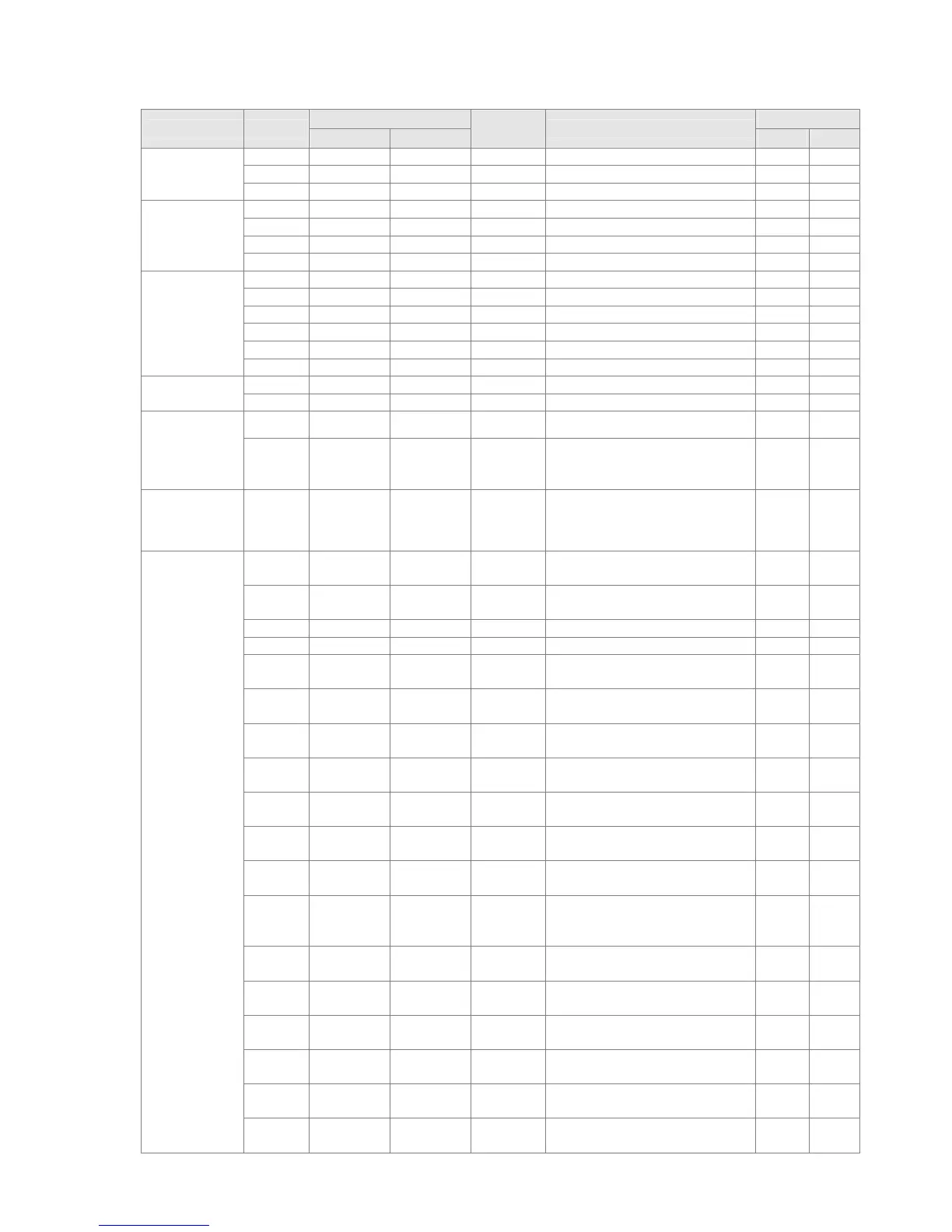
16-6-3 Overview of application commands
Classification API
Command code
P
command
Function
STEPS
16 bit 32 bit 16 bit 32 bit
Circuit control
01 CALL -
Call subprogram 3 -
2 SRET - - Conclusion of subprogram 1 -
06 FEND - - Conclusion a main program 1 -
Send
comparison
10 CMP DCMP
Compares set output 7 13
11 ZCP DZCP
Range comparison 9 17
12 MOV DMOV
Data movement 5 9
15 BMOV –
Send all 7 –
Four logical
operations
20 ADD DADD
BIN addition 7 13
21 SUB DSUB
BIN subtraction 7 13
22 MUL DMUL
BIN multiplication 7 13
23 DIV DDIV
BIN division 7 13
24 INC DINC
BIN add one 3 5
25 DEC DDEC
BIN subtract one 3 5
Rotational
displacement
30 ROR DROR
Right rotation 5 –
31 ROL DROL
Left rotation 5 –
Data Process
40 ZRST –
Clear range 5 -
49 – DFLT
BIN whole number → binary
floating point number
transformation
- 9
communication 150 MODRW –
MODBUS read/write 7 –
Floating point
operation
110 – DECMP
Comparison of binary floating
point numbers
– 13
111 – DEZCP
Comparison of binary floating
point number range
– 17
116 – DRAD
Angle → Diameter – 9
117 – DDEG
Diameter → angle – 9
120 – DEADD
Binary floating point number
addition
– 13
121 – DESUB
Binary floating point number
subtraction
– 13
122 – DEMUL
Binary floating point number
multiplication
– 13
123 – DEDIV
Binary floating point number
division
– 13
124 – DEXP
Binary floating point number
obtain exponent
– 9
125 – DLN
Binary floating point number
obtain logarithm
– 9
127 – DESQR
Binary floating point number
find square root
– 9
129 – DINT
Binary floating point number →
BIN whole number
transformation
– 9
130 – DSIN
Binary floating point number
SIN operation
– 9
131 – DCOS
Binary floating point number
COS operation
– 9
132 – DTAN
Binary floating point number
TAN operation
– 9
133 – DASIN
Binary floating point number
ASIN operation
– 9
134 – DACOS
Binary floating point number
ACOS operation
– 9
135 – DATAN
Binary floating point number
ATAN operation
– 9

 Loading...
Loading...











