Selection criteria
5.
224
Ref.1912
DDS
HARDWARE
· 208 ·
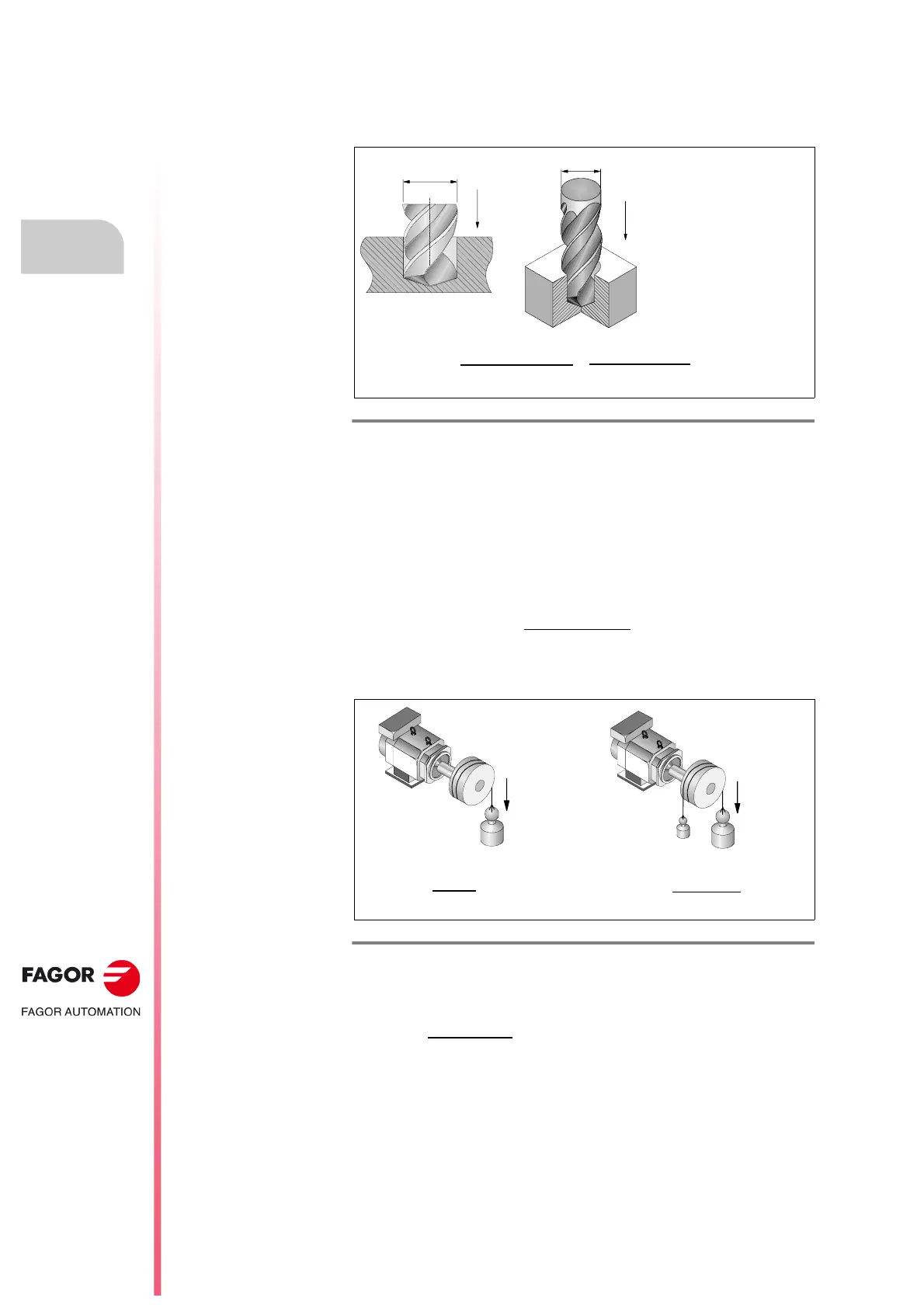
In the case of a drill, the bit is mounted on the spindle itself and turns with this
to drill the material. See figure F. H5/5
.
The power required in this case Pd may be calculated with the following
formula:
In the event of governing a gravitational load
, the power required depends
very much on the presence on absence of balance weights (crane or
elevator). See figure F. H5/6
.
The power required in this case, P
GL
& P
GLC
may be calculated as follows:
Governing a frictional load
, this is the case of horizontal movements such as
a conveyor belt or a movable table, the required power depends on the
friction coefficient µ. See figure F. H5/7.
F. H5/5
Drilling. Required power.
M
Drilling load torque in N·cm
n
Spindle turning speed in rpm
D
Hole diameter in mm
f
Feedrate in mm/min
d
Mechanical efficiency (varies from 0.7 to 0.85)
S
d
Cutting efficiency. Cutting volume per kilowatt every minute
(cm³/kW)/min
F. H5/6
Gravitational load. Required power.
V
Linear speed in m / min
Mechanical efficiency
m
L
Table mass in kg
m
C
Counterweight mass in kg
P
d
M· 2
·n
60·100·1000·
d
=
·D²
·f
4·1000·S
d
·
d
(kW)
=
Drum
Load
Balance
weight
Motor
Speed
 Loading...
Loading...