• No data is lost when a drive fails, as long as no failed drive is mirrored to another failed drive.
• Up to half of the physical drives in the array can fail.
RAID 5
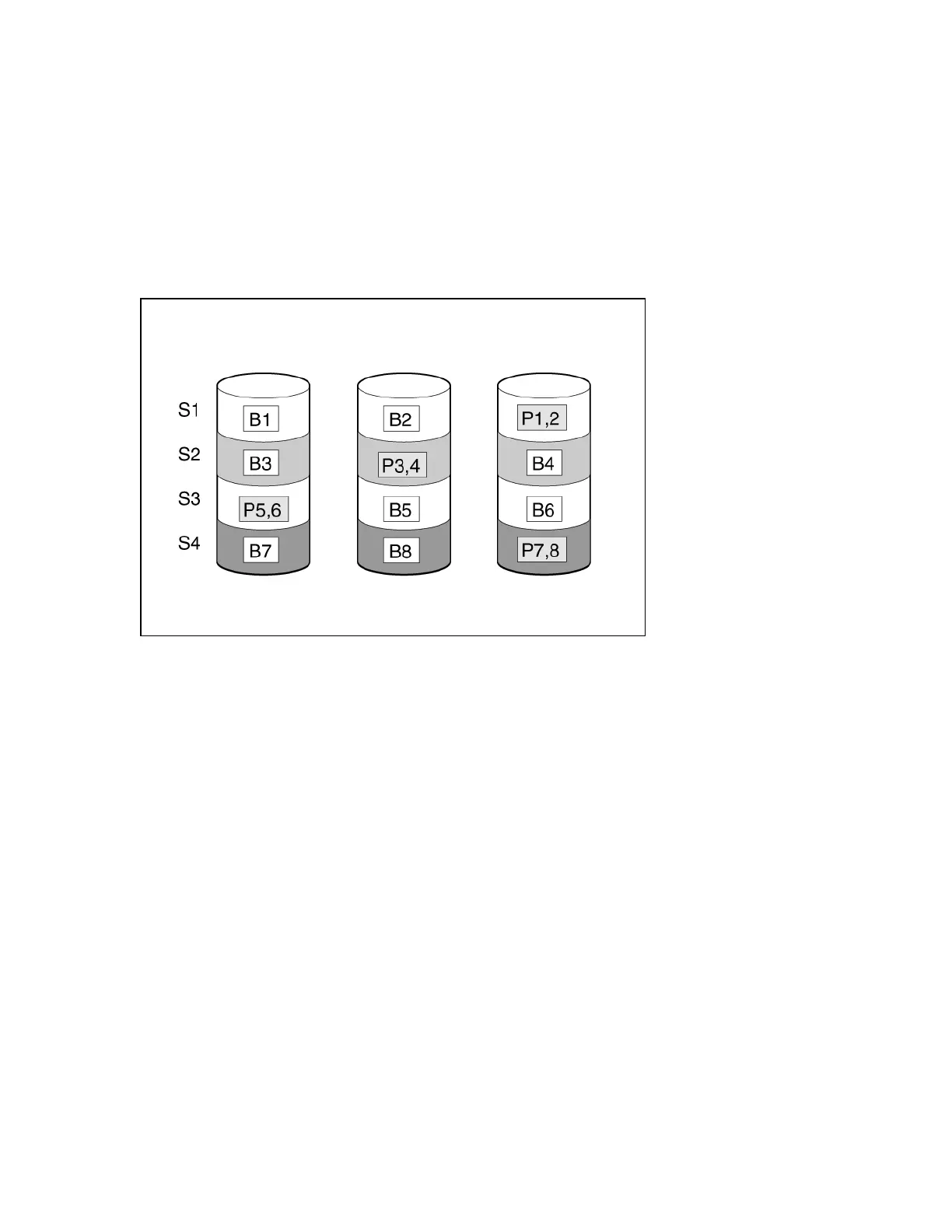
RAID 5 protects data using parity (denoted by Px,y in the figure). Parity data is calculated by summing
(XOR) the data from each drive within the stripe. The strips of parity data are distributed evenly over
every physical drive within the logical drive. When a physical drive fails, data that was on the failed drive
can be recovered from the remaining parity data and user data on the other drives in the array. The
usable capacity is C x (n - 1) where C is the drive capacity with n drives in the array. A minimum of three
drives is required.
This method has the following benefits:
• It is useful when usable capacity, write performance, and data protection are equally important.
• It has the highest usable capacity of any fault-tolerant configuration.
• Data is not lost if one physical drive fails.
RAID 50
RAID 50 is a nested RAID method in which the constituent drives are organized into several identical
RAID 5 logical drive sets (parity groups). The smallest possible RAID 50 configuration has six drives
organized into two parity groups of three drives each.

 Loading...
Loading...











