3 WATER ACTIVITY THEORY AquaLab TDL
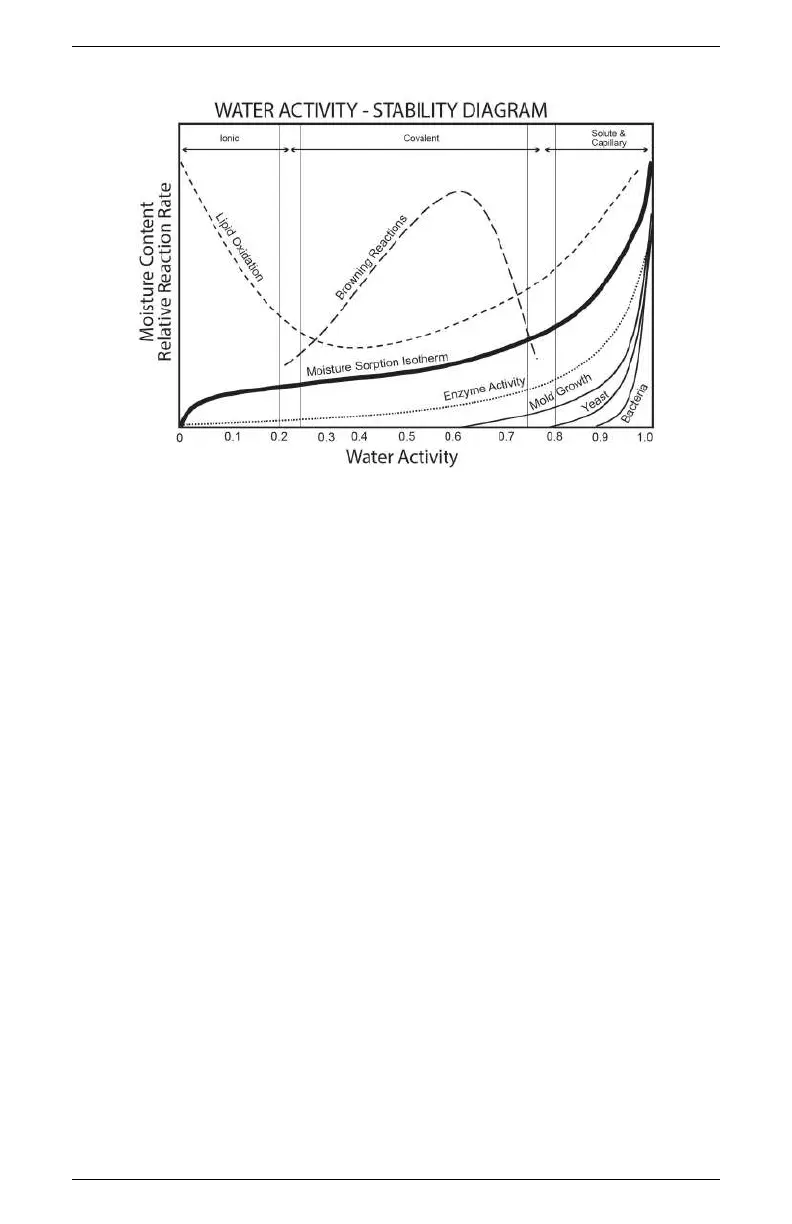
Figure 1: Water Activity Diagram adapted from Labuza
measures the sample temperature. From these measurements, the
relative humidity of the head-space is computed as the ratio of the
partial pressure measured by TDL to saturation vapor pressure at
the sample temperature. When the water activity of the sample and
the relative humidity of the air are in equilibrium, the measurement
of the head-space humidity gives the water activity of the sample.
In addition to equilibrium between the liquid phase water in the
sample and the vapor phase, the internal equilibrium of the sample
is important. If a system is not at internal equilibrium, one might
measure a steady vapor pressure (over the period of measurement)
which is not the true water activity of the system. An example of this
might be a baked good or a multi-component food. Initially out of
the oven, a baked good is not at internal equilibrium; the outer sur-
face is at a lower water activity than the center of the baked good.
One must wait a period of time in order for the water to migrate
and the system to come to internal equilibrium. It is important to
remember the restriction of the definition of water activity to equi-
librium.
8
 Loading...
Loading...