4.5 Functional description
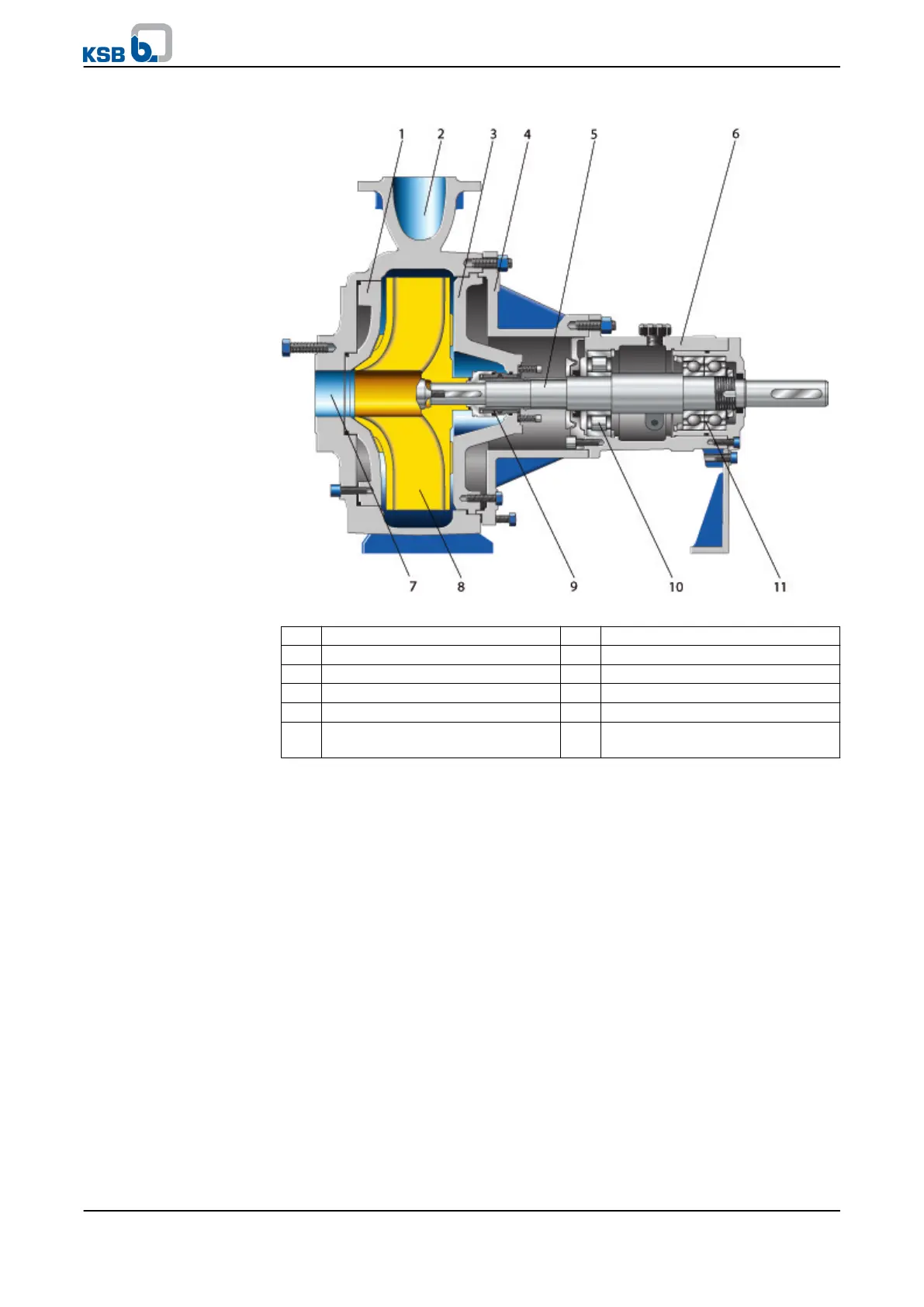
Fig. 8: Sectional drawing
1 Wear plate 2 Casing/discharge nozzle
3 Discharge cover 4 Bearing bracket lantern
5 Shaft 6 Bearing bracket
7 Casing/suction nozzle 8 Impeller
9 Shaft seal 10 Rolling element bearing, pump end
11 Rolling element bearing, motor
end
The horizontal, non-self-priming, radially split volute casing pump in back pull-out
design is designed with an axial fluid inlet and a radial outlet.
The rotor runs in an axially adjustable bearing and is connected to the motor by a
shaft coupling.
The steadily rotating impeller of the centrifugal pump transfers mechanical energy to
the fluid passing through.
The fluid enters the pump axially via the suction nozzle (7) and is moved outwards by
the rotating impeller (8). The flow profile of the pump casing converts the kinetic
energy of the fluid into pressure energy. The fluid leaves the pump via the discharge
nozzle (2).
The casing is fitted with a replaceable wear plate (1). The diagonal clearance gap
prevents frequent deviation of the flow in the clearance gap heading in the direction
of the suction nozzle. This ensures a longer service life if solids-laden fluids are
handled. The axially adjustable bearing allows an optimum adjustment of the width
of the sealing clearance.
The casing is closed by a discharge cover (3). The shaft (5) enters the casing via this
discharge cover. A shaft seal (9) provides reliable sealing towards the atmosphere.
The shaft is supported by oil-lubricated rolling element bearings (10 and 11). The
bearing bracket (6) is connected to the casing via a lantern (4).
The pump is sealed by a shaft seal. Variants:
Design
Function
Sealing
4 Description of the Pump (Set)
20 of 78
KWP
 Loading...
Loading...