29
CHAPTER 5: DESCRIPTION of OPERATION
Bus Remote Interface RS-232 / GPIB
This chapter provides information on the proper use and configuration of bus remote interface
for RS232 and GPIB interface, whereby both interfaces are using exactly same command lists.
These interfaces are optional on 6500 Series AC Power Source.
5.1 RS-232 Interface
Introduction
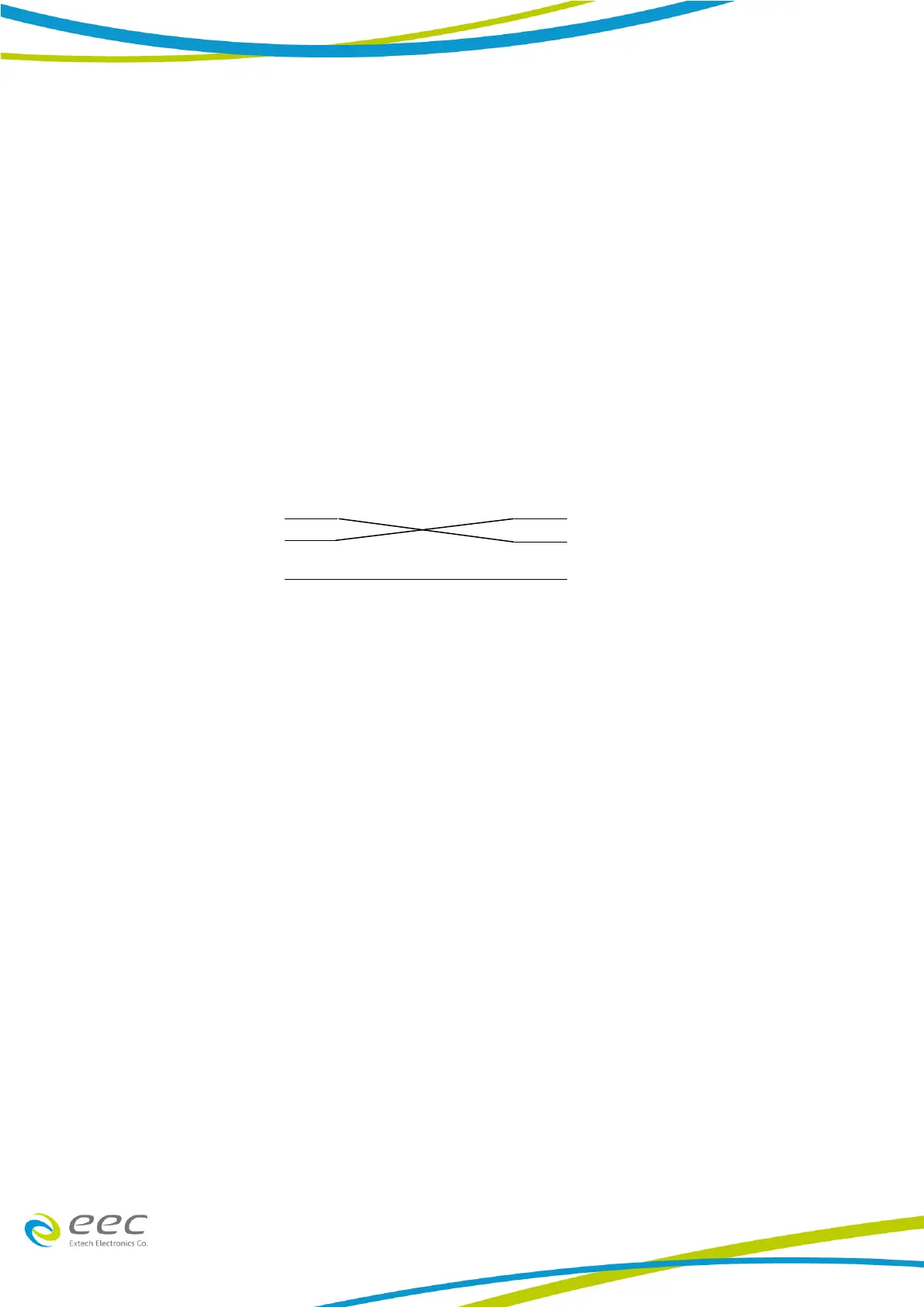
The RS232 connection is configured as follows for a 9 pins Serial Port interface:
The COM port should have the following configuration: 9600 baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no
polarity, and etc. This interface does not support XON/XOFF protocol or any hardware
handshaking. The controller should be configured to ignore the Handshaking Lines DTR (PIN 4),
DSR (PIN 6) and RTS (PIN 9). If the port cannot be configured through software to ignore the lines,
the handshake lines should be then jumped together in two different sets. The PIN 4 and 6
jumped together while PIN 7 and 8 jumped together at the controller end of the cable.
When sending command over the RS232 bus the AC Power Source will send a response string of
06 Hex or 6 decimal and the Acknowledge (ACK) ASCII control code if the transfer was recognized
and completed by the AC Power Source. If there is an error with the command string that is sent,
the AC Power Source will respond with 15 Hex or 21 decimal and the Not Acknowledge (NAK)
ASCII code. The ACK or NAK response allows for software handshaking, in order to monitor and
control data flow. When requesting data from the AC Power Source, it will automatically send the
data back to the controller input buffer. The controller input buffer will accumulate data being
sent from the AC Power Source including the ACK and NAK response strings, until the controller
has read it. When the strings or command has been sent, it must be terminated with LF=(0AH),
such as “TEST”+LF.
6500 Series PC/Bus controller
 Loading...
Loading...