65 / 174
Service Manual Mitsubishi SQ-Series diesel engines
Version 08/2004
PISTONS, CONNECTING RODS,
CRANKSHAFT AND CRANKCASE
ENGLISH
ENGINE MAIN PARTS
10.2.1 Pistons, piston rings and piston
pins
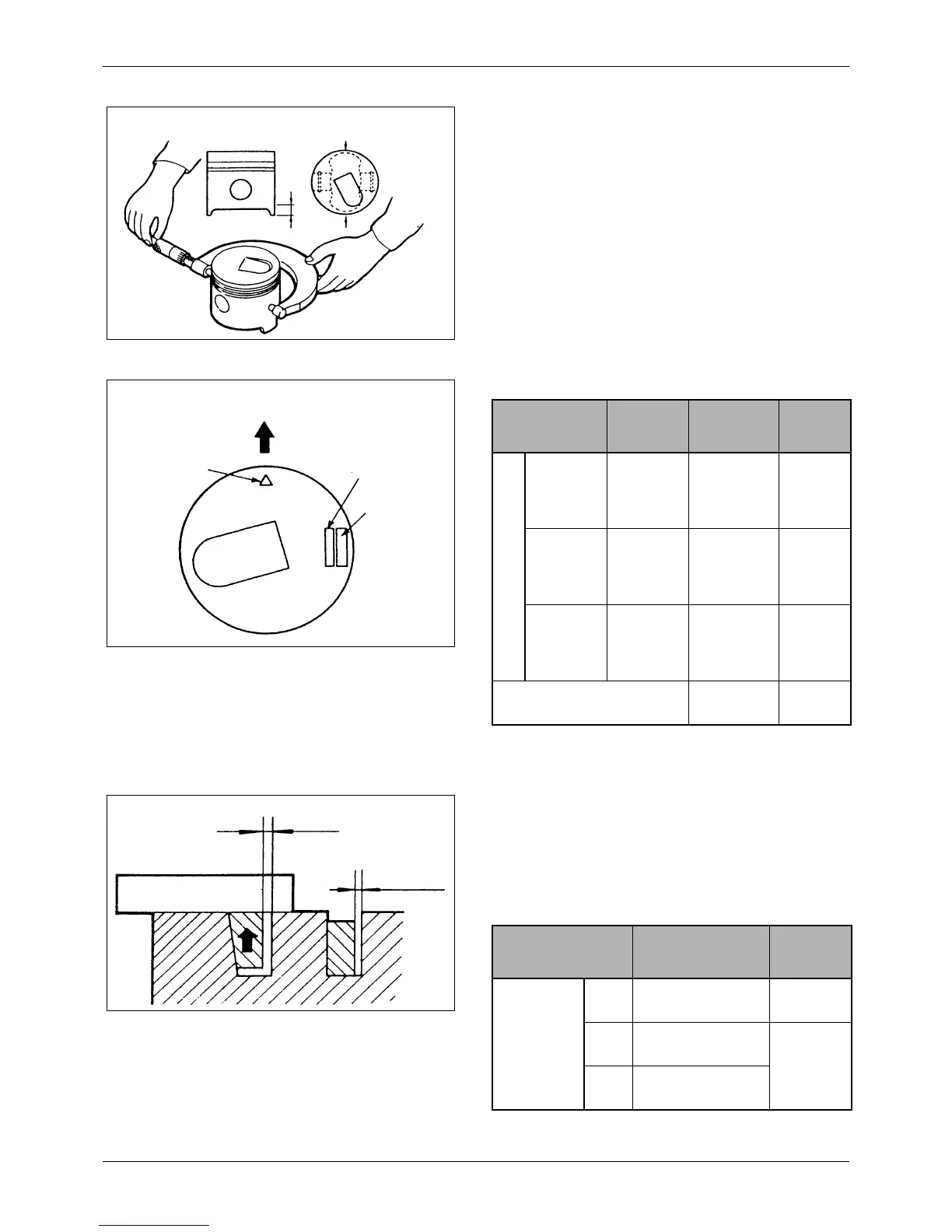
1. Measuring piston diameter
1) Using a micrometer, measure the diameter of
each piston perpendicular to the piston pin (at
the position shown). If the diameter exceeds
the service limit, replace the piston. If any
pistons have to be replaced, select new
pistons so the weight difference in an engine
is within assembly standards.
Unit: mm [in.]
2) The weight of the piston is stamped on the top
of the piston.
2. Checking piston and piston ring
1) Check the clearance between the groove and
the piston ring with a feeler gage, as shown in
the illustration. If the clearance exceeds the
service limit, replace the piston ring.
Unit: mm [in.]
Figure 108 Measuring piston diameter
Direction transverse
to piston pin
14 mm
[0.6 in.]
Figure 109 Identification on top of piston
Size
identification
Weight
identification
Front of engine
“Front” mark
Item
Nominal
Value
Assembly
Standard
Service
Limit
Piston diameter
Standard
87.970
[3.4634]
87.955 to
87.985
[3.4628 to
3.4640]
87.770
[3.4555]
0.25
[0.0098]
oversize
88.220
[3.4732]
88.205 to
88.235
[3.4726 to
3.4738]
88.020
[3.4654]
0.50
[0.0197]
oversize
88.470
[3.4831]
88.455 to
88.485
[3.4825 to
3.4837
88.270
[3.4752]
Weight difference in one
engine
5 g [0.2 oz]
or less
__
Figure 110 Checking between groove and piston ring
No. 1 ring
No. 2 ring
Item
Assembly
Standard
Service
Limit
Clearance
between
groove and
piston ring
No. 1
ring
0.060 to 0.100
[0.0024 to 0.0039]
0.200
[0.0079]
No. 2
ring
0.045 to 0.080
[0.0018 to 0.0032]
0.150
[0.0059]
Oil
ring
0.025 to 0.065
[0.0010 to 0.0026]

 Loading...
Loading...