21
AutoAccompaniment
ChordBasics
ReadingChordNames
SomeChordTypes
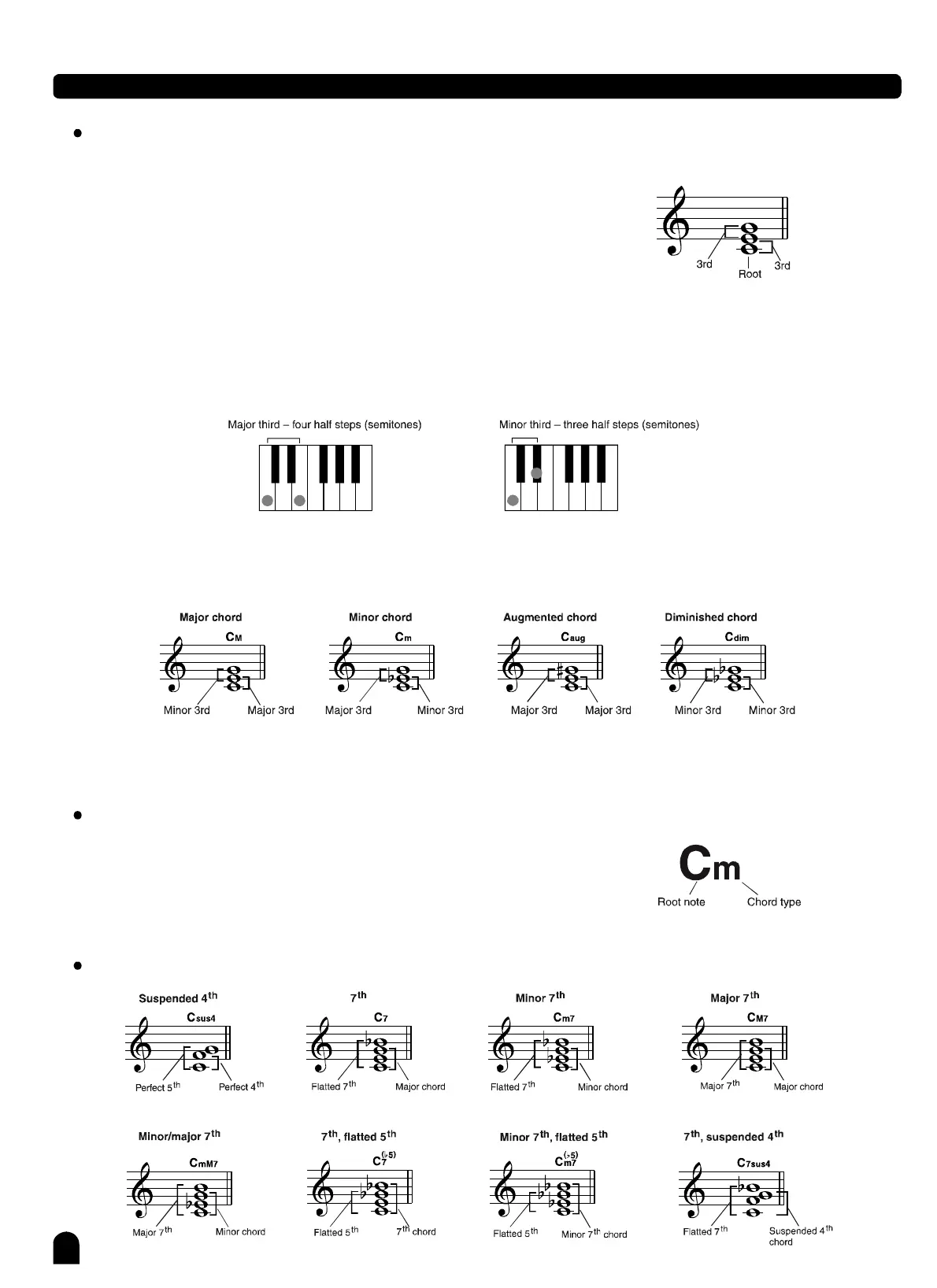
Threeormorenotesplayedtogetherconstituteachord"".
Themostbasicchordtypeisthe"triad"consistingthreenotes:
theroot,third,andfifthdegreesofthecorrespondingscale.
A"Cmajortriad",forexample,ismadeupofthenotesC(theroot),
E(thethirdnoteoftheCmajorscale),andG(thefifthnoteofthe
Cmajorscale).
IntheCmajortriadshownasabove,thelowestnoteisthe"root"ofthechord(thisisthechord"root
position"...usingotherchordnotesforthelowestnoteresultsin"inversion").Therootisthecentral
soundofthechord,whichsupportsandanchorsotherchordnotes.
Thedistance(interval)betweenadjacentnotesoftriadinrootpositioniseitheramajororminorthird.
's
Thelowestintervalinourroot-positiontriad(betweentherootandthethird)determineswhetherthetriad
isamajororminorchord,andwecanshiftthehighestnoteupordownbyasemitonetoproducetwo
additionalchords,asshownbelow.
Thebasiccharacteristicsofthechordsoundremainintactevenifwechangetheorderofthenotestocreate
differentinversions.Successivechordsinachordprogressioncanbesmoothlyconnected,forexample,by
choosingtheappropriateinversions(orchord"voicings").
Chordnamestellyoujustabouteverythingyouneedtoknowabout
achord(otherthantheinversion/voicing).Thechordnametellsyou
whattherootofachordis,whetheritisamajor,minor,ordiminished,
whetheritrequiresamajororflattedseventhandwhatalterations
ortensiondoesituse...allataglance.
PDF 文件使用 "pdfFactory Pro" 试用版本创建 www.fineprint.com.cn
 Loading...
Loading...