30
4 Programming: Fundamentals of NC, File Management,
Programming Aids, Pallet Management
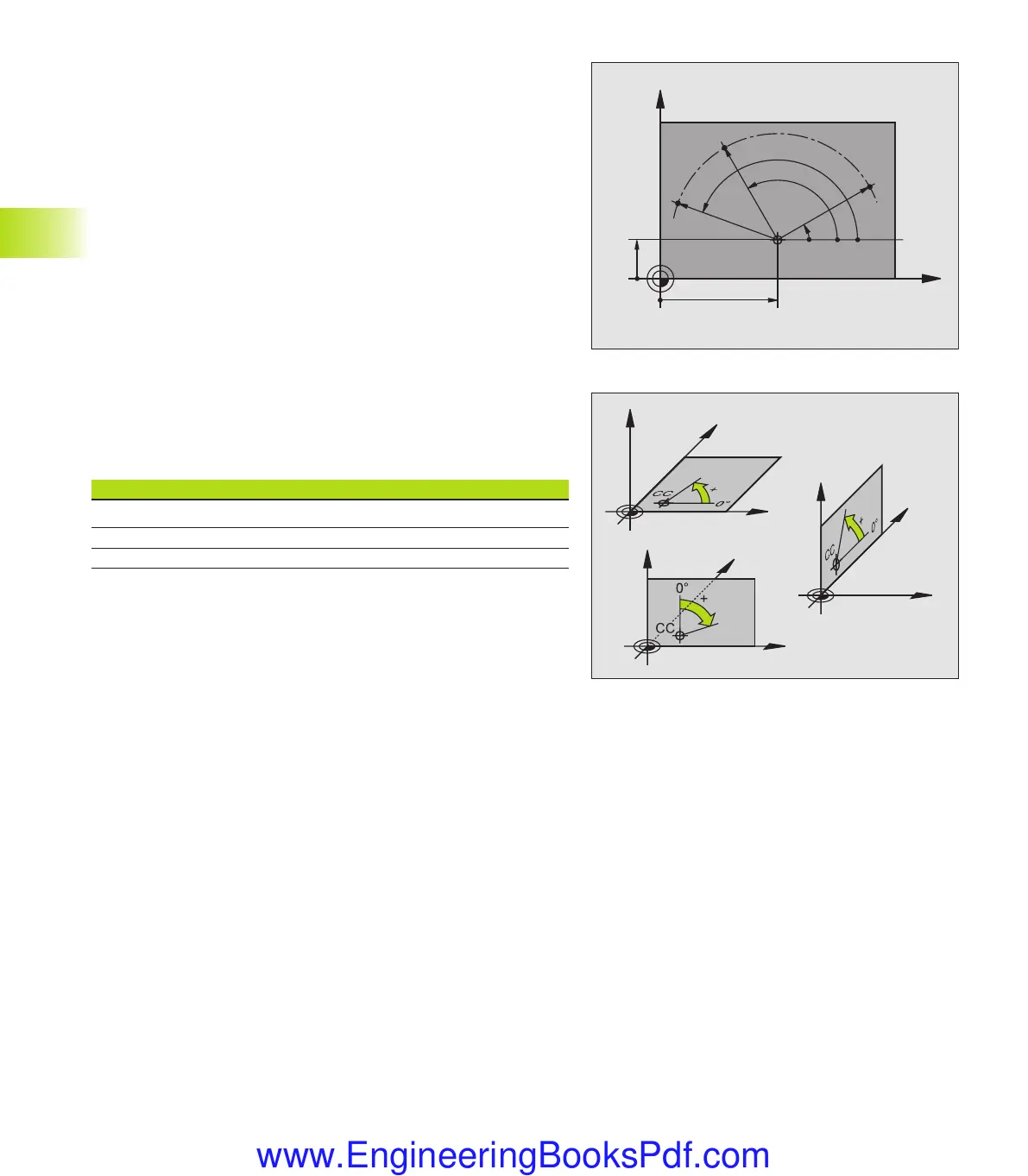
Polar coordinates
If the production drawing is dimensioned in Cartesian coordinates,
you also write the part program using Cartesian coordinates. For
parts containing circular arcs or angles it is often simpler to give the
dimensions in polar coordinates.
While the Cartesian coordinates X, Y and Z are three-dimensional
and can describe points in space, polar coordinates are two-
dimensional and describe points in a plane. Polar coordinates have
their datum at a circle center (CC), or pole. A position in a plane can
be clearly defined by the
■
Polar Radius, the distance from the circle center CC to the
position, and the
■
Polar Angle, the size of the angle between the reference axis and
the line that connects the circle center CC with the position.
See figure at lower right.
Definition of pole and angle reference axis
The pole is set by entering two Cartesian coordinates in one of the
three planes. These coordinates also set the reference axis for the
polar angle PA.
Coordinates of the pole (plane) Reference axis of the angle
XY +X
YZ +Y
ZX +Z
4.1 Fundamentals of NC
X
Y
0°
30
10
CC
PR
PA
1
PA
2
PR
PR
PA
3
X
Z
Y
X
Z
Y
X
Z
Y
Ekap4.pm6 30.06.2006, 07:0330
www.EngineeringBooksPdf.com

 Loading...
Loading...