December 2001 What is a Machine Parameter? 4 – 3
4 Machine Parameters
4.1 What is a Machine Parameter?
A contouring control must have access to specific data (e.g., traverse
distances, acceleration) before it can execute its programmed instructions.
You define these data in machine parameters.
This list of machine parameters is divided into groups according to topic.
If there is more than one input value for a single function (e.g., a separate input
for each axis), the parameter number is extended by indices. Index zero is
always axis 1, index one is axis 2, etc.
Example:
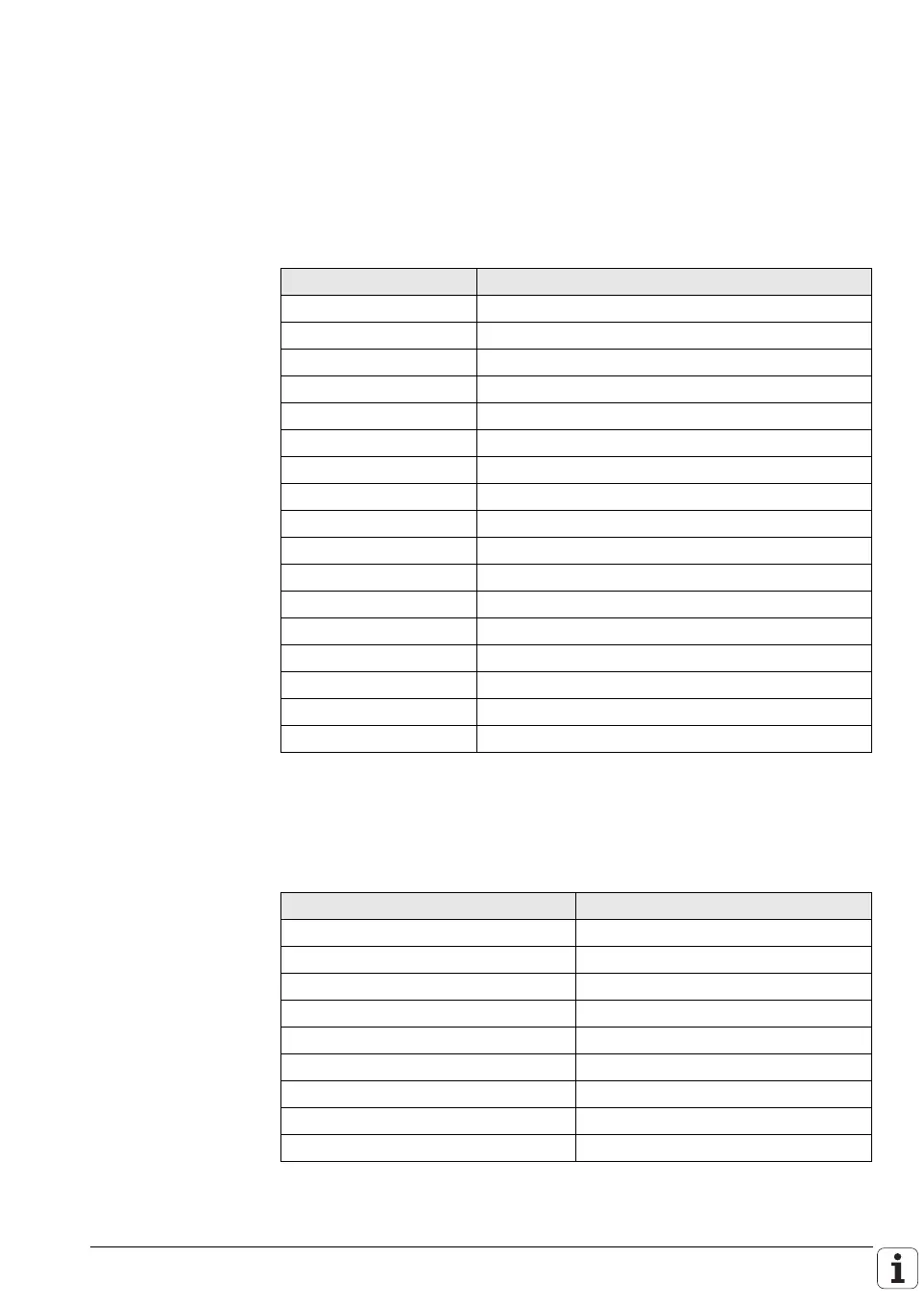
Machine parameters Topics
10 to 999 Encoders and machines
1000 to 1399 Positioning
1400 to 1699 Operation with Velocity Feedforward Control
1700 to 1999 Operation with Following Error (Servo Lag)
2000 to 2999 Integrated Speed and Current Control
3000 to 3999 Spindle
4000 to 4999 Integral PLC
5000 to 5999 Data Interface
6000 to 6199 3-D touch probe
6200 to 6299 Digitizing with triggering touch probe
6300 to 6399 Digitizing with measuring touch probe
6500 to 6599 Tool measurement with triggering touch probe
7100 to 7199 Tapping
7200 to 7349 Programming and display
7350 to 7399 Colors
7400 to 7599 Machining and Program Run
7600 to 7699 Hardware
MP1010.0-8 Rapid traverse
MP1010.0 Rapid traverse for axis 1
MP1010.1 Rapid traverse for axis 2
MP1010.2 Rapid traverse for axis 3
MP1010.3 Rapid traverse for axis 4
MP1010.4 Rapid traverse for axis 5
MP1010.5 Rapid traverse for axis 6
MP1010.6 Rapid traverse for axis 7
MP1010.7 Rapid traverse for axis 8
MP1010.8 Rapid traverse for axis 9

 Loading...
Loading...











