5. MAINTENANCE, ADJUSTMENTS AND CALIBRATION
Page 107 © 1998 DH Instruments, Inc.
5.4 CALIBRATION OF REFERENCE TRANSDUCERS
5.4.1 PRINCIPLE
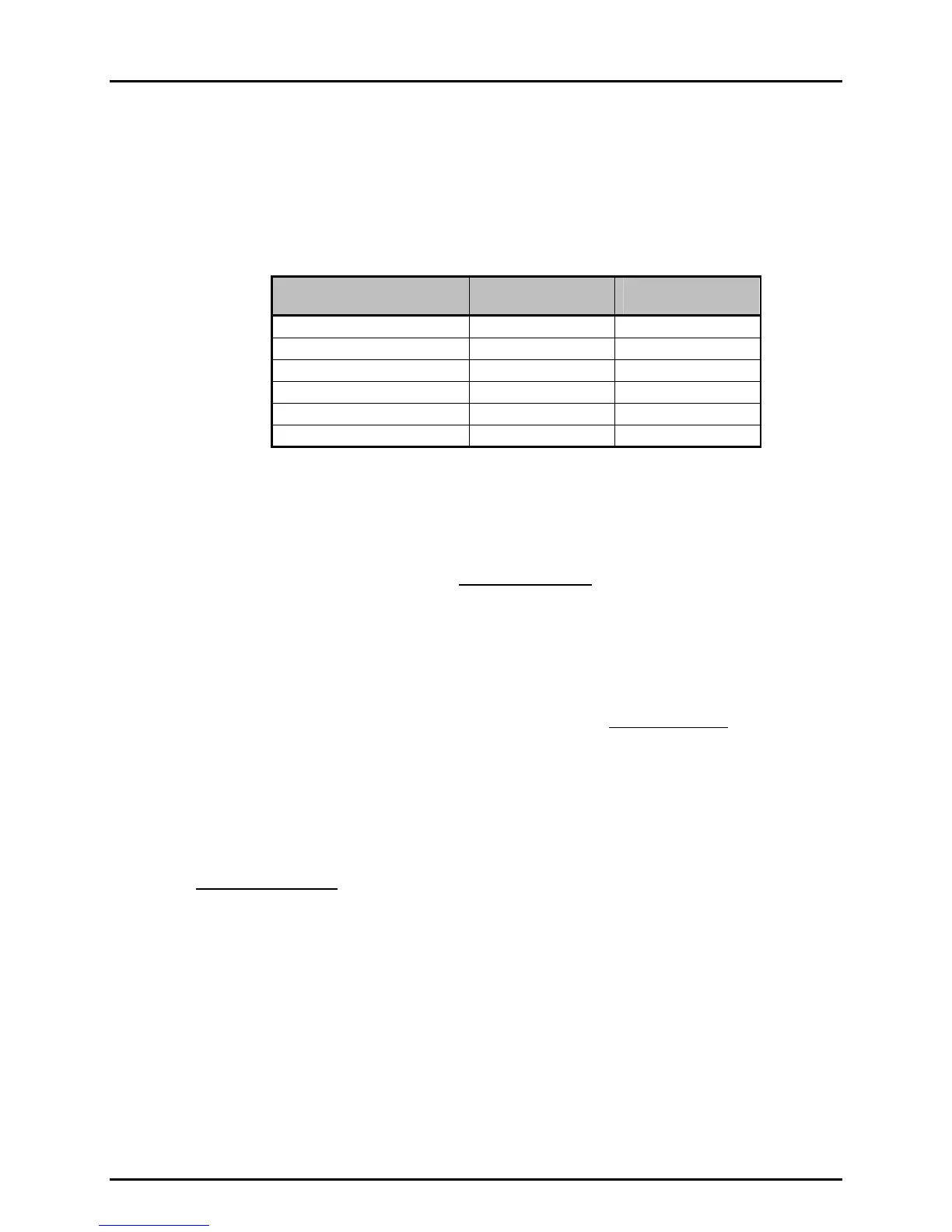
PPC2 AF has two reference pressure transducers that are used as the source of accurate
pressure measurement for the system. Each transducer has three ranges as follows:
REFERENCE TRANSDUCER
AND RANGE NUMBER
RANGE (PSI)
GAUGE/ABSOLUTE
MAIN RUN SCREEN
INDICATION
Lo, 1(Lo) 0/15 L1
Lo, 2(Mid) 15/30 L2
Lo, 3(Hi) 35/50 L3
Hi, 1(Lo) 300/300 H1
Hi, 2(Mid) 600/600 H2
Hi, 3(Hi) 1 000/1 000 H3
To calibrate a range, pressures from a standard are applied to the reference transducer at
ascending and descending pressures over the range. The transducer readings relative to the
pressure standard are recorded at each point and then adjustments are made to fit the
pressure readings to the standard. Fitting the readings means performing a linear regression
to arrive at the lowest value of the residuals of errors of the transducer relative to the
standard. The transducer readings are adjusted using a user setable PA (an adder or offset)
and PM (a multiplier or span set) (see PA/PM Coefficients
below).
The adjustment process is performed independently on each range for each pressure
transducer to arrive at the optimal fit for each range. This technique allows improved
accuracy for individual ranges lower than the transducer full range by taking into account
specific transducer performance characteristics, in particular localized non-linearity and
excursion dependent hysteresis.
The calibration process of a reference pressure transducer has a second step which is the
experimental determination of the value of PA(z)tare (see Setting PA(z)tare
below) to allow
the Autozero function to accurately reset the offset between calibrations (see Section 3.4.4.1).
PPC2 AF supports an on-board calibration routine to step the operator through performing the
complete reference transducer calibration procedure including applying the necessary
pressures to each range, determining PA(z)tare, automatically calculating new PA/PM values,
previewing the results of the new calibration and activating the results of the new calibration
(see Section 5.4.4). The option of performing the calibration without using the on-board
calibration routine is also available (see Section 5.4.5).
PA/PM Coefficients
The coefficients used to adjust transducer readings are designated PA (an adder or offset) and PM
(a multiplier or span set). The coefficients affect the transducer reading following:
Corrected reading = (uncorrected reading • PM) + PA
PA is expressed in units of pressure (always the SI unit, Pa).
PM is dimensionless.
There are individual PA/PM values for each of PPC2 AF's six ranges. The current PA/PM
values used can be viewed in the calibration function (see Section 5.4.6). PA/PM values are
automatically edited when the on-board reference transducer calibration function is used and the
results are activated (see Section 5.4.4). PA/PM values can also be edited directly under the
calibration function (see Section 5.4.5).
 Loading...
Loading...