4 Operation of Each Part
6 Modulation Contrast Method
E-30
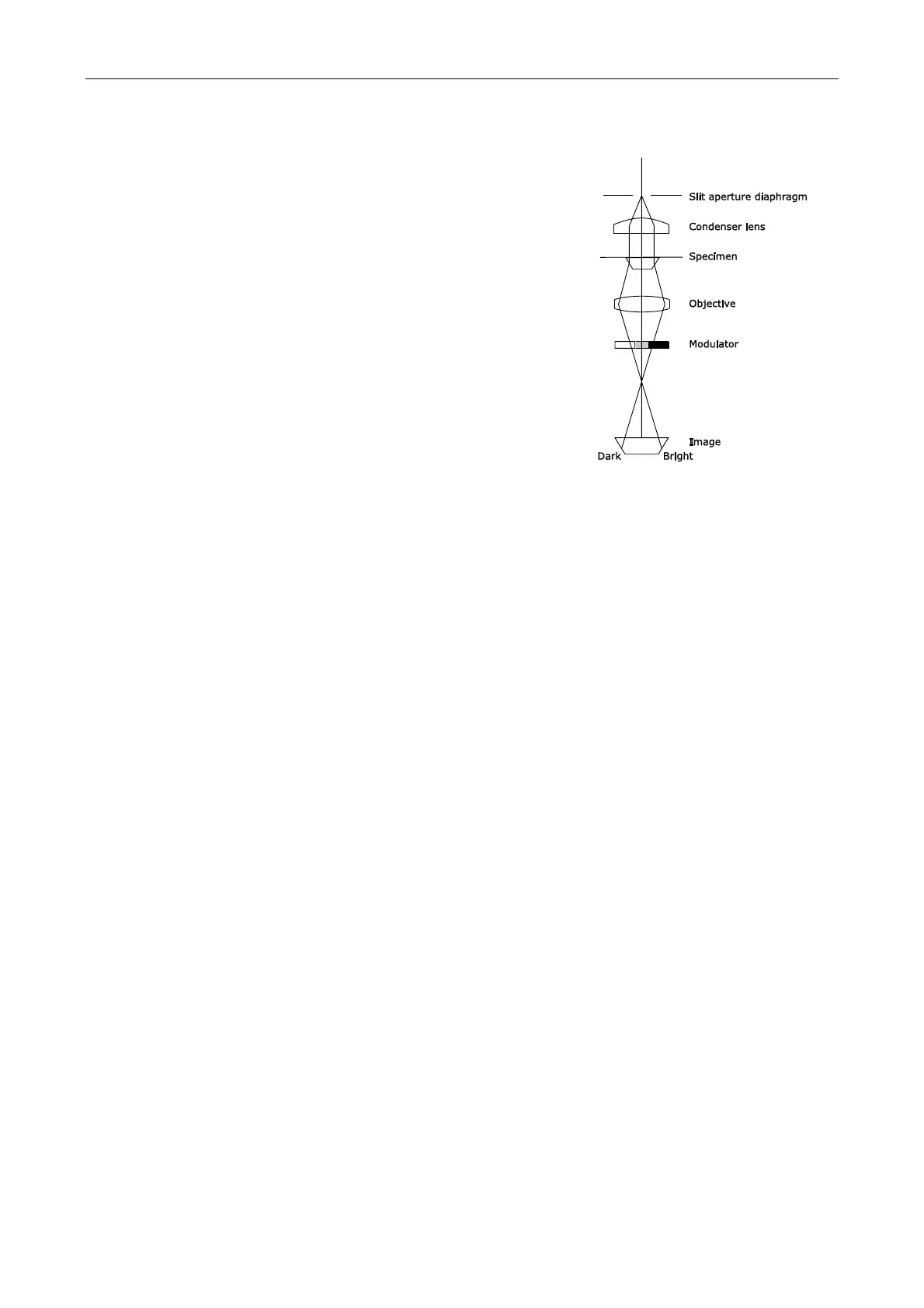
See figure 2 for the principle of the modulation
contrast. There is a slit diaphragm on the condenser
aperture, and modulator inside the NAMC objective.
(The modulator is a density filter placed at the exit pupil
of the NAMC objective. It divides the exit pupil into
three regions, dark, half-dark and transparent.)
If there is nothing on the specimen surface, the light
passes through the half-dark region of the modulator
and appears half-dark. If the light is refracted by the
phase object, it passes either the dark or the bright
region according to the difference in the refracted
angle. The light then appears dark or bright according
to the region the light passed through. In this way, the
phase object is made visible.
In modulation contrast microscopy, the image appears
in relief just like the differential interference contrast
microscopy. The notable point is that there is no
influence of double refraction, thus enabling you to
observe the specimen without double refraction.
Fig. 2
 Loading...
Loading...











