System 450™ Series Modular Control Systems with Standard Control Modules Technical Bulletin
24
Differential Control
The Differential Control feature enables a System 450 control system to monitor and maintain a temperature,
pressure, or humidity differential between two sensors of the same type and control relay, analog outputs, or both
based on the sensed differential value relative to user-selected differential values.
Differential Control application examples include:
• solar heating systems
• pump pressure-drop monitoring and control
• fluid filter pressure-drop monitoring
• air filter pressure-drop monitoring
Setting up an output (relay or analog) for Differential Control requires connecting two identical sensors to input
terminals Sn1 and Sn2 and selecting the same Sensor Type in the System 450 UI for Sensor 1 (Sn-1) and
Sensor 2 (Sn-2). The System 450 control system recognizes the same Sensor Types and makes the functional
Differential Control sensor (Sn-d) available for selection when you set up each of the control system outputs.
Note: Setting up Sn-1 and Sn-2 as the same Sensor Types also enables the functional High Input Signal
Selection sensor (HI-2). See High Input Signal Selection
for more information.
When a Differential Control sensor (Sn-d) is set up, the differential sensor value is always equal to Sn-1 minus
Sn-2. Therefore, depending on the intended control action of the output, the differential value may be either a
positive or negative value.
The sensed differential value (Sn-d) between Sn-1 and Sn-2 is displayed in the System Status screens as either a
temperature differential value (dIFT), pressure differential value (dIFP), or humidity differential value (dIFH). The
unit of measurement associated with the displayed differential value is determined by the Sn-1 and Sn-2 Sensor
Type. See Table 5 on page 24 for Sensor Types and their units of measurement.
When a relay output is set up for Differential Control, System 450 compares the sensed differential value, Sn-d
(Sn-d = Sn-1 minus Sn-2), to the user-selected differential values (dON and dOFF) to control the relay’s On/Off
state.
When an analog output is set up for Differential Control, System 450 compares the sensed differential value, Sn-d
(Sn-d = Sn-1 minus Sn-2), to the user-selected differential values (dSP and dEP) to control the analog output
signal strength.
Note: Because of the way that the System 450 Differential Sensor (Sn-d) is set up and calculated using two
sensors with identical Sensor Types, the Range of Usable Values for each Sensor Type is twice as large as
a single sensor. (Each Sensor Type has an equal number of positive and negative values on outputs that
reference Sn-d.) See Table 5 for a Sensor Type’s Range of Usable Values when an output references Sn-
d.
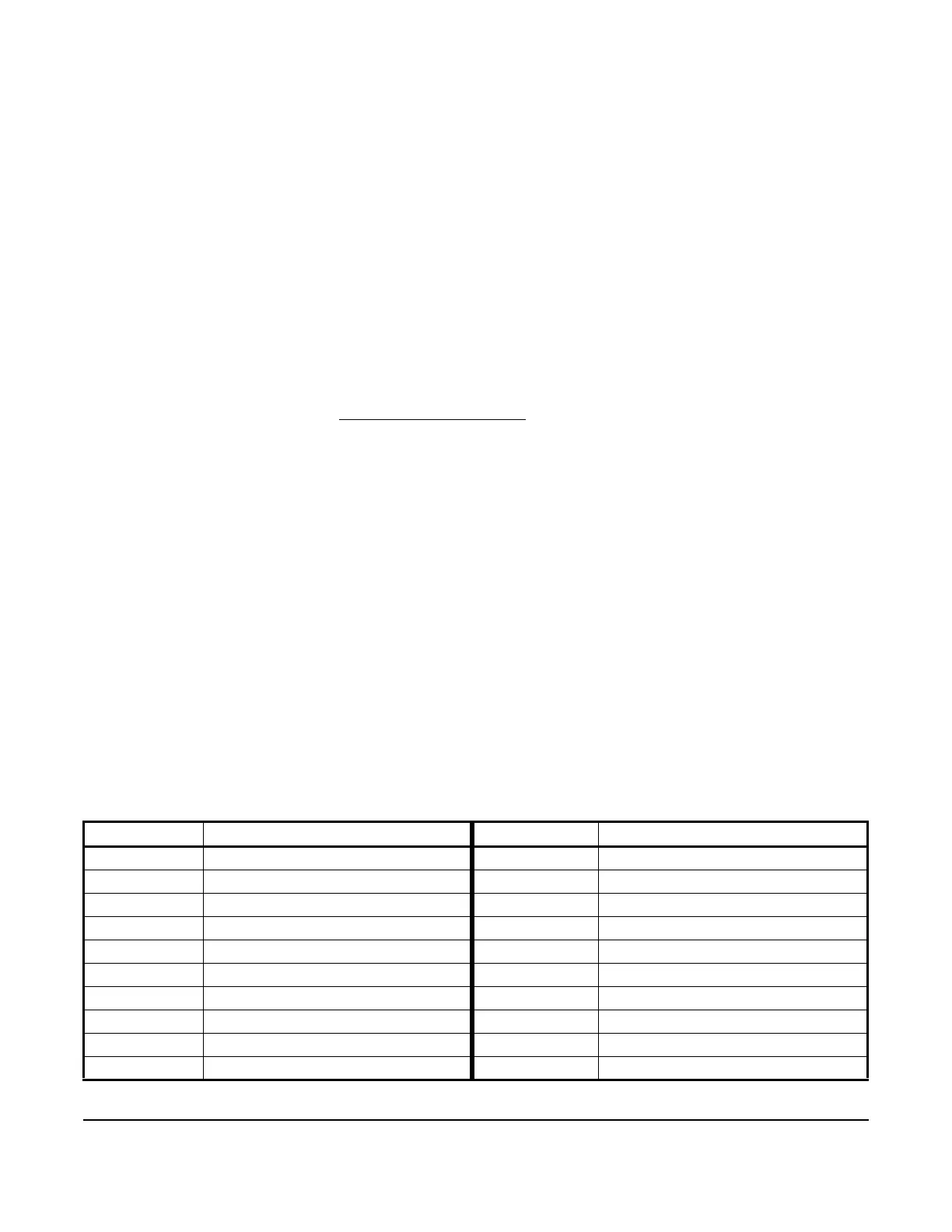
Table 5: Range of Usable Values for Sensor Types in Differential Control Applications
Sensor Type Sn-d Range of Usable Values Sensor Type Sn-d Range of Usable Values
F -290 to 290 P 30 -30.0 to 30.0
C -161.0 to 161.0 P 50 -50.0 to 50.0
rH -95 to 95 P 100 -100.0 to 100.0
P 0.25 -0.500 to 0.500 P 110 -110.0 to 110.0
P 0.5 -0.500 to 0.500 P 200 -200 to 200
P 2.5 -2.50 to 2.50 P 500 -500 to 500
P 5 -5.00 to 5.00 P 750 -750 to 750
P 8 -9.00 to 9.00 HIF -380 to 380
P 10 -10.00 to 10.00 HIC -210.0 to 210.0
P 15 -16.0 to 16.0 -- --

 Loading...
Loading...