21
Clip
HBMA0114-6.3 en
Example 3
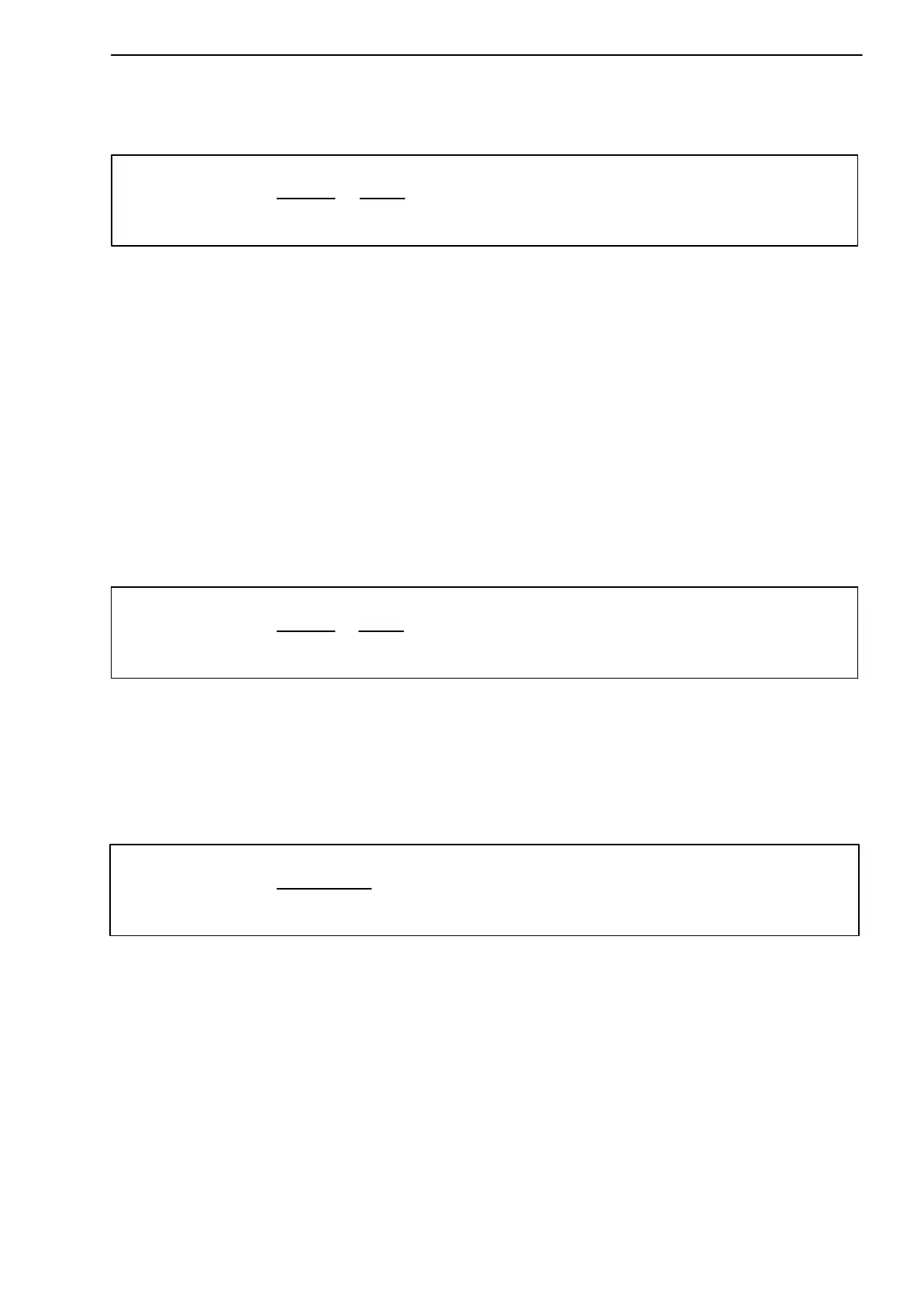
Force transducer 100 N ¢ 2 m V/V; measuring range wanted: 60 N ¢ 10 V
60 N
100 N
•
10 V
10 V
• 2mVńV + 1.2 mVńV
Load transducer with 60 N.
Use S21 to select appropriate interval as given in Tab. 4.2 (page 19) (switch
on 4 + 7), and use P22 to adjust the output voltage to 10 V exactly. The mea-
suring range can also be adjusted with no transducer connected by means of
a calibration unit (e.g. K 3607) that simulates the transducer signal.
• Additive calibration signal
The measuring range can also be adjusted using the additive calibration sig-
nal (0.2 mV/V).
Example 4
Force transducer 100 N ¢ 2mV/V; measuring range wanted: 60 N ¢ 10 V
60 N
100 N
•
10 V
10 V
• 2mVńV + 1.2 mVńV
Calculate nominal measurement value, execute zero balance (see above) and
use S21 to select the corresponding measuring-range interval. Connect addi-
tive calibration signal (set S25 to CAL) and use P22 to adjust with the trans-
ducer under no load. The amplifier has now been calibrated. Adjust S25 to
MEAS.
0.2 mVńV
1.2 mVńV
• 10 V + 1.667 V
• Synchronization
For synchronization of several CF amplifiers, one master device must be de-
fined by adjusting S24 to MASTER. The other devices must be set to SLAVE
using S24. Then, interconnect terminals 8. Synchronization is also possible
with AE501 measuring amplifiers.
 Loading...
Loading...