41
5 Modbus and other protocols over Ethernet
5.1 Modbus/TCP protocol
Modbus/TCP uses the Ethernet interface for communicating with the Modbus data. The Mod-
bus telegrams are transmitted via an Ethernet network (IEEE 802.3) using the TCP protocol of
the TCP/IP protocol family.
The device type 703571 can assume the role of the slave or master here too.
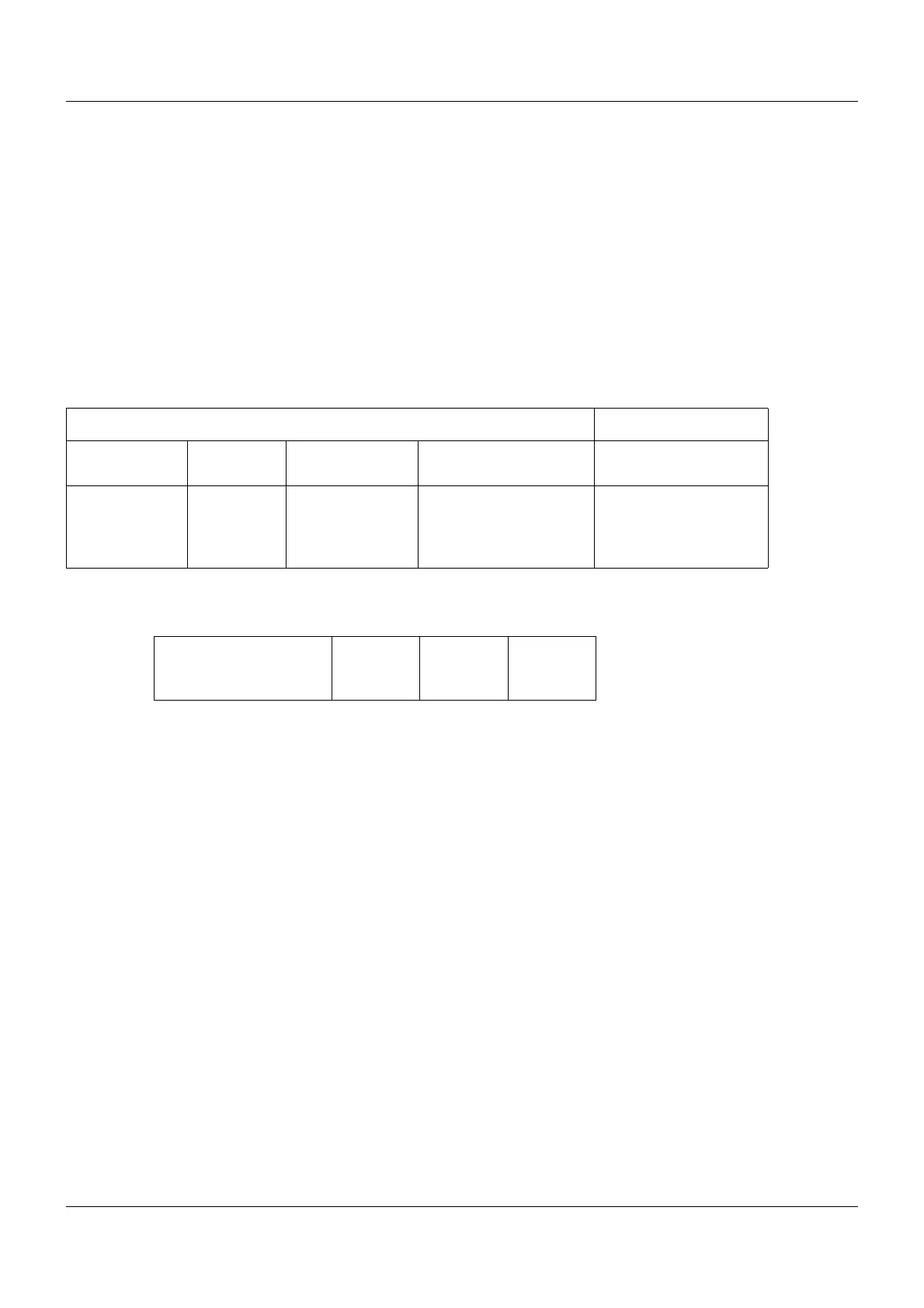
Structure of a Modbus/TCP telegram
Modbus/TCP is a standardized method for encapsulating a Modbus telegram in a TCP seg-
ment and transmitting it via Ethernet.
The Modbus telegram (without CRC) is transmitted with an additional 6-byte or 7-byte "MBAP
header" (Modbus Application Header). The seventh byte corresponds to the first serial byte,
but has a different designation here.
For comparison: The "normal" Modbus telegram
Using this protocol, a suitable process data visualization program can read and write system
values over a company's own Ethernet network, for example. All device variables in the Mod-
bus address tables can be accessed.
Chapter 7 "Modbus address tables", page 59
MBAP header Modbus telegram
2 bytes
Transaction ID
2 bytes
Protocol ID
2 bytes
Length
1 byte
Unit ID
Additional bytes as
below, but without CRC
Identical in
query and
response
Must be 0 for
Modbus
Length of query/
response in bytes
starting with
(incl.) "Unit ID"
Corresponds to device
address and must be
0xFF or 255 for Mod-
bus/TCP
Slave
address
1 byte
Function
code
1 byte
Data field
x bytes
CRC16
2 bytes
 Loading...
Loading...









