already in the rootvg volume group, run the lsvg -p rootvg command. The
following example displays output when you issue the lsvg -p rootvg command:
# lsvg -p rootvg
rootvg:
PV_NAME PV STATE TOTAL PPs FREE PPs FREE DISTRIBUTION
hdisk0 active 515 116 57..00..00..00..59
hdisk1 active 515 515 00..00..00..00..00
Now, determine the space that is currently in use on the disk that you want to
migrate. This is the total physical partitions (PPs) value minus the free PPs value
for the desired disk. In the preceding example, refer to hdisk0, which is using (515 -
116) PPs or 399 physical partitions.
Next, find a disk or disks that have the available space. In this case, hdisk1 has
515 free physical partitions, which is more than the required space of 399 physical
partitions.
The only situation that is specific to rootvg is if the desired disk contains the boot
image. Generally, this is the logical volume called hd5. From the following partial list
of lsvg -l rootvg, this logical volume has a type of boot:
LV NAME TYPE Ps PPs PVs LV STATE MOUNT POINT
hd5 boot 1 1 1 closed/syncd N/A
To determine if the boot image is on the disk that you want to migrate, run the lslv
-l command. The following example displays the output when you issue the lslv -l
command:
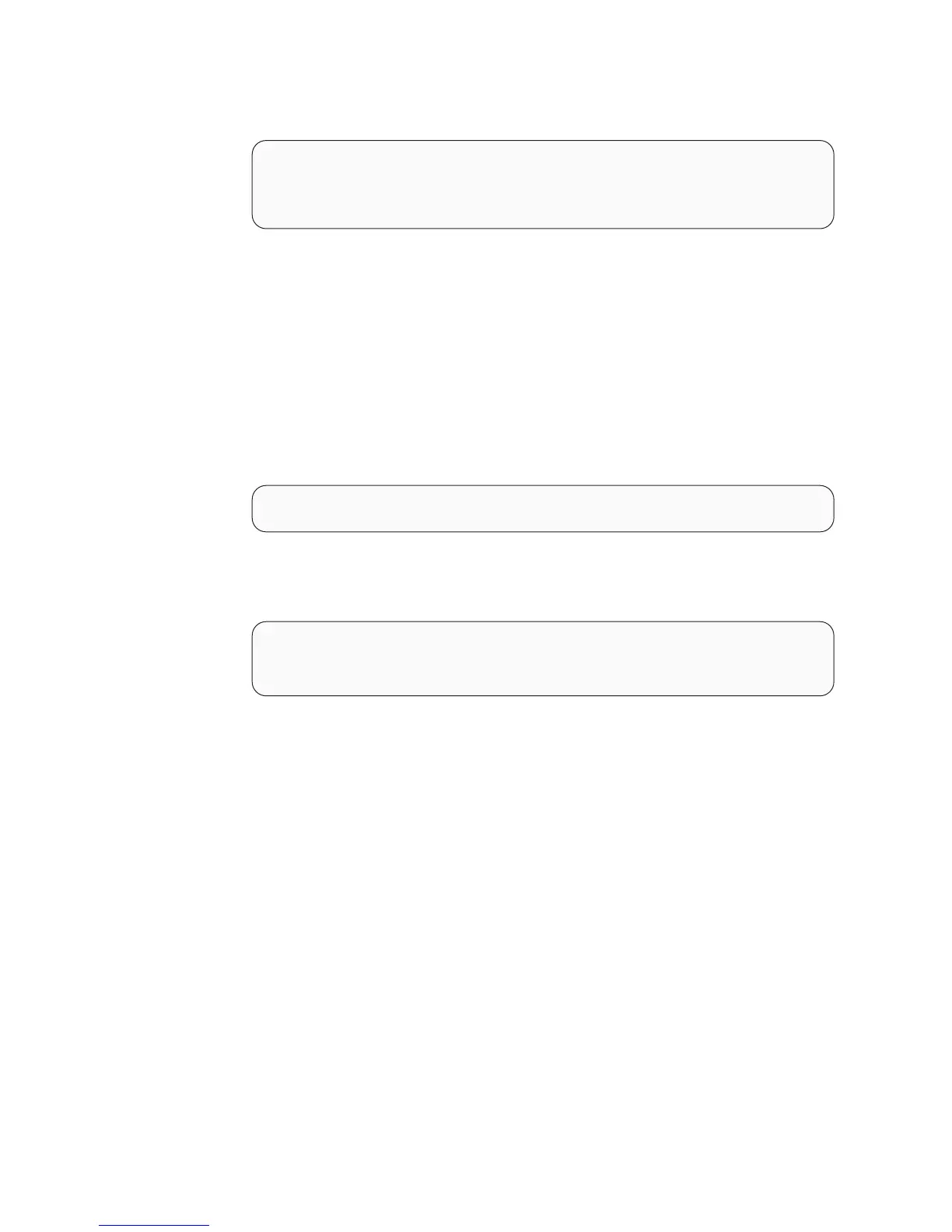
# lslv -l hd5
hd5:N/A
PV COPIES IN BAND DISTRIBUTION
hdisk0 001:000:000 100% 001:000:000:000:000
In this case, the boot image resides on the disk that you want to migrate. You must
first move the boot image with the migratepv -l command.
Using the direct copy method
Use the following information as a guide for how to use the direct copy method to
migrate data.
There are times when you must use the direct copy method to migrate data. While
this method uses the logical volume manager, the primary focus is on the use of the
UNIX find command and the cpio command. The find command generates the list
of files to be migrated. The cpio command migrates the files on the list.
The easiest way to produce the list of files is with the UNIX find command. Pipe its
standard output to the standard input of the cpio command. The following output
shows a typical example of using the cpio command to move data.
132 DS8000 User’s Guide

 Loading...
Loading...











