A 1PPS output is an integral part of the design. An optional 1PPS input allows the unit to track GPS or
other external reference. For more information, refer to Appendix: One Pulse Per Second Source
.Connection (see page 30)
For simple applications, the SA.22c provides a 5 V CMOS-compatible built-in self test (BIST) service and a
lock alarm signal derived from the basic physics operation. The lock signal indicates when the output
frequency is locked to the atomic resonance of rubidium. For more control over the device, an extensive
command control status dialog needs to be used.
In addition to controlling the operation of the oscillator, the microprocessor's built-in firmware allows
an external host computer to communicate with the embedded controller through a serial port
connection. This allows precise frequency control, dynamic frequency selection, enabling and disabling
outputs, querying the system's health, initiating a self test, and acquiring information about the unit's
serial number, operating temperature, fault history, and other performance indicators. The protocol
used is Microsemi Serial Interface Protocol (MSIP).
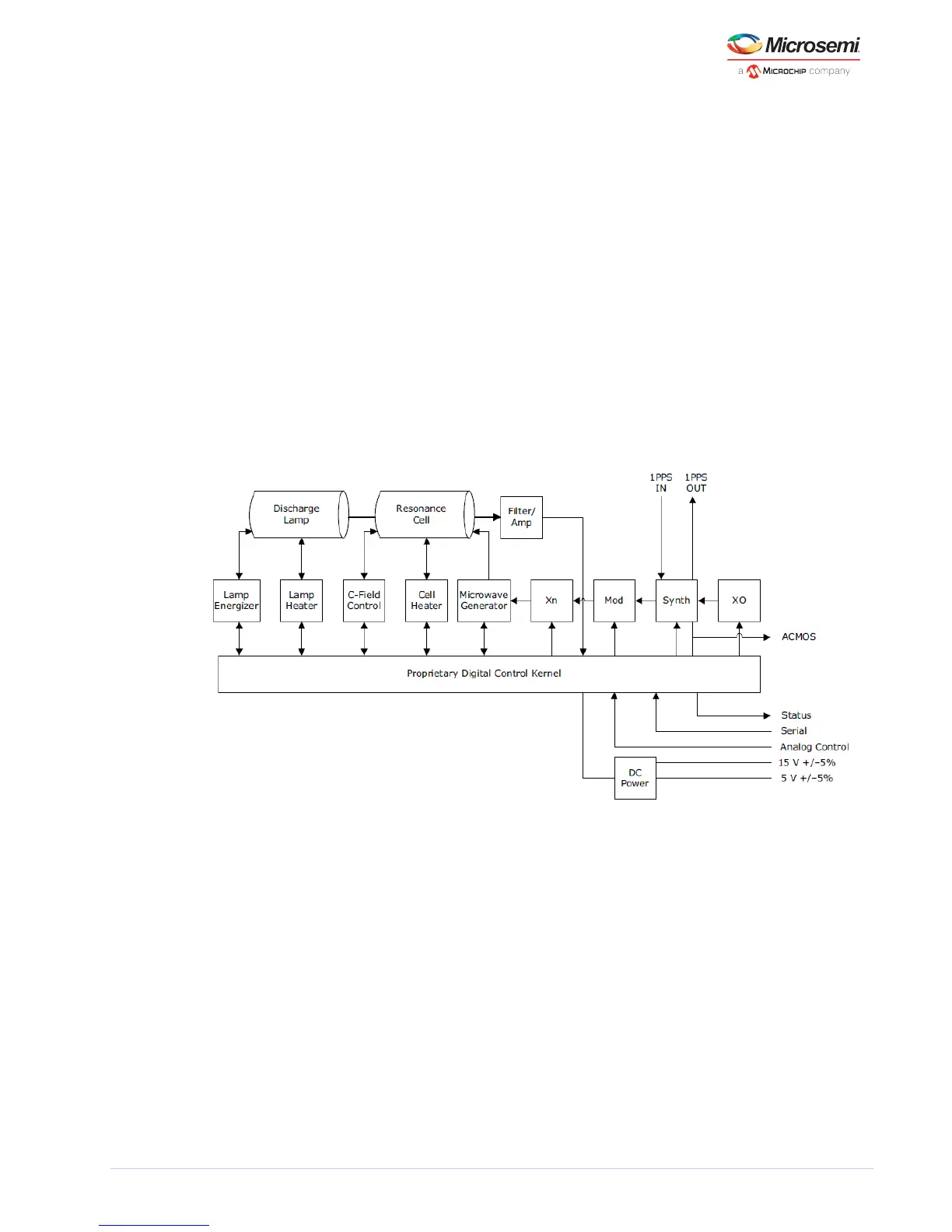
The following block diagram shows the importance of the digital control in the unit, how it controls and
monitors all aspects of operation, such as the heater circuits of the physics package, as well as the
selection of outputs.
Figure 2 • SA.22c Rubidium Oscillator Simplified Block Diagram

 Loading...
Loading...