22
RB SERIES ENGINEERING GUIDE
In ground water situations where scaling could be heavy or where
biological growth such as iron bacteria will be present, a closed
loop system is recommended. The heat exchanger coils in ground
water systems may, over a period of time, lose heat exchange
capabilities due to a buildup of mineral deposits inside. These
can be cleaned, but only by a qualified service mechanic, as
special solutions and pumping equipment are required. Hot water
generator coils can likewise become scaled and possibly plugged.
Water Quality
In areas with extremely hard water, the owner should be informed
that the heat exchanger may require occasional flushing. Failure
to adhere to the guidelines in the water quality table could result in
loss of warranty.
Units with cupronickel heat exchangers are recommended for open
loop applications due to the increased resistance to build-up and
corrosion, along with reduced wear caused by acid cleaning.
Application Notes cont.
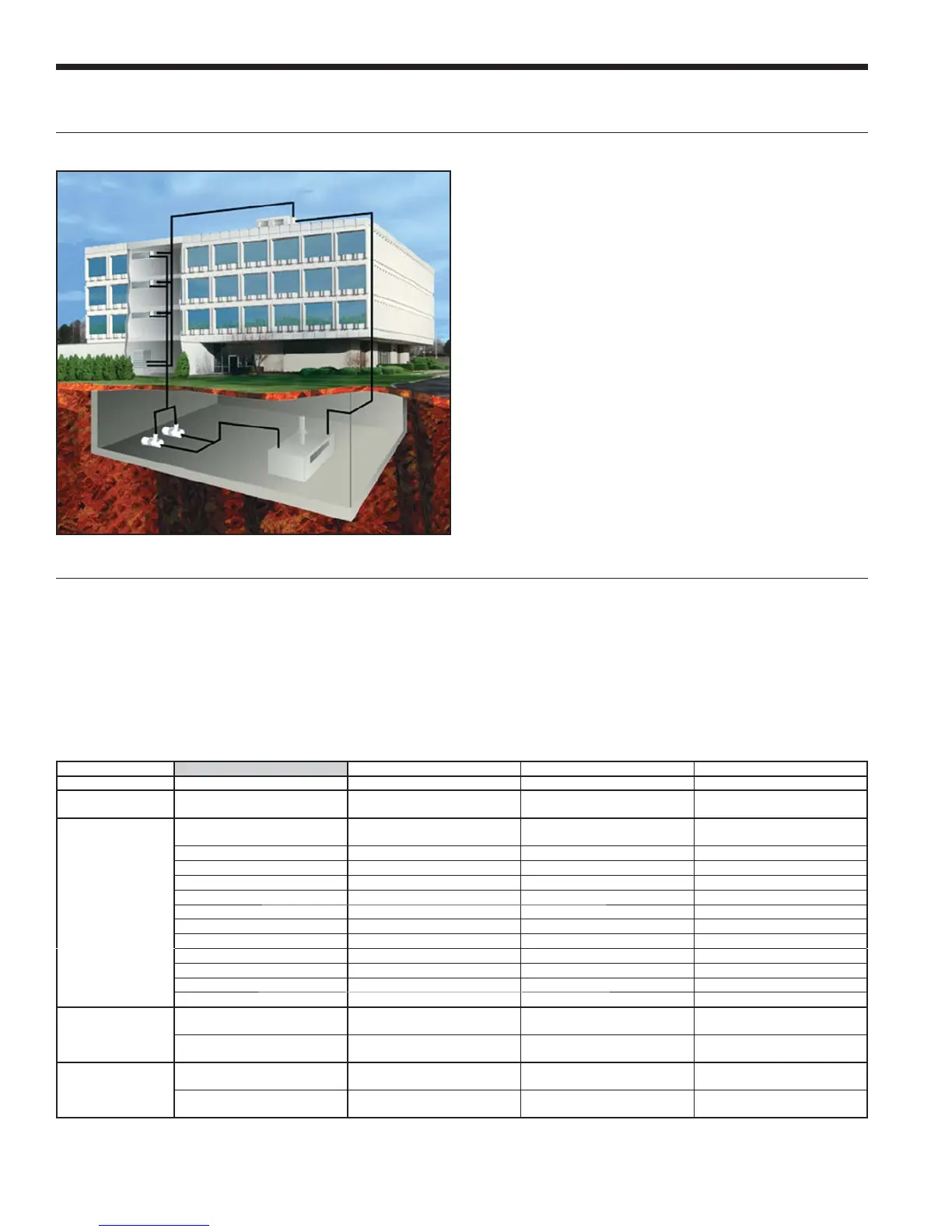
• Closed Loop /Cooler-Boiler Systems utilize a closed heat
recovering loop with multiple water source heat pumps in the more
conventional manner. Typically a boiler is employed to maintain
closed loop temperatures above 60°F and a cooling tower to
maintain loop temperatures below 90°F. These systems are
applicable in medium to large buildings regardless of whether the
load is heating or cooling dominated. Due to the moderate loop
temperatures, AHRI/ISO 13256-1 Water Loop Heat Pumps are
required for this application.
Cooler/Boiler - Closed Loop
Material Copper 90/10 Cupronickel 316 Stainless Steel
pH Acidity/Alkalinity 7 - 9 7 - 9 7 - 9
Scaling
Calcium and
Magnesium Carbonate
(Total Hardness)
less than 350 ppm
(Total Hardness)
less than 350 ppm
(Total Hardness)
less than 350 ppm
Corrosion
Hydrogen Sulfide
Less than 0.5 ppm (rotten egg
smell appears at 0.5 ppm)
10 - 50 ppm Less than 1 ppm
Sulfates Less than 125 ppm Less than 125 ppm Less than 200 ppm
Chlorine Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm
Chlorides Less than 20 ppm Less than 125 ppm Less than 300 ppm
Carbon Dioxide Less than 50 ppm 10 - 50 ppm 10 - 50 ppm
Ammonia Less than 2 ppm Less than 2 ppm Less than 20 ppm
Ammonia Chloride Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm
Ammonia Nitrate Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm
Ammonia Hydroxide Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm
Ammonia Sulfate Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm Less than 0.5 ppm
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) Less than 1000 ppm 1000 - 1500 ppm 1000 - 1500 ppm
LSI Index +0.5 to -0.5 +0.5 to -0.5 +0.5 to -0.5
Iron Fouling
(Biological Growth)
Iron, FE
2
+ (Ferrous)
Bacterial Iron Potential
< 0.2 ppm < 0.2 ppm < 0.2 ppm
Iron Oxide
Less than 1 ppm, above this level
deposition will occur
Less than 1 ppm, above this level
deposition will occur
Less than 1 ppm, above this level
deposition will occur
Erosion
Suspended Solids
Less than 10 ppm and filtered for
max. of 600 micron size
Less than 10 ppm and filtered for
max. of 600 micron size
Less than 10 ppm and filtered for
max. of 600 micron size
Threshold Velocity
(Fresh Water)
< 6 ft/sec < 6 ft/sec < 6 ft/sec
NOTES: Grains = ppm divided by 17
mg/L is equivalent to ppm
2/22/12
 Loading...
Loading...











