User Manual
HV Diagnostics Page 46 Rev 9.0
10 Glossary and Abbreviations
The following explains abbreviations and selected terms used in this
document in alphabetical order.
Term Explanation
Arc
Self-maintained gas conduction for which most of the charge carriers
are electrons supplied by primary
‑
electron emission (source: IEC)
Auto Adjust
Frequency
“0.1 Hz/Auto”
Mode that maximizes output frequency to highest allowable value
• Greatest allowable frequency depends on the test load and test
voltage applied
• For loads greater than nominal load, the instrument automatically
reduces the frequency
DUT Device Under Test
Duty (continuous) Load state in which the unit operates for a long period.
Continuous means: no limitation in operating time based on
temperature limits
Fault
An unplanned occurrence or defect in an item which may result in one
or more failures of the item itself or of other associated equipment
(source: IEC)
Frequency[Hz] Number of cycles per unit of time ; f=1/ Period (Time), units=Hz
1 Hz = 1cycle / 1 second
0.1 Hz = 1cycle / 10 second , etc.
Hipot High potential (voltage)
HV High Voltage: Voltage levels used in power distribution:
• Medium Voltage: up to 36 kV
• High Voltage: up to 110 kV
• Extremely High Voltage: 220 kV, 380 kV or higher
According to VDE0105 / EN50110
IEC International Electrotechnical Commission
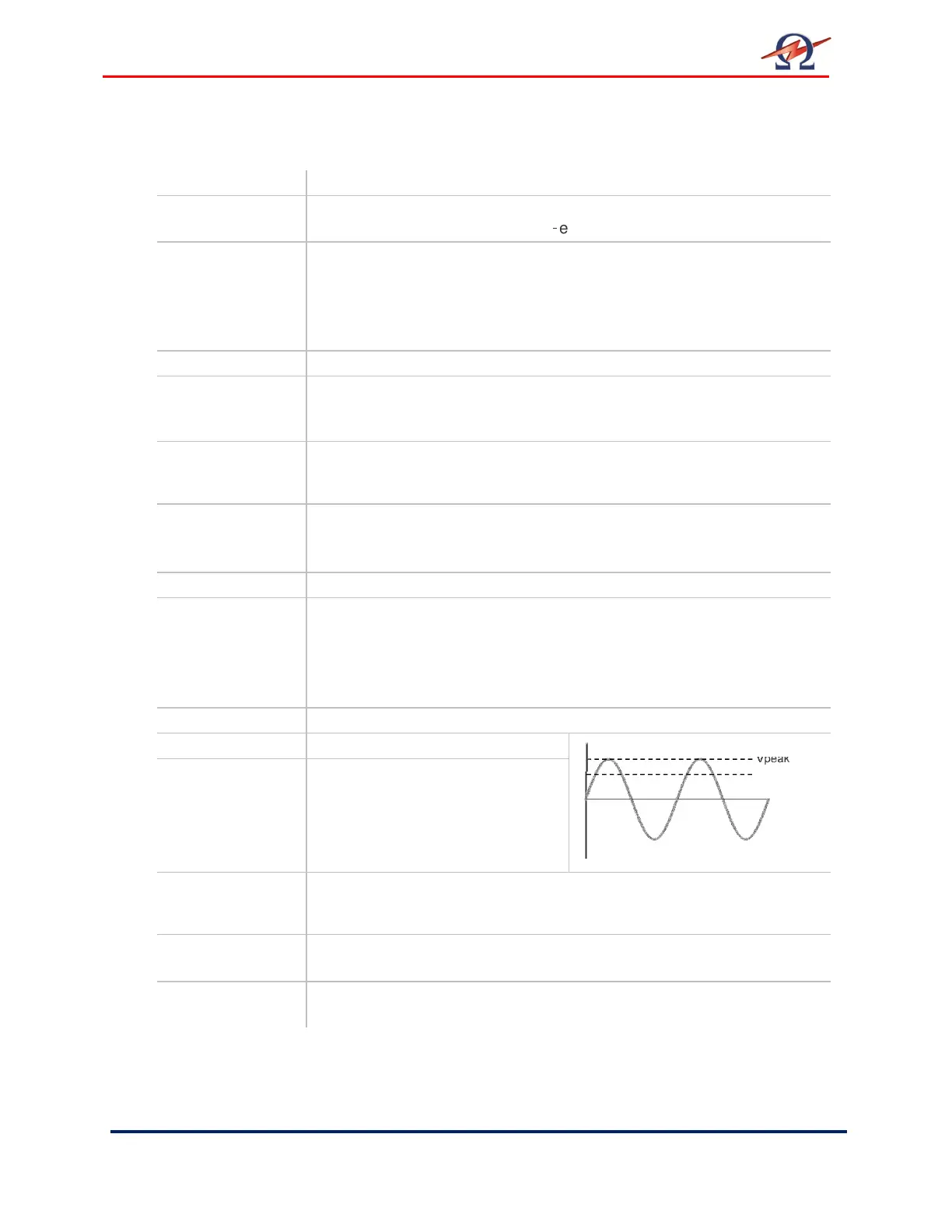
Peak value Maximum Voltage = V
max
RMS value
Root Mean Square voltage
• V
rms
= V
peak
/ √2
for Sinusoidal wave forms
To Short
Forcing the electric potential differences between two or more
conductive parts to be equal to or close to zero
(Infinite current flows in a short circuit)
To Trip Opening the circuit
(no current flows in open circuit)
VLF Very Low Frequency
• Typically between 0.01 - 0.1 Hz
Vpeak
Vrms
V
time
 Loading...
Loading...