5-30
E01 to E03,
E98, E99
Terminal Command Assignment to [X1] to [X3], [FWD] and [REV]
E01 to E03, E98 and E99 may assign commands (listed below) to terminals [X1] to
[X3], [FWD], and [REV] which are general-purpose programmable input terminals.
These function codes may also switch the logic system between normal and
negative to define how the inverter logic interprets either ON or OFF status of each
terminal. The default setting is normal logic, that is "Active ON."
To assign negative logic input to any input terminal, set the function code to the
value of 1000s shown in ( ) in Section 5.1 " Function Code Tables." To keep ex-
planations as simple as possible, the examples shown below are all written for the
normal logic system.
Select multistep frequency (1 to 7 steps)--(SS1), (SS2), and (SS4)
(Function code data = 0, 1, and 2)
㩷
Switching digital input signals (SS1), (SS2), and (SS4) on/off may switch the set
frequency to those defined by function codes C05 through C11 (multistep fre-
quencies). With this, the inverter may drive the motor at 8 different preset speeds.
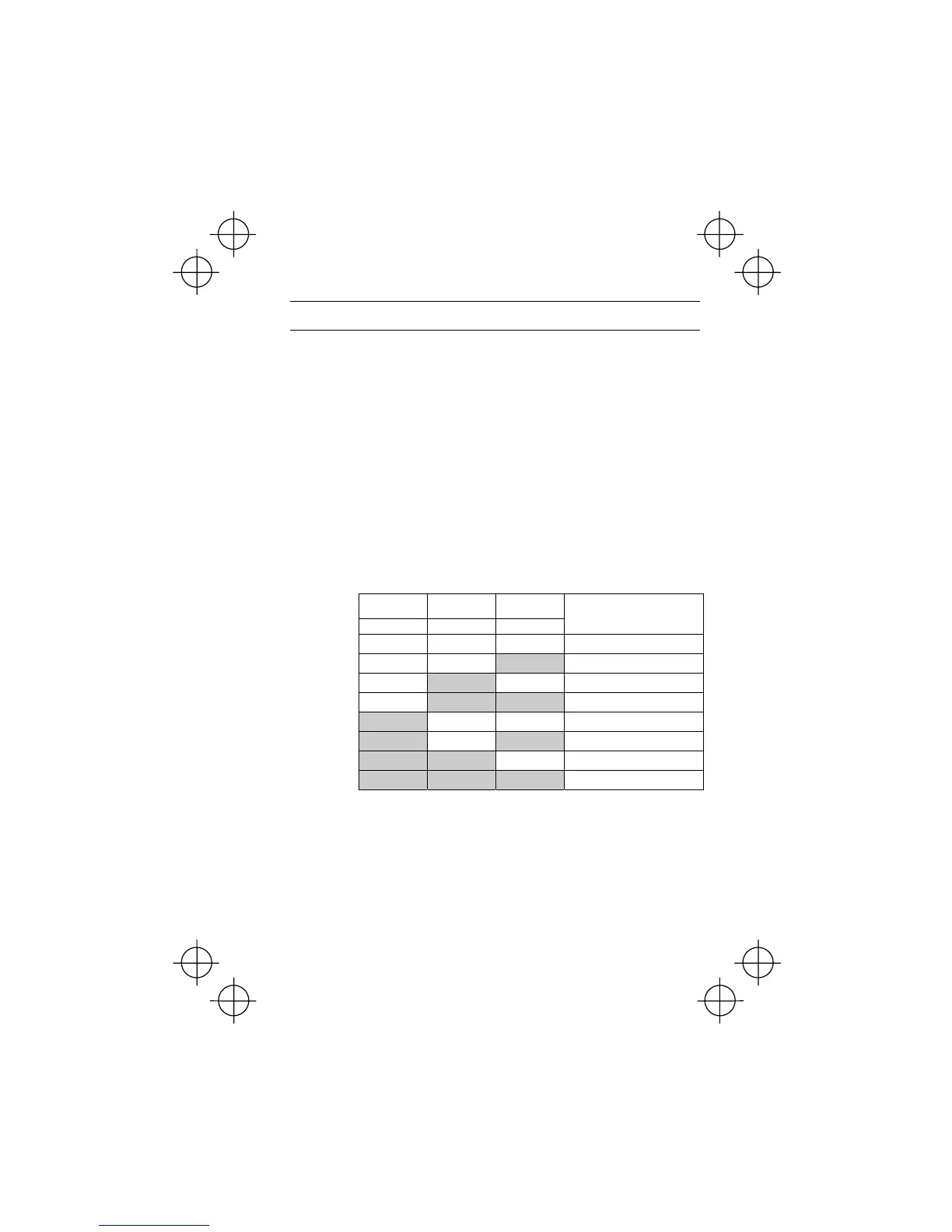
The table below lists the frequencies that can be obtained by the combination of
switching (SS1), (SS2), and (SS4). In the "Selected frequency" column, "Other than
multistep frequency" represents the set frequencies defined by frequency com-
mand 1 (F01), frequency command 2 (C30), or others.
Term i na l [ X 3]
(E03)
Terminal [X2]
(E02)
Terminal [X1]
(E01)
2 (SS4) 1 (SS2) 0 (SS1)
Selected frequency
OFF OFF OFF Other than multistep frequency
OFF OFF ON C05 (multistep frequency 1)
OFF ON OFF C06 (multistep frequency 2)
OFF ON ON C07 (multistep frequency 3)
ON OFF OFF C08 (multistep frequency 4)
ON OFF ON C09 (multistep frequency 5)
ON ON OFF C10 (multistep frequency 6)
ON ON ON C11 (multistep frequency 7)
Select acceleration/deceleration (2 steps)--(RT1)
(Function code data = 4)
㩷
Digital input signal (RT1) assigned to the specified terminal on/off may switch
combinations between acceleration/deceleration time 1 (defined by function codes
F07 and F08) and acceleration/deceleration time 2 (defined by E10 and E11).
Turning (RT1) on, for example, enables the inverter to drive the motor using ac-
celeration/deceleration time 2.
 Loading...
Loading...