MEASUREMENTS
Measuringcentres–M
320,MC330,MC350&MC350H ‐ User’sManual 43
Voltage
Instrumentmeasuresrealeffective(rms)valueofallphasevoltages(U
1
,U
2
,U
3
)connectedtothemeter.Phase‐
to‐phase voltages (U
12
, U
23
, U
31
), average phase voltage (U
f
) and average phase‐to‐phase voltage (U
a
) are
calculatedfrommeasuredphasevoltages(U
1
,U
2
,U
3
).
N
u
=
U
2
n
N
1=n
f
N
2
ynxn
N
1=n
xy
uu
=
U
Allvoltagemeasurementsareavailableviacommunication,serialandcustomizeddisplaysonLCD.
MainmenuMeasurementsPresentvaluesVoltageOK
Current
Thedevicemeasuresrealeffective(rms)valueofphasecurrents,connectedtocurrentinputs.Neutralcurrent
(I
n
),averagecurrent(I
a
)andasumofallphasecurrents(I
t
)arecalculatedfromphasecurrents.
N
i
=
2
n
I
N
1=n
RMS
Allcurrentmeasurementsareavailableviacommunication,serial(exceptI
t
)andcustomizeddisplaysonLCD.
MainmenuMeasurementsPresentvaluesCurrentOK
Active,reactiveandapparentpower
Active power is calculated from instantaneous phase voltages and currents. All measurements are seen via
communicationoraredisplayedonLCD.FormoredetailedinformationaboutcalculationseechapterEquations
onpage72.
MainmenuMeasurementsPresentvaluesPowerOK
Powerfactorandpowerangle
Powerangleiscalculatedasquotientofactiveandapparentpowerforeachphaseseparately(cos
1
,cos
2
,
cos
3
)andtotalpowerangle(cos
t
).Asymbolforacoilrepresentsinductiveloadandasymbolforacapacitor
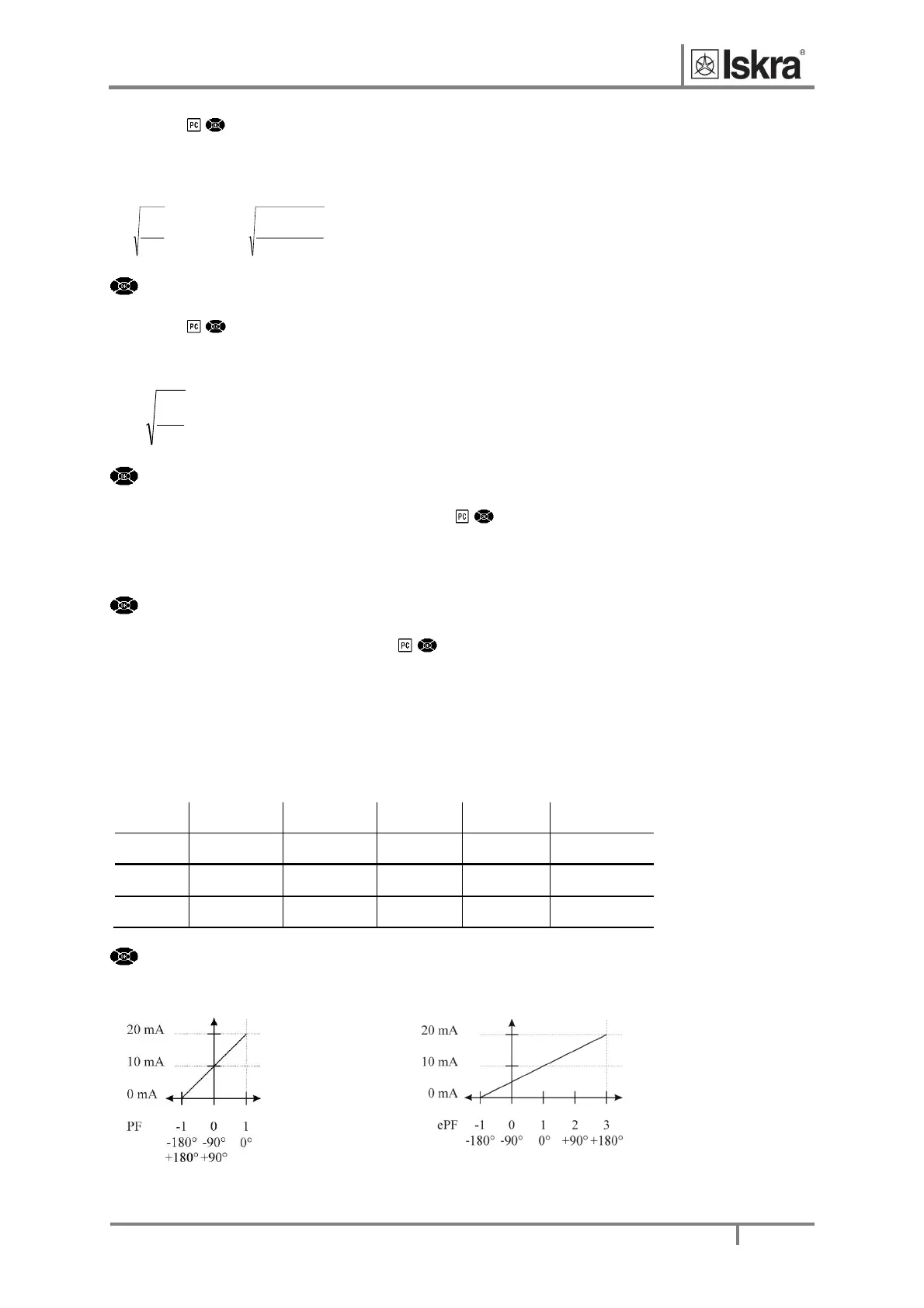
represents capacitive load. For correct display of PF via analogue output and application of the alarm, ePF
(extendedpowerfactor)isapplied.Itillustratespowerfactorwithonevalueasdescribedinthetablebelow.For
adisplayonLCDbothofthemhaveequaldisplayfunction:between‐1and‐1withtheiconforinductiveor
capacitiveload.
Load C
L
Angle[°] ‐180 ‐90 0 +90 +180(179.99)
PF ‐1 0 1 0 ‐1
ePF ‐1 0 1 2 3
MainmenuMeasurementsPresentvaluesPF&PowerangleOK
ExampleofanalogueoutputforPFandePF(MC350andMC350Honly):
 Loading...
Loading...