MCS640 Thermal Imager Manual Principle of Thermal Imaging • 30
Transmission, Absorption, and Reflection of Infrared Energy
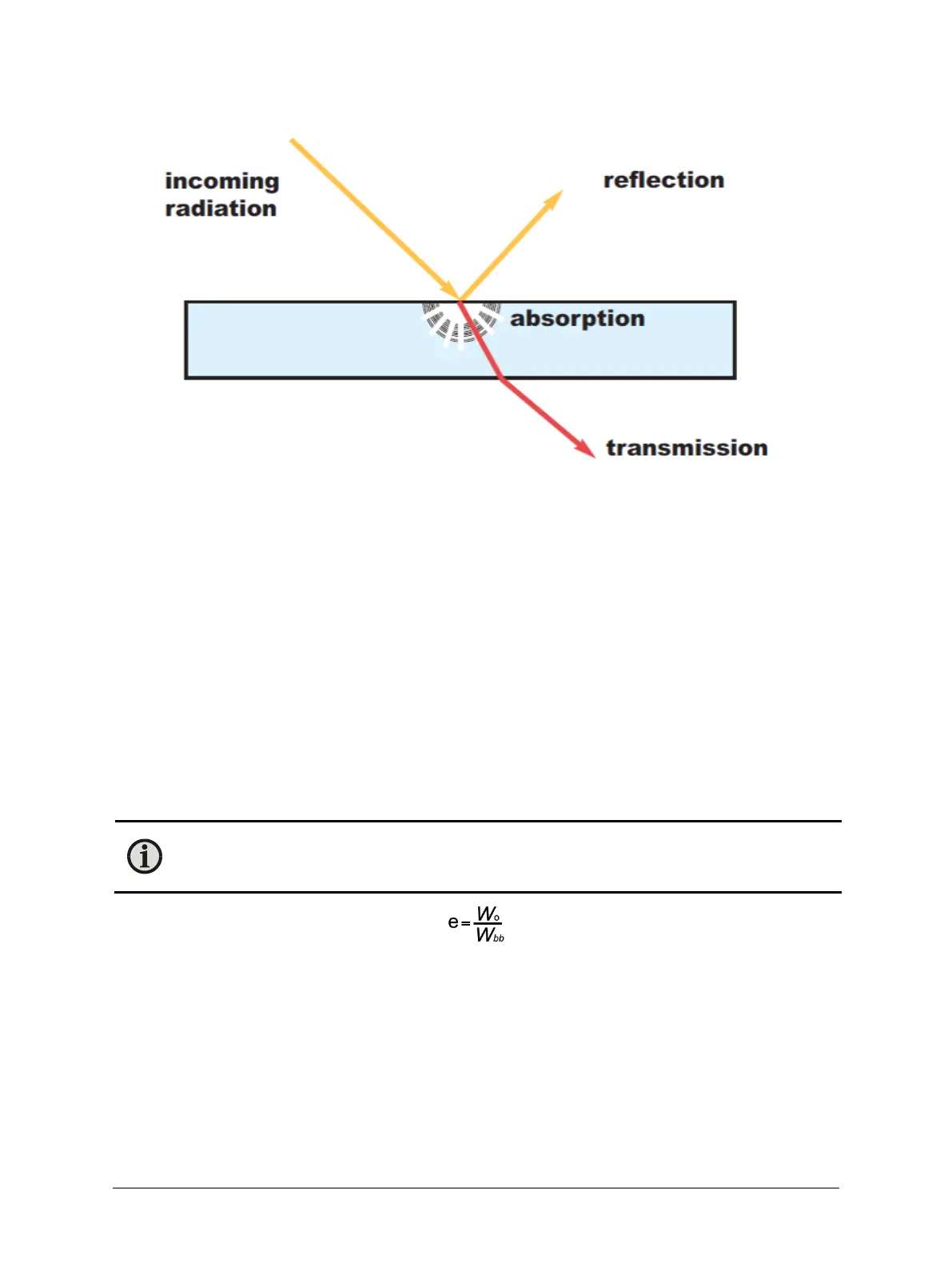
The figure above shows the three modes by which the radiant energy striking an object may be dissipated.
These modes of dissipation are:
a = absorption
t = transmission
r = reflection
The fractions of the total radiant energy, which are associated with each of the above modes of dissipation,
are referred to as the absorptivity (a) transmissivity (t) and the reflectivity (r) of the body. According to the
theory of conservation of energy, the extent to which materials reflect, absorb and transmit IR energy is
known as the emissivity of the material.
4.3 Blackbody Radiation
The emissivity of a body is defined formally by the equation below as the ratio of the radiant energy emitted
by the body to the radiation, which would be emitted by a blackbody at the same temperature.
Note: A blackbody is a theoretical surface, which absorbs and re-radiates all the IR energy it
receives. It does not reflect or transmit any IR energy. Perfect blackbody surfaces do not exist in
nature.
Where,
W
o = total radiant energy emitted by a body at a given temperature T.
W
bb = total radiant energy emitted by a blackbody at the same temperature T.
 Loading...
Loading...