7. POSITIONING CONTROL
7 − 47
Control with ABS
and ABS (absolute data method)
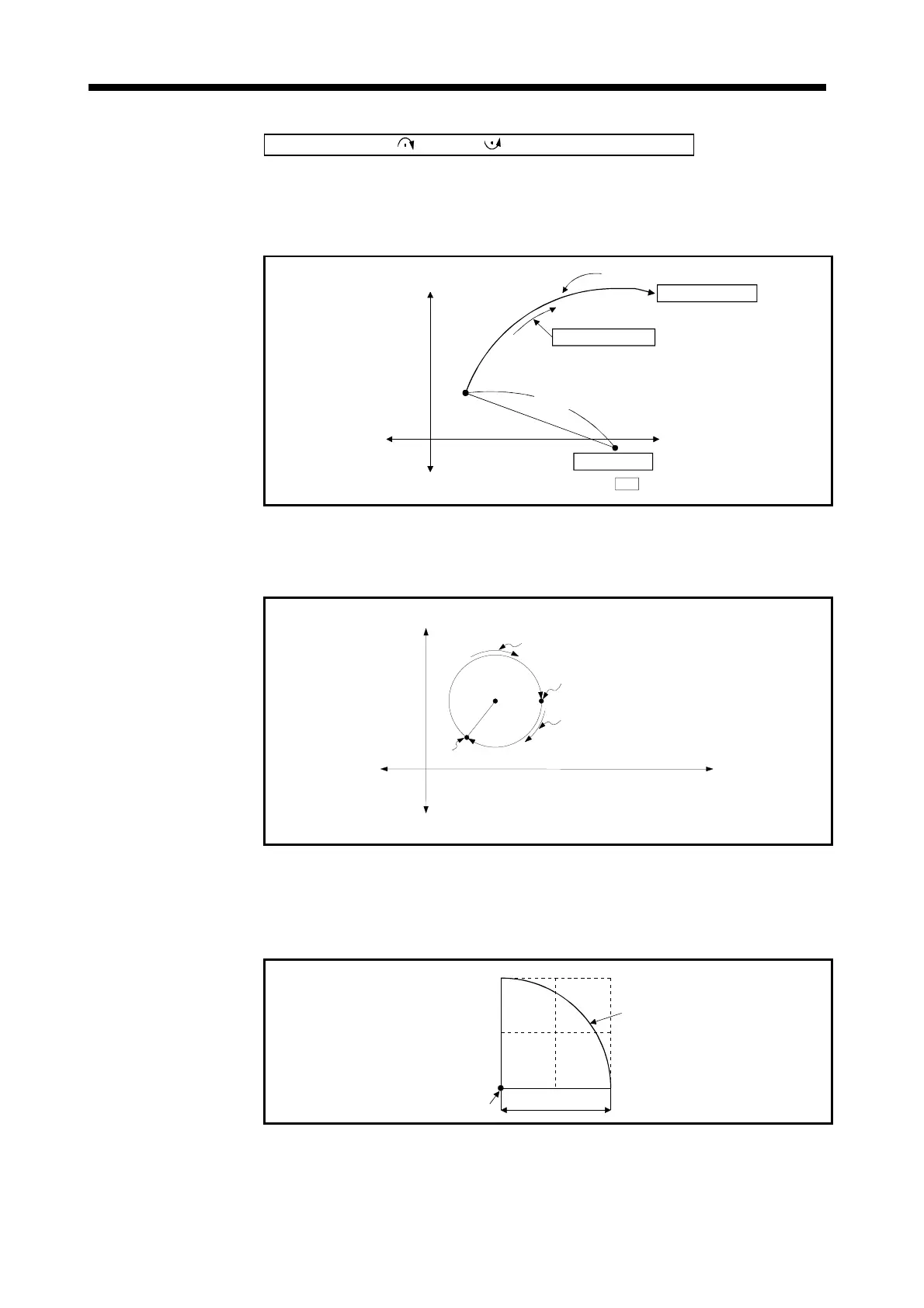
(1) Circular interpolation of an arc with a radius equivalent to the distance between
the start point and center point, between the current stop address (pre-
positioning address used as the start point address) and the designated end
point address, using the home position as the reference.
0
Reverse direction
Forward direction
E
nd address
(X
1
,Y
1
)
Movement due to circular interpolation
Start
point
address
(X
0
,Y
0
)
: indicates set data
Positioning speed
Center of arc
Radius(R)
Reverse direction
Forward direction
Fig.7.17 Circular Interpolation Control by Absolute Date Method
(2) To conduct positioning control of a full circle, divide the circular interpolation
control into two operations.
0
Forward direction
Forward direction
Reverse direction
Reverse direction
1st circular interpolation control
1st end address, 2nd start address
2nd circular interpolation control
1st start address, 2nd end address
Center of arc
Fig.7.18 Positioning Control of a Full Circle
(3) The setting range for the end point address and arc center point is −2
31
to (2
31
−1).
(4) The maximum arc radius is 2
32
−1.
Radius R
Arc center point
2
31
-1
2
31
-1
Maximum ar
-2
31
0
Fig.7.19 Maximum Arc

 Loading...
Loading...











