Rapid Spanning Tree
94
6.5
Example of manipulating the tree structure
Redundanz L2P
Release
5.0
04/09
6.5 Example of manipulating the
tree structure
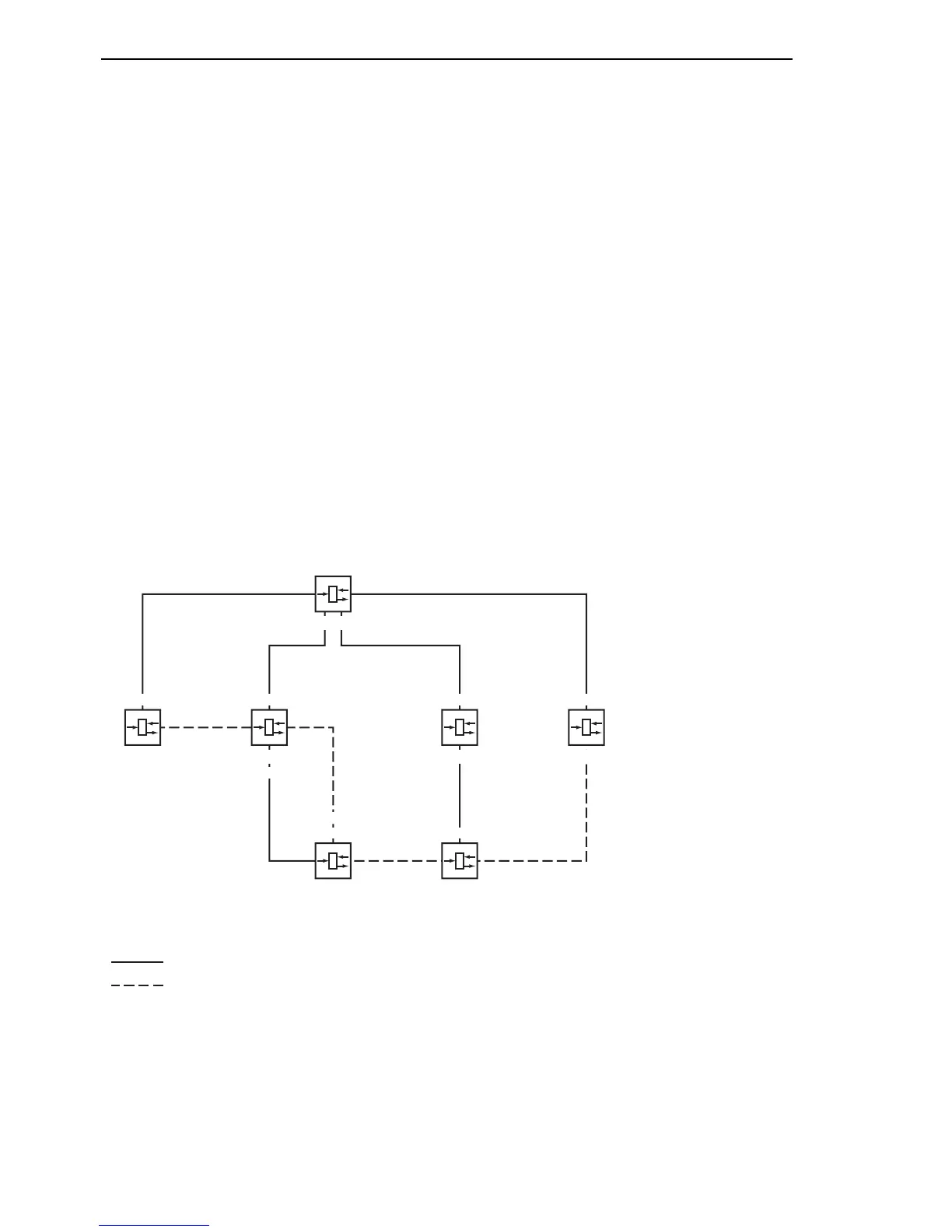
The Management Administrator soon discovers that this configuration with
bridge 1 as the root bridge (see on page 90 „Example of specifying the root
paths“) is unfavorable. On the paths from bridge 1 to bridge 2 and bridge 1 to
bridge 3, the control packets which the root bridge sends to all other bridges
are adding up.
If the Management Administrator makes bridge 2 the root bridge, the burden
of the control packets on the subnetworks is distributed much more evenly.
The result is the configuration shown here (see fig. 49). The distances
between the individual bridges and the root bridge are now shorter.
Figure 49: Example of manipulating the tree structure
Bridge 5
P-BID = 28
672
Bridge 7
P-BID = 40
960
P-BID = 20
480
Bridge 3
P-BID = 24
576
Bridge 1
P-BID = 32
768
Bridge 2
P-BID = 16
384
P-BID = 36
864
Bridge 6
Port 3
Bridge 4
Port 1
Port 2
Root path
Interrupted path
P-BID
Priority of the bridge identifikation (BID)
= BID without MAC Address

 Loading...
Loading...











