ML0035 September 27, 2017 - 80 - Copyright 2017 Bitronics, LLC
true Watts. The per-element VAs are calculated from the product of the per-element
Volts and Amps. The per-element VARs are calculated from fundamental VARs.
In any connection type, the Total Watts and Total VARs is the arithmetic sum of the
per-element Watts and VARs. The sign conventions are shown in Figure 9.
When used on 2-element systems, the reference phase voltage (typically phase B)
input, is connected to the Neutral voltage input, and effectively causes one of the
elements to be zero. It is not required to use any particular voltage phase as the
reference on 2-element systems. When used on 2-element systems the per-
element Watts, VARs, and VAs have no direct physical meaning, as they would
on 2½ and 3 element systems where they represent the per-phase Watts, VARs, and
VAs.
When used on 2½ element systems, one of the phase-to-neutral voltages is
fabricated, as described in Section 6.3. In all other respects, the 2½ element
connection is identical to the 3 element connection.
6.6.1 Geometric VA Calculations
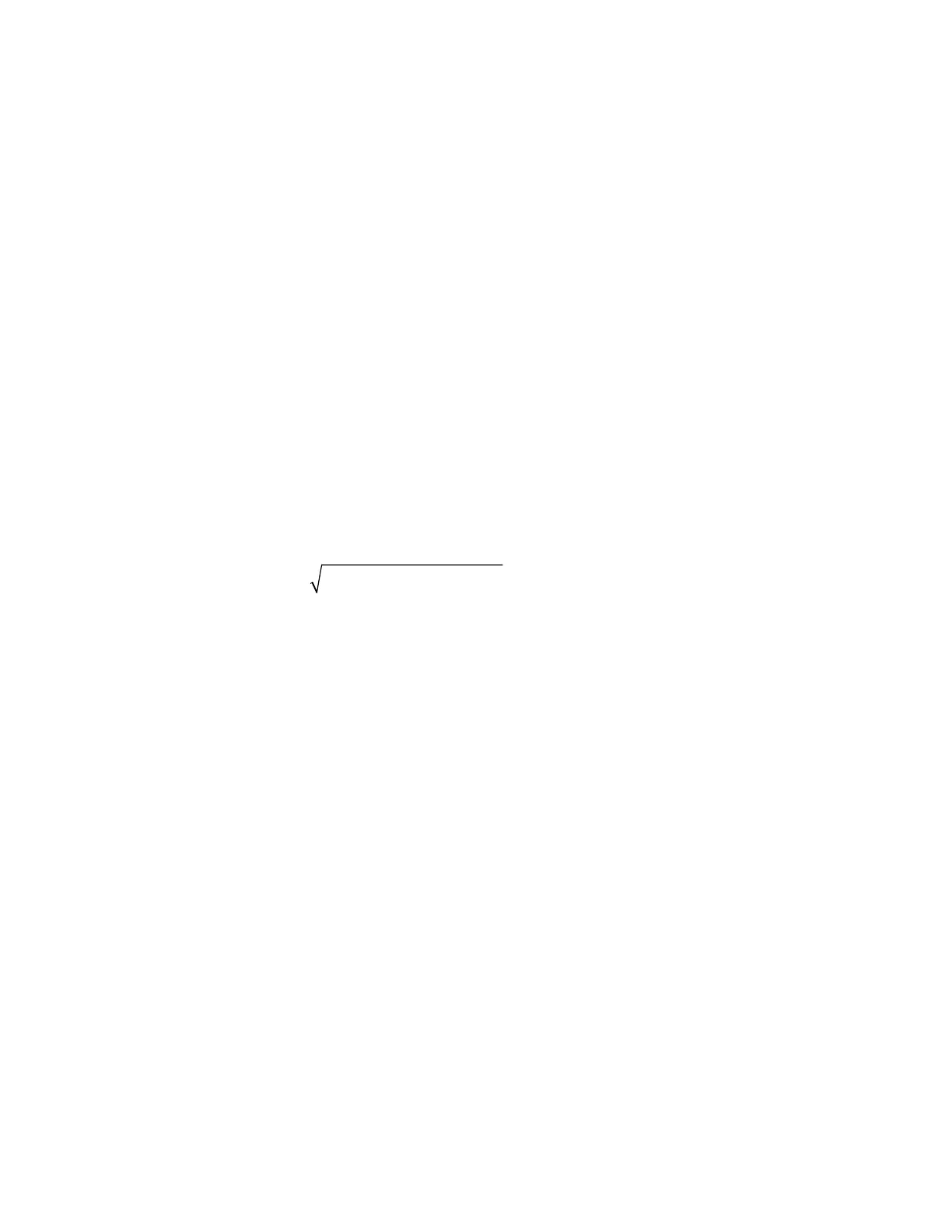
22
TOTAL TOTAL TOTAL
GEOMETRIC VA Watts VARs
This is the traditional definition of Total VAs for WYE or DELTA systems, and is the
default method for Total VAs calculation. The value of Total VAs calculated using this
method does not change on systems with amplitude imbalance, relative to a balanced
system.
There is also a relationship to the Total Power Factor, which is described in Section
6.4. Total Power Factor calculations using the Geometric VA method will still indicate
a "1" on a system with phase amplitude imbalance, or canceling leading and lagging
loads.
For example, on a system with a lagging load on one phase and an equal leading load
on another phase, the Geometric VA result will be reduced relative to a balanced
system but the Total Power Factor will still be "1".
 Loading...
Loading...