1
Configuring ACLs
Overview
An access control list (ACL) is a set of rules for identifying traffic based on criteria such as source IP
address, destination IP address, and por t number. The rules are also called permit or deny
statements.
ACLs are primarily used for packet filtering. "Configuring packet filtering with ACLs" provides an
example. You can use ACLs in QoS, security, routing, and other modules for identifying traffic. The
packet drop or forwarding decisions depend on the modules that use ACLs.
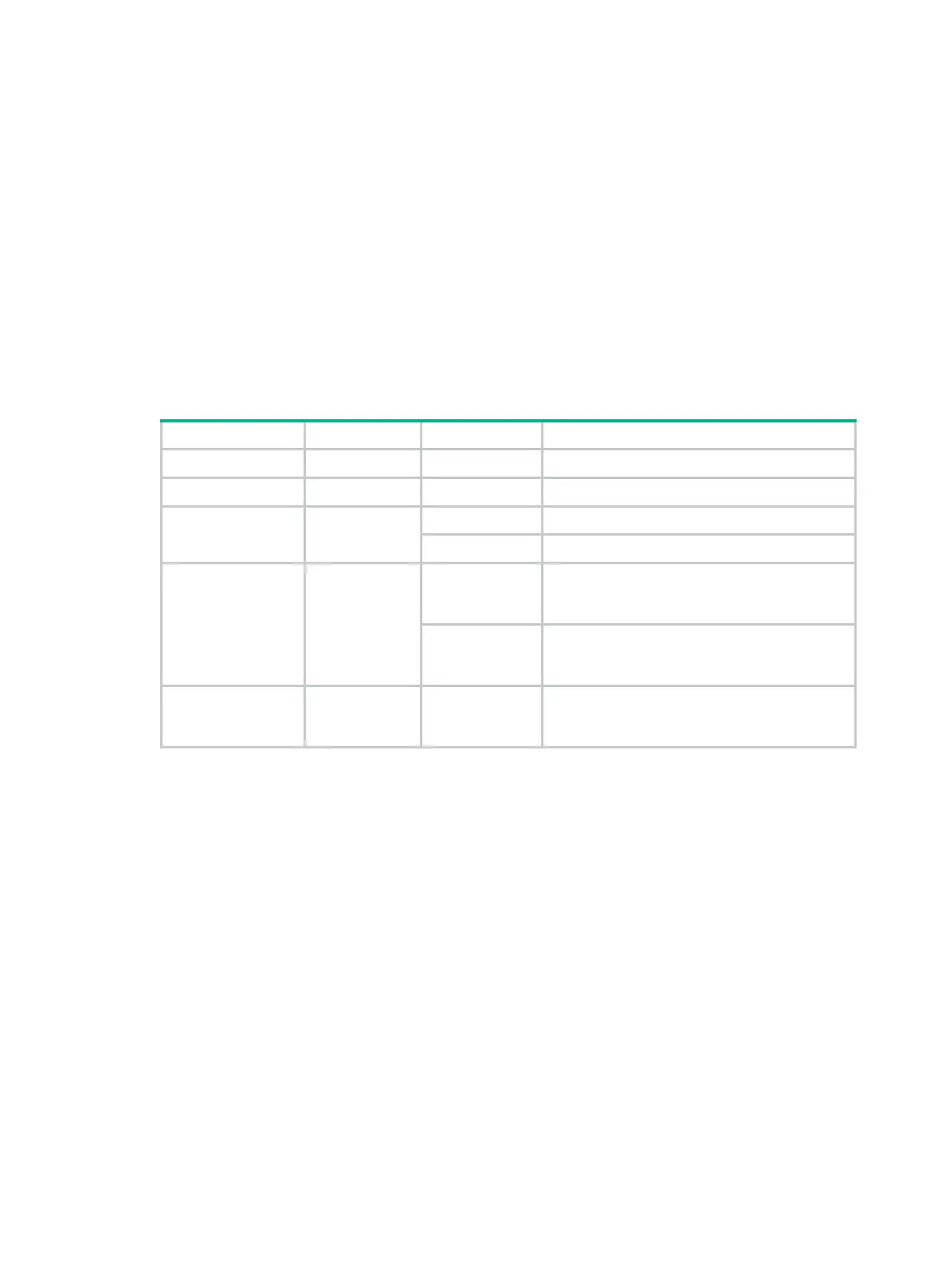
ACL types
WLAN client ACL 100 to 199 IPv4 and IPv6 SSID.
WLAN AP ACL 200 to 299 IPv4 and IPv6 AP MAC address and AP serial ID.
Basic ACLs 2000 to 2999
IPv4 Source IPv4 address.
IPv6 Source IPv6 address.
Advanced ACLs 3000 to 3999
IPv4
Source IPv4 address, destination IPv4
address, packet priority, protocol number, and
other Layer 3 and Layer 4 header fields.
IPv6
Source IPv6 address, destination IPv6
address, packet priority, protocol number, and
other Layer 3 and Layer 4 header fields.
Layer 2 ACLs 4000 to 4999 IPv4 and IPv6
Layer 2 header fields, such as source and
destination MAC addresses, 802.1p priority,
and link layer protocol type.
Numbering and naming ACLs
When creating an ACL, you must assign it a number or name for identification. You can specify an
existing ACL by its number or name. Each ACL type has a unique range of ACL numbers.
For an IPv4 basic or advanced ACL, its ACL number or name must be unique in IPv4. For an IPv6
basic or advanced ACL, its ACL number and name must be unique in IPv6. For a Layer 2, WLAN
client, or WLAN AP ACL, its number or name must be globally unique.
Match order
The rules in an ACL are sorted in a specific order. When a packet matches a rule, the device stops
the match process and performs the action defined in the rule. If an ACL contains overlapping or
conflicting rules, the matching result and action to take depend on the rule order.
The following ACL match orders are available:
• config—Sorts ACL rules in ascending order of rule ID. A rule with a lower ID is matched before
a rule with a higher ID. If you use this method, check the rules and their order carefully.

 Loading...
Loading...