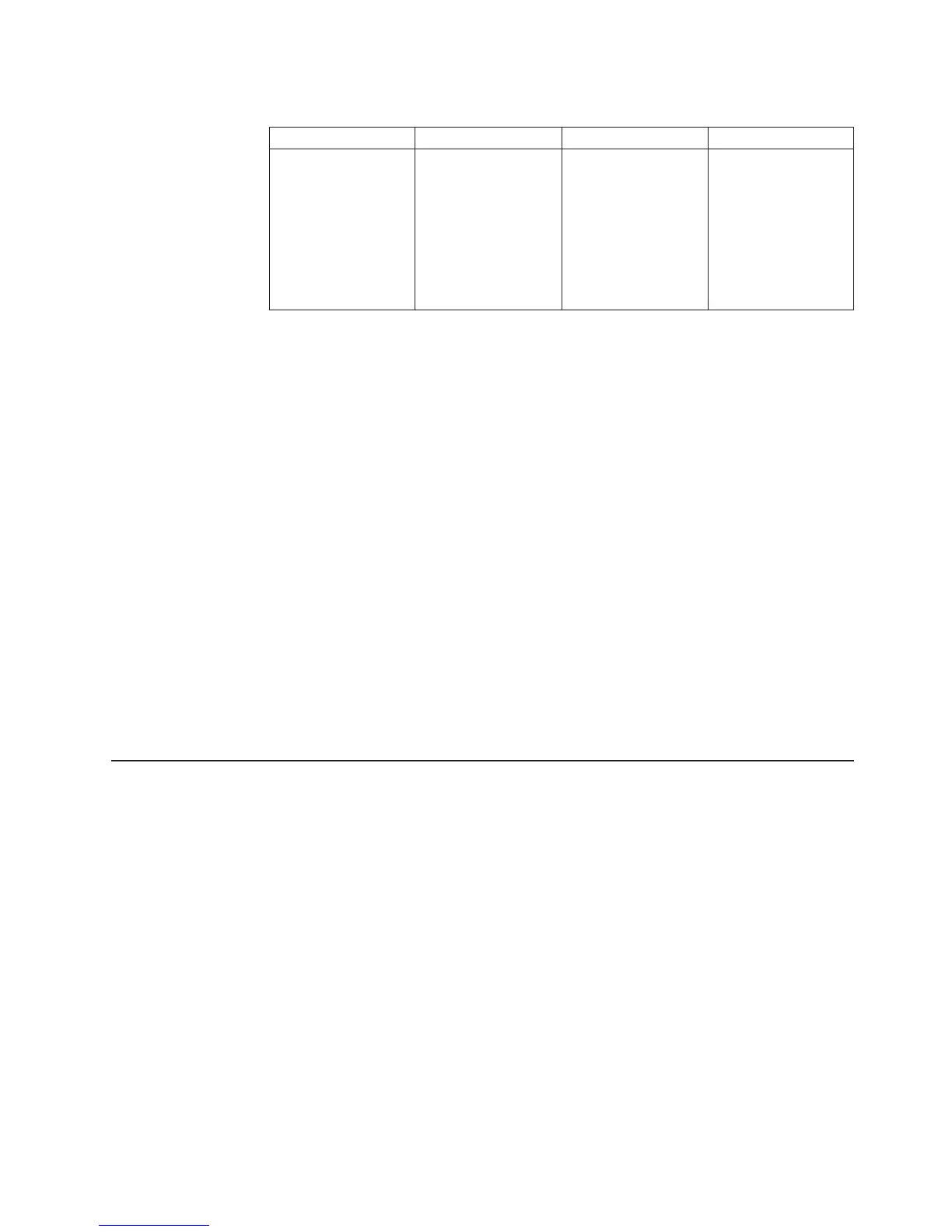
Table 2. Comparison of licensed functions (continued)
Licensed function Description Advantages Considerations
z/OS Global Mirror Asynchronous copy
controlled by z/OS
host software
Nearly unlimited
distance, highly
scalable, and very
low RPO.
Additional host server
hardware and
software is required.
The RPO might grow
if bandwidth
capability is
exceeded or host
performance might be
impacted.
Parallel Access Volumes
The use of parallel access volumes (PAVs) enables a single zSeries server to
simultaneously process multiple I/O operations to the same logical volume, which
can help to significantly reduce device queue delays. This is achieved by defining
multiple addresses per volume.
With dynamic parallel access volumes, the assignment of addresses to volumes is
automatically managed to help the workload meet its performance objectives and
minimize overall queuing.
You must configure both your storage unit and operating system to use PAVs. You
can use the logical configuration definition to define PAV-bases, PAV-aliases, and
their relationship in the storage unit hardware. This unit address relationship creates
a single logical volume, allowing concurrent I/O operations.
The storage unit supports concurrent or parallel data transfer operations to or from
the same volume from the same system or system image for S/390 or zSeries
hosts. An S/390 with PAV software support enables multiple users and jobs to
simultaneously access a logical volume. Read and write operations can be
accessed simultaneously to different domains. (The domain of an I/O operation is
the specified extents to which the I/O operation applies.)
DS8000 limitations
The following list describes known limitations for the DS8000.
v The 65,520 cylinder 3390 volume is not supported with z/OS Global Mirror and
z/OS Metro/Global Mirror.
v The amount of physical capacity within a 2107 system that can be logically
configured for use will be enforced by the 2107 licensed machine code (LMC) to
maintain compliance with the extent of IBM authorization established for licensed
functions activated on the machine. The 2107 LMC will not allow the logical
configuration of physical capacity beyond the extent of IBM authorization (except
when activating Standby CoD capacity).
v The deactivation of an activated licensed function, or a lateral change or
reduction in the license scope, is a disruptive activity and requires a machine IML
(Model 921 and Model 922) or reboot of the affected image (Model 9A2). A
lateral change is defined as changing the license scope from fixed block (FB) to
count key data (CKD) or from CKD to FB. A reduction is defined as changing the
license scope from all physical capacity (ALL) to only FB or only CKD capacity.
v The following activities are disruptive:
Chapter 1. Introduction to IBM TotalStorage DS8000 series 21

 Loading...
Loading...











