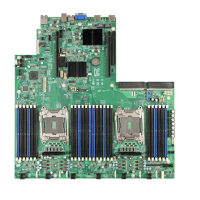
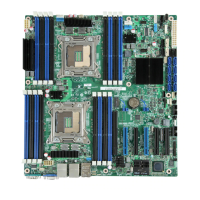
Connector/Header Locations and Pin-outs Intel® Server Board S1200BT TPS
Revision 1.0
Intel order number G13326-003
Combined system BIOS and the Integrated BMC support provide the functionality of the various
supported control panel buttons and LEDs. The following sections describe the supported
functionality of each control panel feature.
Note: Control panel features are also routed through the bridge board connector at location
J1C1 as is implemented in Intel
®
Server Systems configured using a bridge board and a hot-
swap backplane.
7.4.1 Power Button
The BIOS supports a front control panel power button. Pressing the power button initiates a
request that the Integrated BMC forwards to the ACPI power state machines in the chipset. It is
monitored by the Integrated BMC and does not directly control power on the power supply.
Power Button — Off to On
The Integrated BMC monitors the power button and the wake-up event signals from the
chipset. A transition from either source results in the Integrated BMC starting the power-
up sequence. Since the processor are not executing, the BIOS does not participate in
this sequence. The hardware receives the power good and reset signals from the
Integrated BMC and then transitions to an ON state.
Power Button — On to Off (Operating system absent)
The System Control Interrupt (SCI) is masked. The BIOS sets up the power button
event to generate an SMI and checks the power button status bit in the ACPI hardware
registers when an SMI occurs. If the status bit is set, the BIOS sets the ACPI power
state of the machine in the chipset to the OFF state. The Integrated BMC monitors
power state signals from the chipset and de-asserts PS_PWR_ON to the power supply.
As a safety mechanism, if the BIOS fails to service the request, the Integrated BMC
automatically powers off the system in 4 to 5 seconds.
Power Button — On to Off (Operating system present)
If an ACPI operating system is running, pressing the power button switch generates a
request using SCI to the operating system to shut down the system. The operating
system retains control of the system and the operating system policy determines the
sleep state into which the system transitions, if any. Otherwise, the BIOS turns off
the system.

 Loading...
Loading...